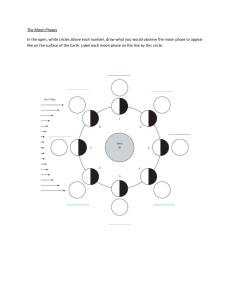
SCIENCE PRAXIS 5005 Created on 5/25/2020 EARTH & SPACE: - PALEONTOLOGY: Studies the history of life on Earth. - Earth is believed to be 4.5 billion years old. - EARTH’S MAGNETIC FIELD: Deep w/in the Earth, protects the Earth from harmful Solar Wind particles. Responsible for the Northern Lights (Aurora Borealis) - SOLAR WIND: Charged particles escape form sun’s gravitational pull. - What would be most different about an object on Mars than Earth-Weight. - 4 inner planets= solid, 4 outer=gas (MVEM(Mars)JSUN) - SUPER NOVA: When a star explodes. Create almost all heat elements in world. ASTRONOMY: The study of space. SUN: Star at the center of Earth’s solar system. Hydrogen & helium. 109 Earths would fit. NUCLEAR FUSION: How the sun shines and produces heat. When lighter elements become heavier. - Earth is much closer to the sun that is to other stars. -RADIATION: Heat comes from sun to earth. -Includes asteroids and comets, small rocky or icy objects that orbit the sun. Clustered in the asteroid belt (btwn. the orbits of Mars and Jupiter). -Our solar system is part of a bigger star system called a GALAXY: Made up of stars, dust, & gas (the galaxy that is home to Earth: Milky Way). - Planet most like Earth’s size: Venus. -COMET: Mostly made of ice, dust, gas. -METEROID: Light flashing in sky - If you drop ball from space: fall slower/take longer. -ABSOLUTE MAGNITUDE: Light emitted by star - Star explodes 15 light yrs. away, we see it in 15yrs. -Venus: Planet that orbits closet to Earth. Most like Earth’s size - Jupiter has the shortest days. - Mercury: Terrestrial planet -Uranus: Planet w/ abnormal tilt on axis -The tilt of the Earth’s axis causes days/times to differ. -Burning fossil fuels & volcanic activity= carbon dioxide on earth’s atmosphere. -Largest planet furthest from the sun: Neptune (4th largest in Solar system). Smallest of the gas giants but termed “ice giant along with Uranus. Color is b/c of methane. Longest orbit around the sun. Smaller than gas giants: Saturn and Jupiter. -It takes Earth one day to rotate on its axis. It takes one year for the Earth to revolve around the Sun (The cycle of night and day and seasonal cycle are determined by this and seasons are caused by the Earth’s tilt). The moon revolves around Earth in one month (27 days). - Earth is much closer to the sun it is to other stars. -Earth sees different moon phases b/c the sun lights different parts of the moon. - Nitrogen makes up 78% (Earth’s largest quantity of gas) of the Earth’s atmosphere. -LUNAR ECLIPSE: When the Earth moves btwn. the moon and the sun (Sun, Earth, Moon). SOLAR ECLIPSE: When the moon lines up btwn. Earth and the sun (blocking sunlight/cast shadow over earth). TOTAL SOLAR ECLIPSE= NEW MOON. - Carbon is the most common element in the universe. - BLACK HOLE: A massive star with a gravitational field so strong that even light cannot escape. -AURORA: Occurs when particles from the solar wind are trapped in the Earth’s magnetic field. EARTH’S LAYERS: -CRUST: Everything we can directly see and study. It is cracked, split into tectonic plates. The edges of plates go under the ocean, called contintental shelves. 2 TYPES: 1) Oceanic: Bottom of oceans, below continental crust. Consists of: Basalt 2) Continental: Thicker on land. Contains: Granite. - THE MANTLE: Thickest layer of Earth (84% of Earth’s volume). Always in motion. Divide into layers based on seismologic properties. A) UPPER MANTLE: Extends from where the Crust ends. Is sticky but formed from rock (Peridotite). B) LOWER MANTLE: Extends from Upper Mantle. Made up of Magnesium. 3) THE CORE: The inner and outer core works together as the temps cool down, more of the outer core develops and becomes part of the inner core. A) INNER CORE: Solid. Temperatures and pressures are extreme. Solid inner core rotates faster within the outer the outer molten core. b) OUTER CORE: Solid, 6,000ft below. Made of iron. Low viscosity but certainly not liquid. Malleable. Site of violent convection (transfer of heat by the movement of a fluid (liquid or gas) btwn. areas of different pressure). The churning of the outer core is responsible for the Earth’s magnetic field. - LITHOSPHERE: Solid, outer part of the Earth’s surface (Crust and Upper Mantle) Includes tectonic plates). LAYERS OF EARTH’S ATMOSPHERE: (FIRST-LAST): ATMOSPHERE: Layer of gases surrounds the Earth. Retained by Earth’s gravitational pull. Where majority of Earth’s nitrogen is found (78%) 21% Oxygen.1) TROPHOSPHERE: Lowest layer of atmosphere, contains weather. Gets colder as you go up. 80% of Earth’s atmosphere. 