FALLSEM2021-22 EEE2004 ETH VL2021220101177 DA-2 QUIZ-1 QP KEY DA II
advertisement

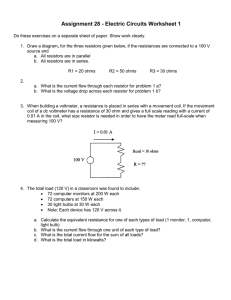
Digital Assignment II Answer only to the question corresponding to your register number in a Neat A4 size paper, after writing your name and registration number along with the question. REGISTER NO NAME 18BEE0320 19BEE0004 19BEE0086 19BEE0097 19BEE0155 19BEE0213 19BEE0300 19BEE0346 19BEE0362 19BEE0406 19BEE0414 20BEE0001 20BEE0009 20BEE0011 20BEE0014 20BEE0016 20BEE0037 20BEE0052 20BEE0054 20BEE0056 20BEE0067 20BEE0075 20BEE0081 20BEE0085 20BEE0094 20BEE0104 20BEE0105 20BEE0107 20BEE0127 20BEE0139 20BEE0145 20BEE0150 20BEE0172 20BEE0176 RIJU MALLICK SHIVAM RAJPUT HARSH PANDEY ARSHIT YADAV NILAY MISHRA C VIHITHA REDDY PANTRA DHAMINI RAO ISHAN MAHAJAN ADWAIT GIRISH MAHAJAN MANICKAM S MANOJKUMAR M SIDDHARTH S MAHESH NAMBOODIRI MONISHKUMAR P SRINIVASAN R DIPTANSHU DE VIJENDRA SINGH HARI HARAN G ARHAM DODAL SANCHIT AGARWAL PRIYANSHU KUMAR RISHVANTH SK WINSTON ARFIN V GAUTAM KARTHIK V AKHIL KODALAPURAM MAYANK SHAH P ARKA DEY VISHAL GARG SHUBHAM SHARMA RAJVEER M JOHN JOSE KORATH SUBASH S YASH SHARMA VIDHYA SAKAR Q. NO 9 33 26 31 5 45 18 36 29 55 60 41 39 49 25 37 3 6 21 34 64 58 8 16 7 62 65 4 2 30 28 48 23 61 REGISTER NO 20BEE0181 20BEE0185 20BEE0191 20BEE0199 20BEE0209 20BEE0214 20BEE0224 20BEE0225 20BEE0229 20BEE0232 20BEE0233 20BEE0234 20BEE0238 20BEE0243 20BEE0252 20BEE0261 20BEE0268 20BEE0271 20BEE0278 20BEE0320 20BEE0321 20BEE0322 20BEE0323 20BEE0324 20BEE0336 20BEE0344 20BEE0346 20BEE0351 20BEE0354 20BEE0356 20BEI0031 Name RITHICK SARATHI M B PRATHAM SUDHIR DEVANSHU SHARMA SAURABH VIJAY MUNJAL ADITYA RAJ RAJ DIGAMBAR FALKE SURENDRA AGRAWAL NABEEL MOHAMMED VIKAS SHARDUL DEEPAK RAVINUTHALA MOHAMMAD MUAZZAM JEEVAA SR MATHIVANNAN S NITHIN K AMIT KUMAR GUPTA SIDDARTH S PIYUSH CHAURASIA ANUJ MATHUR SHANMUGARAJ P SAKTHIVEL A VANITHA P JAGANATHAN R RAMAMOORTHI S DAXAY SOJITRA ANUSHA Y MILIND CHATURVEDI HARSHIT SAH SUMIT DUTTA NADAGOUDA ABHISHEK SUNDER M Q.No 46 24 17 32 20 38 43 1 27 11 22 54 52 42 14 47 13 35 50 56 40 53 10 15 51 63 44 57 19 12 59 1. A 200V 10A dynamometer type wattmeter has resistance of current and pressure coils as 0.8Ω and 10,000Ω respectively. Determine the percentage errors due to resistance for each of the two methods of connections when 0.75 power factor lagging loads at 200V, and current 1) 1A and (2) 8A is applied. Neglect errors due to inductance of pressure circuit. 2. The measurement of resistance of a resistor gives the following results 101.2, 101.7, 101.3, 101.0, 101.5, 101.3, 101.2, 101.4, 101.3 and 101.1 ohms. Assuming the random errors are present calculate (i) arithmetic mean, (ii) the standard deviation of the reading (iii) the probable error of average of 10 readings. 3. Following readings were obtained in respect of measurement of resistor. 0.903, 0.895, 0.892, 0.899, 0.901, 0.890, 0.906, 0.897, 0.912, 0.892, 0.898, 0.902. Determine (a) the arithmetic mean, (b) standard deviation of the readings (c) the probable error of mean value 4. A 250V moving iron voltmeter has coil resistance of 500 ohms coil inductance of 1.04 and a series resistance of 2kiloohms. The meter reads correctly at 250V dc. What will be the value of capacitance to be used for shunting the series resistance to make the meter read correctly at 50Hz. 5. The inductance of a certain moving iron ammeter is (8 + 4 - ½ 2)H where is the deflection in radians form zero position. The control spring torque is 12 x 10–6 Nm per radian. Calculate the scale position in radians for a current of 4A. 6. The inductance of a moving iron ammeter in micro – henry is given by the expression L = 20 + 10 - 3 2 where is the deflection in radians from zero position. Determine the deflection of ammeter for a current of 10A if the spring constant is 8 x 10–6 Nm/rad 7. The moving coil comprises of 100 turns of insulated copper wire wound on a former of length 3 cm and breadth 4 cm. The resistance of the coil is 2000 ohms. The field strength of the magnet is 600 lines / cm2. The torque exerted by the control spring is 0.02 gm-cm per degree. Estimate the deflection of instrument when a voltage of 120V is applied across it 8. A coil of moving iron voltmeter has a resistance of 300 ohms and an inductance of 1 H. The series resistor is 2,200 ohms. The meter reads 250V when a direct voltage of 250V is applied. What will be the reading when 250V at 50Hz is applied? 9. A modified Wheatstone bridge network is constituted as follows: AB is a resistance in parallel with resistance p, BC is a resistance Q in parallel with a resistance a, CD and DA are resistances R and S respectively. The nominal values of P,Q and S are each of 10 Ω. With resistance R in the circuit, balance is obtained with p = 30,000 Ω and q = 25,000 Ω. With R replaced by a standard resistance of 10 Ω, balance is obtained when p = 15,000 Ω and q = 40,000 Ω. Calculate the value of R. 10. Pointer of moving coil instrument gives full scale deflection of 20mA. The potential difference across the meter when carrying 20mA is 200 mV. This instrument is intended to be used on 200A for full scale indication. Find out the shunt resistance required to achieve this. If the instrument is used as a voltmeter for full scale reading with 1000V find out the series resistance to be connected in it 11. The coil of a moving coil voltmeter is 4 x 3 cm wide and has 100 turns wound on it. The control spring exerts a torque of 2.5 x 10–4 N-m, when the deflection is 50 divisions on scale. If the flux density on the magnetic field in the air gap is 1T, estimate the resistance that must be put in series with the coil to give 1V/div. Resistance of the voltmeter is 10,000V 12. The inductance of a moving iron ammeter in micro – henry is given by the expression L = 10 + 2 5 - where is the deflection in radians from zero position. Determine the deflection of ammeter for a current of 3 and 5A if the spring constant is 1.2 x 10–5 Nm/rad 13. A 100V moving coil voltmeter gives a full scale deflection of 100 degree. The moving coil has dimensions of 3 cm x 2.5 cm and number of turns equal to 75. The air gap flux is 0.12 wb/m 2. Determine the swamping resistance of the voltmeter when the spring constant is 3.5 x 10 –7 Nm per degree and the coil resistance is 5 ohms. 14. A 20A dynamometer ammeter is controlled by springs having the spring constant of 5 x 10–6 Nm per degree. Determine the inductance of the instrument for full scale deflection of 100 degree. Initial inductance is 2 micro henry and the change is linear. 15. Two ammeters A and B have resistance of 1.2 ohms and 1.5 ohm respectively and both give full scale deflection with a current of 150mA. Calculate the suitable values of shunts are placed in parallel in a circuit in which the total current flowing is 15 A. Find the reading on each instrument. 16. The coil of an instrument has a resistance of 2 ohms and the instrument reads upto 250V when a series resistance of 5 Kohm is connected in series with it. Find (a) the current range of the instrument when used as an ammeter with the coil connected across a shunt of resistance 2 milliohms and b) the exact value of the shunt resistance for the instrument to give a full – scale deflection with the current of 75A 17. A wattmeter with resistances of the two coils as 0.01 ohms and 1000 ohms is used to measure the power supplied to a resistive load. The load current and load voltage may be taken as 20A and 30V respectively. Show the two ways in which the voltage coil can be connected and find the error in the reading in each case. 18. A 230V single phase watthour meter has a constant load of 4A passing through it for 5 hours at 0.8 p.f. If the meter disc make 883 revolutions during this period, find the meter constant in revolutions per kwh. If the power factor is unity, what number of revolutions will the disc make in the above time 19. In a potentiometer measurement, a standard cell of 1.0186 V balances at 60cm of the slide wire, while an unknown emf source balances at 90 cm. When a voltmeter of 250 ohm resistance is used to measure the unknown emf, it reads 1.5V. Determine the internal resistance of the unknown source 20. The resistance of one meter long slide wire of a potentiometer is 25 ohms, across which a battery of 4.2V is connected to supply the potentiometer current. An another cell of 1.4V connected in series with a 10 ohms resistor is balanced on the potentiometer. Determine the position of the slider. 21. The voltage between two points in a d.c circuit is measured by a potentiometer that gives a reading of 1.2V. A 20kohms per volt d.c voltmeter reads only 0.6V on its 2.5V range when connected to the same two points in the circuit. Calculate the circuit resistance between the two points. 