2) STRATOSPHERE: Temp. gets warmer as you go up. Ozone layer. Protects from UV rays. 3) EXOSPHERE: Highest layer. Planet’s first line of defense against sun’s rays, meteors, asteroids. End of atmosphere, beginning of space. 4) THERMOSPHERE: Very Hot. Has Aurora Borealis. - BIOSPHERE: Where life exists. .BUILDING UP LAND INQUIRY: EXPLAINATION OF EARTH’S CHANGING CRUST: When rocks melt underground, magma (thick, fiery liquid) is formed. Hot gases and steam that are released when rocks melt, mix with magma and build great pressure. This pressure forces the agma to squeeze into cracks or weak places under the Earth’s crust. Magma may push up and bend rock layers above w/out coming to the surface. This can make a dome mtn. Earthquakes may also change the Earth’s surface with the moving of the tectonic plates. -Most recently found parts of earth’s crust: Mid ocean ridge. - PANGEA: ALFRED WEGENER’S belief that continents were once a huge landmass (supercontinent). -CONTINTENTAL DRIFT: Slow movement of tectonic plates, gradually shifting continents to their current positions. Continents are still moving. EARTHQUAKES: happen along plate boundaries, when the earth’s crusts breaks under the strain of deforming forcing. -FAULT: Cracks in the earth’s crust. Where parts of the crust may move horizontally, vertically, or diagonally. BLOCK MTS. When large blocks of rock are uplifted and titled sideways. Develop through tilted or vertical movements along a fault (Sierra Nevada Range). FOLDING: Mts. that develop when forces push parts of the crust into giant wrinkles (Appalachians). -DIVERGENT PLATE BOUNDARIES: Occurs when tectonic p lates are moving away from one another. Can form new ridges or ocean basins. (East African Rift Valley) - CONVERGENT PLATE BOUNDARIES: 2 tectonic plates collide and one plate is pushed upward on top of the other, forming mts. OR one is pushed down, forming trenches. The plate pushed downwards melts into the fiery mantle. - TRANSFORM PLATE BOUNDARIES: When plates move in opposite directions along a boundary. (San Andres Fault) -OCEAN FLOORS: Form when 2 plates drift apart. Magma pushed up from the mantle and fills the gap btwn. plates. VOLCANOES: Formed by the moving DIVERGENT/CONVERGENT plate boundaries and HOT SPOT HOT SPOT: Hot upwelling areas of magma in the mantle. Magma rises through plates of Earth’s Lithosphere. As plates move across the hot spots. New volcanoes form. EX: Hawaiian Islands. Vents in the Earth’s crust that allow molten rock to reach the surface, mainly occurs along the edges of tectonic plates. - RING OF FIRE: A string of underwater volcanoes and earthquake sites around the edges of the Pacific Ocean. (Runs through 15 countries including USA, Indonesia, Mexico, Japan, Canada, Guatemala, Russia, Chile, Peru, and Philippines). Hawaii sits smack dab in the middle of the ROF. - Most of the active volcanoes on earth are underwater. -Adds new rock to surface=volcanic activity. - COMPOSITE VOLCANO (STRATO-VOLCANO): Cone-shaped, w/ steep sides. Made of layers of solid lava, ash, and rock. - SHIELD VOLCANO: Dome shaped, w/ sloping side, made mostly of fluid lava flows. -CINDER VOLCANO: Small, steep hill formed by ash and debris surrounding a single lava vent and often has crater at the top. - An earthquake’s magnitude refers to the energy released during the earthquake. FOUR MAJOR TIME PERIODS IN EARTH’S HISTORY: 1) PRECAMBRIAN ERA: Earth’s formation until life began to appear. 2) PLAEOZOIC ERA: Plants and animals emerged. About 95% of all life on Earth became extinct at the end of this period. 3) MESOZIC ERA: Age of the dinosaurs. Their extinction is believed to be caused by an asteroid. 4) CENOZOIC ERA: Current time period. Birds, flowering plants, mammals (including humans). WEATHERING AND EROSION: Continuous process - WEATHERING: Breaking down of rocks into smaller parts. EROSION: Includes weathering plus the transporting weathered material from one place to another (actions of water, wind, & glaciers). Water is the most erosive force on earth. -Falling rain picks up small amount of carbon dioxide in the air and forms carbonic acid. Slowly wears down Limestone. - CHEMICAL WEATHERING: Oxygen and water in the air + rock surfaces=rust. Reddish soils contain oxidized iron compounds. - Frozen water contributes to weathering b/c many ricks are porous. As absorbed water