22. The four arms of wheat stone bridge have the following resistances P = 100 ohms Q = 10 ohms X = 50 ohms and S = 4 ohms. Calculate the current flowing through the galvanometer of 20 ohms resistance when the supply voltage is 10V. What should be the resistance of X for no deflection in the galvanometer? 23. An AC bridge is balanced for the following parameters: the arm AB = 0.2micro farad, the arm BC = 500 ohms, the arm CD unknown, arm DA 300 ohm in parallel with 0.1 micro farad. Find the constants in series 24. In a Wheatstone bridge, the ratio arms AB = 10 Ω and BC = 100 Ω; standard resistance across CD = 10 Ω. The shunt across 10 Ω ratio arm has to be changed from 2230 to 27670 Ω, when the resistor R2 was changed from R1 in the arm DA. Calculate in magnitude the difference between the resistances of R1 and R2. The bridges is balanced in both the cases. 25. The four arms of an AC bridge are given as follows Arm AB = 2 kilo ohms and 0.2 micro farad in parallel, BC = 1.5 kilo ohm, CD = 500 ohm and 0.8 henry in series, DA = 2 kilo ohms. The frequency of supply is 1 kHz and the voltage is 20V. The supply terminal are A and C. a) Is the bridge balanced, If not find the new constants of the arm CD for the bridge to be balanced. b) Find the voltage across the high impedance detector for the original bridge constants. 26. The arm AB and BC of a bridge contain pure resistances of 1500 ohms and 1000 ohms respectively. The unknown impedance is connected in the arm CD. The values of capacitance and series resistance in the arm DA are adjusted to 0.1 micro farad and 10 ohm respectively for balance. The supply with a voltage of 15V is connected between terminals B and D. The supply frequency is 1000 Hz. A) Find the unknown resistance b) Find the voltage across a high impedance detector connected across A and C. If the resistance of the arm BC is changed to 1010 ohms 27. Four arm of the bridge are given below: Arm AB, R = 1000 ohms and C = 0.159 micro farad in parallel, BC = 1000 ohms, CD = 500 ohms and DA = unknown resistance and 0.636 in series a) Find the frequency for which the bridge is in balance. B) Find the value of unknown in the arm DA 28. An impedance bridge is arranged as follows: the arm AB = unknown inductive coil, BC = 100 ohms, arm CD = 300 ohms and the arm CE = 0.75 micro farad arm ED = 3000 ohms and DA = 300 ohms. Calculate the resistance and inductance of the coil. 29. The four arms of a bridge contain the following elements AB is an unknown air cored reactor BC a 450 ohm resistor, CD a 1250 ohm resistor shunted by a loss – free capacitor of 1.02 micro farad, DA a 500 ohm resistor. All the resistors are non – inductive and bridge is balance with the above mentioned elements. An a.c supply of 1000Hz is connected to points A and C of the bridge and a detector to points B and D. By deriving the balance conditions for the bridge circuit determine a) the resistance and b) the inductance of the unknown reactor. Draw a vector diagram to represent the conditions at balance. 30. The four arms of an a.c bridge contains the following elements AB = a coil of unknown impedance, BC a non – inductive resistor of 1000 ohms, CD a non – inductive resistor of 833 ohms in series with a standard capacitor of 0.38 micro farad. DA non reactive resistor of 16800 ohms. The supply frequency of 50 Hz is connected to points A and C and a detector to points B and D. Determine the inductance and resistance. 31. An Anderson bridge is arranged as follows: arm AB and BC consists of non- inductive resistances of 600 ohms each, the arm BE and CD of non – inductive variable resistances, the arm EC of a capacitor of 1 micro farad, arm DA of an inductive resistance. The a.c supply is given to A and C and the detector to E and D. A balance is obtained when the resistance of the arm CD is 800 ohms and that of the arm BE is 400 ohms. Calculate the resistance and inductance of the arm DA. 32. The four arm of a Schering bridge are arranged as arm AB = imperfect capacitor, BC of a resistance of 20000 ohms, CD of a resistance of 1200 ohms shunted by a capacitor of 300 pico farad, DA of a standard capacitor of 0.05 micro farad. All the resistors are non – inductive. The supply of 1 kHz is connected to points A an dC and the detector to points B and D. Calculate a) the capacitance, b) the equivalent series and c) tan. 33. When testing a sample of insulating material balance was obtained with the following values of elements in the arms of the bridge: 0.5 micro farad in parallel with 1000/ ohms resistor in arm CD, 260 ohms in arm BC and standard 106 pico farad in arm DA. The frequency of supply was 50Hz. Calculate a) the capacitance b) the equivalent series resistance and c) tan for the specimen 34. A resistive position transducer has a shaft stroke of 10cm. The total resistance of the potentiometer is 5000 ohms and the applied voltage is 50 V. When the wiper is at 2 cm from down, what is the value of the output voltage measured by the voltmeter a) when the voltmeter has infinite resistance, b) when it has 1 kilo ohm resistance. 35. An a.c. LVDT has the following data: input 6.3V output 5V and range 2.5cm. Determine a) the output voltage when the core is 1.75cm from centre b) the plot of output voltage versus core position for a core movement going from + 2 cm to – 1 cm. 36. In a wheat stone R2 = R3 = 130 ohms, and R4 = 130 ohms when un-strained and R4 = 130.5 when strained. If the gage factor is 2, calculate the strain 1.12 x 10 –3 37. What is the true value of current in the 15 kilo ohm resistor as shown, If an ammeter of 2 kilo ohm resistance is used to measure the current in the 15kilo ohm resistance, what will it read? If a loading accuracy of 99 percent is desired in measuring the current, what should be ammeter resistance be. 38. A moving coil milli voltmeter has a resistance of 200 ohms and the full scale deflection is reached when a potential difference of 100mV is applied across the terminals. The moving coil has effective dimensions of 30mm x 25mm and is wound with 100 turns. The flux density in the gap is 0.2 wb/m2. Determine the control constant of the spring if the final deflection is 100 degree and a suitable diameter of copper wire for the coil winding if 20 percent of the total instrument resistance is due to the coil winding. Resistivity of copper is 1.7 x 10 –8 ohm meter. 39. The coil of a measuring instrument has a resistance of 1 ohm, and the instrument has a full scale deflection of 250 V when a resistance of 4999 ohms is connected in series with it. Find a) the current range of the instrument when used as an ammeter with the coil connected across a shunt of 1/499 ohms and b) the value of the shunt resistance for the instrument to give a full scale deflection of 50A. 40. A watthour meter is calibrated to measure energy on a 250V supply. On test a steady current of 15A is passed through it for 5 hours at unity power factor. If the meter readings before and after the test are 8234.21kwh and 8253.13 kWh respectively, calculate the percentage error. If the spindle turns through 290 revolutions during 5 minutes when a current of 20A is passing through the meter at 250V and 0.87 power factor, calculate the meter constant. 41. The current and flux produced by series magnet of an induction watthour meter are in phase but there is an angular departure of 3 degree form quadrature between voltage and the shunt magnet flux. The speed of disc at full load and unity power factor is 40 rpm. Assuming the meter to register correctly under this condition, calculate its speed at ¼ full load and 0.5 power factor lagging. Also find the percentage error. 42. An electrodynamometer type wattmeter has a field system which may be considered as long compared with the diameter of moving coil, the mean diameter of moving coil is 30mm, and is wound with 500 turns. If the current through the moving coil is 50mA and the wattmeter is measuring power flowing in a circuit having a power factor of 0.7, estimate the torque, if the axes of the field and the moving coils are at a) 45 degree and b) 90 degree. 43. The pressure coil of an electrodynamometer wattmeter has a resistance of 6600 ohms. When the voltage applied to the pressure coil is 120V and a current of 20A flows in the series coil, the deflection is 160 degree. What additional resistance must be connected in the pressure coil circuit to make the constant of the meter equal to 20W per degree? 44. A 250V, 10A electrodynamometer wattmeter has a resistance of current and potential coils of 0.5 ohms and 12500 ohms. Find the percentage error due to each of the two methods of connections with unity power factor at 250V with current a) 4A and b) 12A. 45. The ratio arms of a Kelvin bridge are 100 ohms each. The galvanometer has an internal resistance of 500 ohms and a current sensitivity of 200 mm/micro amps. The unknown resistance is 0.1002 and the standard resistance is set at 0.1000 ohms. A d.c current of 10 amps is passed through the standard and the unknown resistance from a 2.2V battery in series with a rheostat. Calculate the deflection of the galvanometer. Neglect the resistance of the link. Find also the resistance unbalance to produce the deflection of 1mm 46. A standard cell of 1.0185 V used with a simple potentiometer balances at 50cm. Calculate a) the emf of the cell that balances at 72cm. b) the percentage error in voltmeter which balances at 64.5 cm when reading 1.33V c) the percentage error in an ammeter that reads 0.43 A when balances at 43.2 cm with the voltage drop across a 2 ohm resistor in the ammeter circuit. 47. A slide wire potentiometer is used to measure the voltage between two points of a certain d.c circuit. The potentiometer reading is 1 volt. Across the same two points when a 10,000 ohm/volt voltmeter is connected, the indicated reading on the voltmeter is 0.5V on its 5V range. Calculate the input resistance between two points. 48. A slide wire potentiometer has a battery of 4V and negligible internal resistance. The resistance of slide wire rheostat is adjusted so that balance is obtained when the sliding contact is at 101.8 cm. a) Find the working current of the slide wire and the rheostat setting. B) if the slide wire has divisions marked in mm and each division can be interpolated to one fifty, calculate the resolution of the instrument. 49. The a.c bridge is used to measure an unknown inductance Lx that has inherent resistance Rx. The bridge parameters are R1 = 20000 ohms, R2 = 500000 ohms C2 = 0.003 micro farad, = 106 rad /s. C1 is adjustable from 10 pF and R4 is adjustable from 0 to 10000 ohms. A) Show that the equations for resistance and reactive balance are independent of each other. Derive expression for Rx and Lx in terms of R1, R2 R4 C1 and C2. b) determine the largest values of Rx and Lx that can be measured with the given parameters 50. The four arms of a bridge network are made up as follows ab, a resistor of 50 ohms in parallel with an inductor of 0.1H, bc, a resistor of 100 ohms, cd, an unknown resistor R in parallel with an unknown capacitor C, da a resistor of 1000 ohms, A 50 Hz voltage supply is applied across ac. Find R and C when a vibration when a vibration galvanometer connected across bd is undeflected. 51. A four branch bridge network ABCD balanced at 1000 Hz has branches AB and BC of pure resistance of 1000 ohms and 1250 ohms respectively. An unknown impedance forms the arm CD and the branch DA consists of a standard capacitor fo 0.1micro farad capacity and negligible resistance connected in series with a non – inductive resistance of 10 ohms to give balance. The supply voltage is 15V and the supply is given at the points B and D. Find the components of unknown impedance. 52. The circuit for measurement of effective resistance and self – inductance of an iron cored coil is as follows: arm ab the unknown impedance, arm bc a pure resistance R3, arm cd, a lossless capacitor C2. arm da a capacitor C2 in series with a resistance. Under balance condition R3 = 10 ohms, R2 = 842 ohms, C2 = 0.135 micro farad C4 = 1 micro farad. Calculate the value of effective resistance and self – inductance at a supply frequency of 100 Hz. Derive equation for balance. 53. A capacitor bushing forms arm ab of the Schering bridge and a standard capacitor of 500 pF capacitance and negligible loss, forms arm ad, Arm bc consists of a non – inductive resistance of 300 ohms. When the bridge is balanced arm cd has a resistance of 72.6 ohms in parallel with a capacitance of 0.148 micro farad. The supply frequency is 50Hz. Calculate the capacitance and dielectric loss angle of capacitor. 