expands, bits of rock are broken off. Ice may wedge apart cracked rocks. - EXFOLIATION OF ROCKS: is caused when the difference btwn. the hot surface and the cooler interior of a rock produce strains that cause parts to flake off. - WIND EROSION became apparent to Americans during the Dust Bowl (1934-1935). Prairie lands originally covered by grass, had been broken up for agriculture. A combo of dry weather and marginal farming practiced in the most destructive dust storm ever seen in the U.S. -GLACIAL EROSION: Huge deposits of snow build up when snowfall exceeds the melting rate. Snow compacts into ice moving the glacier slowly downhill. When glaciers move, their tremendous weight scoops out basins and levels hills. As they melt, huge deposits of soil and rocks are left at the sides and leading edge. Effects of glaciation: New England and the N. central states. Motion of glaciers is caused by erosion. -CONTINENTAL GLACIERS: Large glaciers. Much of them covered N. America but now cover much of Greenland and Antarctica. Gravity forces these glaciers to spread out as more snow piles on top. INTERPLANETARY WEATHERING: Involves the study of the samples of soils and rocks that the Apollo astronauts retrieved from the surface of the moon. Allowed scientists to understand the effect of impacts and solar wind on the moon. Recently, GALILEO spacecraft images of asteroids 951 Gaspra and 243 Ida revealed to geologists that these asteroid surfaces undergo space weathering. GALILEO and Cassini spacecrafts may provide results for space weathering about surfaces such as the icy moons of Jupiter and Saturn. SOIL AND IT’S MAKEUP - Not until decomposed plant and animal matter is added (or manufactured chemicals applied) does soil become productive enough to support agriculture. - HUMUS: Organic matter that supplies plants with nitrogen, phosphorous, potassium, & other essential elements. The decomposition of organic material is done by soil bacteria. Acids released in decomposition also dissolve other minerals in the soil particles. Humus retains water (keeps soil from drying out). The darkish color of humus soil absorbs sunlight which speeds up plant growth and reduces seed failure. -IMPORTANCE OF EARTHWORMS: Break up soil and allow air & water to reach plant roots. As they eat through soil, they mix it and leave castings that contain rich fertilization ingredients. - SOIL MAKEUP: Organic (once living), broken down rock. Pebbles settle first, followed by sand, silt, and clay. Humus at top. SILT and CLAY have small particles that retain water. Having been eroded from rocks rich in minerals, they contain elements that plants need for healthy growth. SAND or CLAY soil lacks porosity (not good for watering plants). - Farmers put pesticides and fertilizers in their soil, causes water pollution. - TO PRESERVE SOIL: 1) TERRACE FARMING: Sloped plain that has been cut into a series of flat surfaces or platforms. Preserves topsoil. 2)CONTOUR PLOWING: Used to plow around hilly land to eliminate gullies being formed during rain or irrigation.3) STRIP CROPING: Alternates a row crop that has much care soil exposed (corn) with a ground cover crop (clover). Reduces wind erosion.4) TREE WINDBREAK: Helps if a field is located where a strong wind usually blows in one direction.5) CHECK DAMS: Stones or logs may be used to slow water in a stream or prevent a gully from widening. 6)RESIDUE MANAGEMENT: Does away with the plow. Leaves the residue from harvested crops on the field to hold soil and moisture. Tractor pulled machines gouge places for seeds which then sprout and grow through the decomposing residue. ROCK CYCLE: - ROCK: Naturally occurring solid. Can be inorganic or organic and is composed of one or more minerals. Classified based on how they were formed. 3 TYPES OF ROCKS: 1) IGNEOUS: Result of tectonic processes that brings magma (melted rock) to the earth’s surface. Can form either above or below the surface. Forms crystal like, glassy rocks when magma cools. EX: Granite, Basalt, Pumice 2) S EDIMENTARY: Formed when rock fragments/ sediments are compacted as a result of weathering and erosion. Chane by pressure. Usually found in layers, older layers at bottom. EX: Limestone, Dolemite, Sandstone. 3) METAMORPHIC: Form where extreme temps. and pressure change the structure of preexisting rocks. EX: Slate, Marble. Limestone can change into marble. Sandstone can change into Quartz. ROCK CYCLE: How rocks form & break down MINERAL: Naturally occurring, solid, crystalline structure. Found in Earth’s crust. Granite- Mica and Feldspar. EX: Gold, Copper, Nickel, Diamond, Lead. . ROCK RECORD: What Paleontologists use to retain biological history in the form of FOSSILS: Preserved remains and traces of ancient life. Can only be found in SEDIMENTARY ROCK. Made of animal bones, water, mud, silt. Can be used to learn about the evolution of life including bacteria, plants, & animals. 1st fossil found: Amphibians. - CHEMICAL WEATHERING: Break up of rocks by air/water caused by chemicals. Water is most related to this. MECHANICAL WEATHERING: Break up of rocks caused by temp. GEOSPHERE: Minerals and rocks found on Earth. - Where to find water aquifers: porous, permeable rocks. - Warm, moist climates- most weathering. Hot, dry climates- little weathering. - MOHS HARDNESS SCALE: Measures whether harder materials can scratch softer ones. HYDROLOGY: - HYDROLOGY: The study of water on Earth. HYDROSPHERE: All the bodies of water on earth. OCEANS are the largest bodies of water. - Oceans= 71% of Earth’s surface and 97% of Earth’s water. - Best fishing found on along the Continental Shelf. - Pacific Ocean=Largest Ocean TIDES: From the gravitational pull of the moon. CURRENTS: Movements of ocean water caused by differences in salt or temp. WAVES: Carry energy through the water; caused by wind blowing. - OTHER BODIES OF WATER: Lakes (freshwater), s eas (saltwater), rivers (rain that falls on land), Streams (Moving bodies of water that flow into bigger bodies of water), watershed/drainage basin )When all the rain that falls on a given area of land flows into a single body of water), groundwater( water stored underground in rick formations called aquifers). -Much of Earth’s water is stored as ice. - WATER CYCLE: Circulation of water throughout the Earth’s surface, atmosphere, and hydrosphere. Water on Earth evaporates (liquid to gas) and becomes water vapor. Water vapor comes together to form clouds. When it cools, water vapor condenses into a liquid (precipitation). Precipitation replenishes ground water and water features. METEROLOGY: The study of weather - WEATHER: Determined by humidity (amount of water vapor in the air) and temp. CLIMATE: Long-term weather condition in a location. CLIMATE ZONE: Large area that has similar avg. temp and precipitation. - JET STREAM: Strong winds in atmosphere. Huge impact on our weather and climate. - CLIMATE ZONES: 3 major: Polar, temperate, tropical. Divided into subclimates: Tropical: warm temps. Divided into wet, tropical wet & dry, semiarid, and arid. TEMPERATE: Mod. Climate. Divided into Mediterranean, humid subtropical, marine W. Coast, humid continental, and subartic. POLAR: Cold temp. Divided into tundra, highlands, nonpermanent ice, ice cap, experience long, dark winters sue to the tilt of the axis. WARM FRONT: Warm air moves over and replaces cold air. COLD FRONT: Cold air moves under and replaces warm air. ISOBAR: Equal barometric pressures. - Temp, pressure, density does not increase as altitude increases in the troposphere. - CLOUD: Made up of water droplets or ice crystals. Defined by location in sky and shapes. CIRRUS CLOUD: Highest in sky, then & wispy, not much precipitation. STRATUS: Flat, wispy, white or gray, lower level of sky. CUMULUS: Tall, puffy, dark at bottom, white at top. NIMBUS: Have a lot of water vapor (most precipitation). ALTO PREFFIX: Middle of the sky, produce precipitation that does not reach ground. - SPRING EQUINOX: 12hr day/12hr night. - SUMMER SOLSTACE: Tropic of Cancer. Sun directly overhead at noon. Beginning of summer in N. latitudes June 21st - WINETR SOLSTACE: Tropic of Capricorn. Sun is directly overhead at noon. Beginning of Winter in N. Hemisphere. Dec. 21. LIFE SCIENCE: - HOMEOSTASIS: Equilibrium maintained by healthy living organisms. - BIOMOLECULES: - CARBS: Sugars (source of energy). LIPIDS: Fats. Stores energy, helps with cell function. PROTEINS: Composed of amino acids. ENZYME: Special type of protein, can cause or speed up a chemical reaction. Important in the digestive system b/c the help break down & extract energy from different kind of food. - NUCLEIC ACIDS: DNA and RNA. Store genetic code which is info for an organism to function. DNA and RNA- made up of small molecules called nucleotides. Linked together by the dbl. helix. DNA: 4 types of nucleotides: adenine, cytosine, guanine, & thymine. RNA: Subs uracil for thymine. - NUCLEUS: Membrane bound body that holds a cell’s DNA. Where nucleic acids are stored in some organisms. Where DNA is packed into units called chromosomes. Separate from cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells. . STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF CELL: - Mitochondria: Produces energy - ORGANISM: Living things w/one cell. Smallest unit of life. Can reproduce on its own. UNICELLULAR ORGANISMS: Amorbas. Made of one cell. MULITCELLULAR ORGANISMS: Many cells. - 2 TYPES OF CELLS: 1) PROKARYOTIC: No Nucleus. Some single cell organisms (bacteria & prokaryotes). 