54. A Schering bridge is used for measuring the power loss in dielectrics. The specimens are in the form of discs 0.3 cm thick and have a dielectric constant of 2.3. The area of each electrode is 314 cm2 and the loss angle is known to be 9 for a frequency of 50Hz. The fixed resistor of the network has a value of 1000 ohms and the capacitance is 50pF. Determine the value of the variable resistor and capacitor required. 55. In a balanced bridge network, AB is a resistance of 500 ohms in series with an inductance of 0.18 H, BC and DA are non – inductive resistances of 1000 ohms and CD consists of a resistance R in series with a capacitance C. A potential difference of 5Volt at a frequency of 5000/2 Hz is established between the points A and C. Determine the values of R and C. 56. The ratio arms of a Kelvin bridge are 100 ohms each. The galvanometer has an internal resistance of 500 ohms and a current sensitivity of 200 mm/μA. The unknown resistance is 0.1002 and the standard resistance is set at 0.1000 ohms. A d.c current of 10A is passed through the standard and the unknown resistance from a 2.2 V battery in series with a rheostat. Calculate the deflection of the galvanometer. Neglect the resistance of the link. Find also the resistance unbalance to produce a deflection of 1mm. 57. The inductance of a moving iron ammeter in micro – henry is given by the expression L = 10 + 5 – 2 where is the deflection in radians from zero position. Determine the deflection of ammeter for a current of 3 and 5A if the spring constant is 1.2 x 10–5 Nm/rad after deriving an expression for that type of meter 58. The four arms of a Wheatstone bridge are as follows. AB = 100Ω; BC = 10 Ω; CD = 4 Ω; and DA = 50 Ω. The galvanometer has a resistance of 20 Ω and is connected across BD. A source of 10V dc is connected across AC. Find the current through the galvanometer. What should be the resistance in the arm DA for no current through the galvanometer 59. A displacement capacitive transducer uses a differential arrangement with two outer plates which are fixed and a central plate which is movable. The distance between fixed and movable plates is 5 mm when no displacement is applied. A voltage of 1000V rms is applied across the fixed plates. Find the differential output voltage if a displacement of 0.01 mm is applied to the central plate. Find also the sensitivity of the transducer. 60. Two plates of parallel plate capacitive transducer are 30mm apart and the space is filled with two different dielectric materials, one material is 1 cm thick with a dielectric constant of 5 and the other material is 20mm thick with a dielectric constant of 10. If the capacitive transducer were to be made up of single dielectric material what is the dielectric constant of the material. 61. In a variable capacitive transducer, the diaphragms are 20mm in diameter and 4 mm apart. If a pressure produces an average deflection of 0.25mm, calculate the value of capacitance after the application of force. The capacitance before application of force is 400pG. 62. A barium titanate crystal has dimensions of 5mm x 1.5 mm. The Young’s modulus of barium titanate is 12 x 104 N/m2, its charge sensitivity is 150pV/N and permittivity is 112.5 x 10–9 F/m. A capacitance of 10pF in parallel with 100MΩ resistance is connected across the crystal. Calculate the rms value of voltage under open circuit and load conditions when a force of 0.0142sin100t newton is applied to the crystal, calculate the rms value of deflection. The resistance of the crystal may be neglected. 63. The inductance of a moving iron ammeter with a full scale deflection of 90 at 1.5A, is given by the expression L = (200+4θ2 – θ3) μH, where θ is the deflection in radian from the zero position. Estimate the angular deflection of the pointer for a current of 1.0A. 64. For a certain dynamometer ammeter the mutual inductance M varies with deflection θ (expressed in degrees) as M = –6 cos(θ+30) mH. Find the deflecting torque produced by a direct current of 50mA corresponding to a deflection of 60. 65. In a particular instrument, the total resistance of the voltage coil circuit is 8200 Ω and the mutual inductance changes uniformly from – 173μH at zero deflection to +175 μH at full scale, the angle of full scale being 95. If a potential difference of 100V is applied across the voltage circuit, and a current of 3A at a power factor if 0.75 is passed through the current coil, what will be the deflection, if the spring control constant is 4.63 x 10–6 Nm/rad?