2) EUKARYOTIC: In both plants and animals. Contain nucleus where genetic material is stored. Found in multicellular organisms. - CELLS: Inside cell membrane (protective covering). Consists of cytoplasm and genetic material (DNA). Basic structure of every living organism. - CELL DIVISION (mitosis): Produces two cells with the same DNA as the original cell. 5 STEPS: 1) PROPHASE: Cell gets ready to divide to duplicate DNA. 2) METAPHASE: Chromosomes line up in pairs along the central axis of the cell. 3) ANAPHASE: When pairs begin to split, w/ one of the chromosomes moving to one side of the cell, and one to the other. 4) TELEPHASE: Once split, the cell membrane splits and 2 new cells are formed. 5) I NTERPHASE: The 2 new cells return to normal resting state. ACRONYM to remember steps I Picked My Apples Today. Mitosis= 2xs as many offspring, genetically identical, cell division= Asexual. Mitosis: produces 2 daughter cells that have the same number of chromosomes in the parent cell. -MEOSIS: Formation of reproductive cells (gametes=egg and sperm). 2 parents/not identical-new combo of genes-DNA, genes= Sexual. PHASES: 1) C hromosomes are duplicated, pairs of choromosomes align & exchange genetic material w/ one another during the prophase. 2) Metaphase, anaphase, & telophase proceed like mitosis. 3) The interphase btwn. the two division processes is short, DNA not duplicated before 2nd division cycle. Instead, each chromosome divides in half, each new cell gets ½ of the genetic material contained in the original parent cell. - ZYGOTE: When egg is fertilized by sperm. ½ of chromosomes come from father, ½ from mother. Reproductive cells have 23 chromosomes, body cells have have 46 (one set of 23 from each parent). - CELLULAR METABOLISM (CELLULAR RESPIRATION): How cells produce energy. Cells use oxygen to break down the sugar glucose & store the energy in the form of a chemical called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP: Provides the energy for the cell to grow and reproduce. 38 molecules are produced. - 3 PARTS: 1) GLYCOSIS: Prep. Phase. One molecule of ATP is used to produce 2 molecules of pyruvate. Happens when cell cytoplasm in bot eukaryotes and prokaryotes & with/without oxygen. When process uses oxygen: anerobic: 1 glucose molecule is converted into 2 lactate molecules and 2 ATP molecules. 2) KREBS-CYCLE/CITRIC ACID CYCLE: Inside the cytoplasm in prokaryotes and in mitochondria of eukaryotes. Chemical process that produces energy-carrying molecules (NADH & FADH2). 3) ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN (ETC): 30-32 molecules of ATP for every molecule of glucose. Electrons are transferred btwn. membrane-bound complexes which moves hydrogen ions to created proton membranes. OXYGEN ACTS AS THE FINAL ELECTRON RECEPTOR AT THE END OF ETC. GENETIC & EVOLUTION -GENETIC: Info that is passed to the next generation after reproduction (DNA) - GENES: Within DNA. Not static. Code needed to produce a specific protein. Responsible for TRAITS: Characteristics (eye color, flower color,etc.). DOMINANT: Expressed. RECESSIVE: Not expressed. - MUTATIONS: Changes in genetic code. 4 types. 1) SUBSTITUTION: One nucleotide is exchanged w/ another. 2) INSERTION: Extra nucleotide pairs are inserted into DNA. 3) DELETION: Removal of nucleotide pairs from DNA. 4) F RAMESHIFT: When insertion or deletion of nucleotides causes the gen to be misread. - SEXUAL REPRODUCTION: Child receives 2 copies of each gene, 1 from mother, 1 from father. -PUNNETT SQUARE: Shows all genetic combos from parents with given genotypes. - GENETIC DISORDER: When genetic code is Damaged. CYSTIC FIBROSIS: Causes difficulty In bodily functions. Damaged gene CFTR. DOWN SYNDOME: Developmental delay. One person has 3 copies of Chromosome 21 (they received 2 copies from one parent in meiosis). - NATURAL SELECTION: When beneficial mutations help an organism reproduce, trait appears more often. EVOLUTION: Results from natural selection. Developed by Charles Darwin when he realized finches had different beak shapes/sizes that help them eat, allowing birds to coexist. - 4 TYPES OF SPECIATION BASED ON ISOLATION: 1) ALLOPATRIC: Pop. Is divided by geological features into 2 isolated populations. 2) PERIPATRIC: When small subpopulations form & become genetically isolated from main pop. 3) PARAPATRIC: Two species that are partially isolated by geography develop characteristic that make them reproductively incompatible. 4) SYMPATRIC: 2 different species from one pop. occupy one location. -Animal body part responsible for removing Nitrogen: Liver CLASSIFICATION OF ORGANISMS: Uses a taxonomic system - SPECIES: Smallest, yet most fundamental level of taxonomic classification. - KINGDOM: Highest level of taxonomic classification. 5 kingdoms: 1) MONERA: Bacteria (unicellular organisms, no nucleus. 2) PROTISTS: Unicellular, have nucleus. (1 & 2 reproduce asexually by cellular division). 3) FUNGI: EX. MUSHROOMS, MOLD. Unicellular & multicellular. Have cell walls. Can reproduce asexually (cell division) or sexually through spores. Are decomposers, attain energy by breaking down organic matter in the environment. 4) PLANTS: Use energy from sunlight to make food (sugar glucose) through photosynthesis. 5) ANAMALIA: Largest of the kingdoms. Mulitcellular organisms. Can move around and eat other organisms for energy. Includes: VERTEBRATES: Backbone/spine. INVERTEBRATES: No backbone/spine. Classifies as: ECTOTHERMS: Body heat from environment, cold bolded (Frogs). OR ENDOTHERMS: Body heat from metabolic processes, warm blooded (Birds, mammals). - ANTHROPODS: Joined legs & cellulose skin. HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS: - GAL BLADDER: Stores bile. -Responsible for common cold-Virus. - AMINO ACIDS: linked together by protein. -Our body sweats to remain at room temp. LIPIDS: Only waxy fat found in living things. -Communicable disease: Tuberculosis, Influenza. RIBOSOMES: An amino acid that makes p rotein. -LYMOSOMES: Filter waste - X will pass= father to daughter. - TISSUE: When cells are grouped together in multicellular organisms. ORGANS: Grouped tissue. Further grouped into organ system (ex. Digestive or respiratory systems). The heart pumps blood throughout the body. - ANATOMY: Studies structure of organisms. PHYSIOLOGY: How these structures function. HOMEOSTASIS: Stabilization of internal conditions. -SYSTEMS: 1) DIGESTIVE: Breaks down food into nutrients for the body’s cells to use. Absorbs nutrients in body. Produces insulin for pancreas. Food enter through mouth, moves to esophagus to stomach, where it is physically and chemically broken down. Tongue processes food into smaller pieces and helps mix it w/ saliva.Food particles move to small intestine (nutrients are absorbed) then to large intestine (mostly absorbs water, waste leaves through anus). Includes: Liver, gal bladder, and pancreas (help digest food). 2) EXCRETORY STSYTEM: R emoves waste. Includes: Liver (breaks down harmful substances, filters blood from digestive tract), kidney ( part of urinary tract, filters blood and waste, makes urine), bladder and urinary tract (expels waste), lungs (expels carbon dioxide created by metabolism. Contain small structure called, alveoli: exchanges gases btwn. the blood and air), skin (secretes salt=perspiration). 3) R ESPRITORY SYSTEM: Takes in oxygen, gets rid of carbon dioxide. Ari travels down trachea and bronchi into the lungs. 4) CIRCULATORY SYSTEM: C arries oxygen, food, & waste products in blood to and from all the cells of the body. The heart is a 4 chambered muscle that pumps blood throughout the body. Four chambers of heart: a) right atrium: Deoxygenated blood enters. b) right ventricle: gets the deoxygenated blood and sends it to the pulmonary artery to the lungs, collects oxygen. c) left atrium: Where oxygen-rich blood is received and pumped to the d) left ventricle: pumps blood to rest of body. 5) SKELETAL SYSTEM: Body’s bones and joints. Provides support for body and helps w/ movement. Bones store some nutrients and produce specific cells. Humans have 237 bones in body, many fuse during childhood. Adults have 206 bones. Bones shapes: long, short, flat, irregular. 6) MUSCULAR SYSTEM: Allows body to move, moves blood. 3 types of muscles: a) Skeletal: voluntary/ controlled muscles. Attached to bones to move body. b) Smooth muscles: Involuntary, create movement in digestive tract, blood vessels, & reproductive system. c) Cardiac muscles: Involuntary. Contracts heart to pump blood. 7) IMMUNE SYSTEM: Protects body from infection. Includes: skin. Has adaptive immune system: Can recognize and respond to foreign substances once exposed= why we have vaccines. Antibodies: fight foreign substances. Memory cells: Remember antigens so immune system can respond quickly. 8) NERVOUS SYSTEM: Processes external stimuli and processes it to body. Made of two parts: a) Central nervous system (CNS): Includes: Brain and spinal cord & is where info is processed and stored. Brain has 3 parts: a) Cerebrum: Biggest part, front and top, controls thinking, hearing, vision, touch and smell. B) Cerebellum: Back of brain. Controls motor movements. c) Medulla: Brain stem. Where brain connects w/ spinal cord and controls breathing and heartbeat. B) (PART2 OF NERVOUS SYSTEM): Peripheral nervous system (PNS): Includes neurons to transmit info throughout body using electrical signals. Neurons are made of 3 parts: a) cell body: Main part of cell, organelles live. b) Dendrites: Communicates info to other dendrites through synapse (like a web). c) Axons: Off of cell body, relays messages to muscles. 9) E NDOCRINE SYSTEM: Produce, store, secretes hormones from circulatory system (regulates bodily processes). Regulates hunger, sleep, mood, reproduction, and temp. Includes: adrenal, pituitary, thyroid. 10) REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: Sexual reproductive organs (testes, vas deferens, urethra, prostate, penis, ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, vagina. NOT NEEDED FOR SURVIVAL - THYROID: Produces hormones, controls metabolic rate, heart & digestive function muscle control, brain development. - LOUIS PASTEUR: Known for his principles on vaccines/pasteurization. -LYMPHATIC SYSTEM: Reduces bacteria and viruses in body. PLANTS: Multicellular, eukaryotic organisms - Ex of asexual reproduction: Flower. -VENUS FLY TRAP: Carnivours plant. STATES OF MATTER: 1) Solid: densely packed molecules. Volume or shape doesn’t change. 2) Liquid: Loosely packed molecules, shape changes but not volume. 3) Gas: Widely dispersed molecules. Can change shape & volume. - PLASMA MEMBRANE: Protects cell from its environment. -- ORGANELLES: Within cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Perform specific functions. Includes MITOCHONDRIA: Produces energy, RIBOSOMES: Produce protein, VACUOLES: Store water. - PLANT CELLS: Include structures not found in animal cells such as 1) CELL WALL: Hard outer structure. 2) CHLOROPLAST: Contains PHOTOSYNTHESIS: Plants store energy, made by carbon dioxide) from sunlight as sugars (plant’s main source of energy for cell functions). CALVIN CYCLE: 2nd part of photosynthesis. Harnesses energy from photons from light. Plants cells have chloroplast, animals don’t. -Difference btwn. plant & animal cells: presence of a cell wall. - CHLOROPHYL: Absorbs energy for photosynthesis. - PLASMA MEMBRANE: Protects cell from environment. - TRANSPORTATION: Water vapor through stoma-plant loses through leaves. PARTS OF VASCULAR PLANTS: Flowering or nonflowering -LEAVES: Organ, captures sunlight and used by the chlorophyll to produce food for photosynthesis. STEM: Provides structure and supports weight of plant. Transports nutrients throughout plant. XYLEM: Transports water and mineral. PHLOEM: Transports sugar and nutrients. ROOTS: Anchor plants and absorb water/nutrients from soil. -FLOWERING: Flowers are reproductive organs. PETALS: Brightly colored leaves. SEPALS: Help form calyx. The leaves on the steam to give support. STAMEN: Male reproductive organ. Includes anther (end of stalk, part of filament. POLLEN: Male reproductive cell. Produced in stamen, stored in anther. PISTIL: Female reproductive organ. Center of flower. Composed of carpel (ovary) & stigma (where pollen is received) - NONFLOWERING: Can either use seeds or spores to reproduce. USE SEEDS: Called GYMNOSPERMS: Produce seeds w/out covering (ex. fruits on trees). USE SPORES: Ferns and mosses. Distributed by wind ANGIOSPERMS: 1) Parallel leaf veins (one cotyledon) = MONOCOT (ex. Grasses, orchids) 2) Reticulate leaf veins (two cotyledons) = DICOT ECOLOGY: Study of interactions w/ each other and environment. - CARRYING CAPACITY: Highest # of ppl. an environment can support. Environments that outgrow this=increased death rates until pop. reaches stability. - If grasshopper pop. increases= owl pop. increase - PARASITIC RELATIONSHIP: One species benefits at the downfall of another. - FOOD WEB: Where every species consumed or gets consumed by another. TROPHIC LEVEL: An organism’s place in the food web. TROPHIC LEVELS (LOWEST TO HIGHEST): 1) LOWEST TROPHIC LEVEL: Producers (plants and algae) 2) PRIMARY CONCUMERS: Herbivores/plant eaters (COWS). 3) SECONDARY CONSUMERS: Carnivores. Consume herbivores. 4) TERTIARY CONSUMERS: Carnivores that consume carnivores. - Global climate change is most likely to cause extinction of warm-blooded carnivores. - DECOMPOSERS: Organisms that break down dead matter -ECOSYSTEM: Collection of living and nonliving things in a location. Constantly developing through ecological succession: a) Primary succession: Changes that occur during development. b) Secondary succession: Changes made by previous developments that have been disrupted by events (forest fires). - Water is an abiotic part of an ecosystem. Producers/consumers: biotic - COLIFORM BACTERIA TEST: Decides if water is contaminated or not. -BIOMES: Plant and animal communities that exist w/in specific climates. BIOSPHERE: All of living and nonliving parts on earth. POPULATION DENSITY: # Of ppl. in a specific area. Different Biomes; 1) DESERT: Extreme temps., low rainfall, specific plants, small mammals. 2) TROPICAL RAINFOREST: Hot & wet. Biome w/ greatest diversity. 3) TEMPERATE GRASSLANDS: Mod. Rain & distinct seasons w/ mostly grasses and shrubs (Prairies of N. America). 4) TEMPERATE BROADLEAF FOREST: Mod. Rain and temps. Deciduous trees dominating (China, N. America). 5) TUNDRA: Extremely low temp & short growing seasons w/ little or no tree growth. 6) CORAL REEF: Marine (saltwater), high levels of diversity (Largest coral reef: Great Barrier Reef). 7) LAKE: Enclosed body of fresh water. - SAVANNA: Terrestrial biome, tropical, dominated by grasses, has poor soil. - Poor reproduction (species inability to reproduce), climate change, overexploitation by humans are causes of extinction. NOT habitat conservation. PROPERTIES OF MATTER: - ATOM: Basic unit of all matter. - NEUTRONS: No charge. In nucleus. PROTONS: Positive charge. In nucleus or center of the atom. ELECTRONS: Negative charge. Orbit nucleus. ANIONS: Neg. charged atoms that have more electrons than protons. - MOLECULE: 2 or more atoms join together. COMPOUND: Water. Combines 2 or more different elements. IONIC BOND: One or more electrons transferred from one element to another=two ion w/ opposite charges & bind together. COVALENT BOND: Atoms share one or more valence electrons. - EX of a molecule: Oxygen Why does cold water flow beneath warm water: cold water=high density. - DENSITY: Amount of matter to its volume. MASS: How much matter is in something Triple Beam Scale or balance measures this. Measure in grams. VOLUME: Quantity of a 3-D space that is holding liquid, solid, or gas. Measured by Graduated cylinder. - The mass of an atom = adding #’s of protons, neutrons, & electrons. ATOMIC MASS: Total number of protons and neutrons in nucleus. Electrons have little mass= add mass of protons and neutrons. ATOMIC NUMBER: # of protons in a nucleus of atom. Atoms with neutral charge: Atomic number= # of electrons. -Physical change= boiling water. When water boils it release Water vapor. C ONDENSATION: Gas becomes liquid. SUBLIMATION: Solid becomes gas. STATES OF MATTER: 1) Solid: densely packed molecules. Volume or shape doesn’t change. 2) Liquid: Loosely packed molecules, shape changes but not volume. 3) Gas: Widely dispersed molecules. Can change shape & volume. CHANGING STATES OF MATTER: PHYSICAL CHANGE: does not alter chemical composition of substance. 1) Melting: Solid to liquid 2) Freezing: Liquid to solid 3) Evaporation: Liquid to gas 4) Condensation: Gas to liquid 5) Sublimation: Solid to gas. 6) Deposition: Gas to solid. - SOLUTE: Substance being dissolved. SOLVENT: Substance dissolving a substance. EX: Heating salt water until the water evaporates will separate a saltwater solution, leaving salt behind. SOLUBILITY: Amount of solute that will dissolve in a solvent. CONDUCTIVITY: How a material conducts heat or electricity. Silver, copper, aluminum, iron=poor conductors. -CHEMICAL CHANGE: Occurs when bonds btwn. atoms are made or broken=new substance. CHEMICAL REACTION: Either heat is released or energy is required for the reaction to occur. COMMON CHEMICAL REACTIONS: 1 ) Oxidation: Substances lose electrons (Iron rusts when exposed to oxygen, forming iron oxide). 2) Combustion: Produces heat, carbon dioxide, & water (Burning fuel). 3) Synthesis: When two substances combine=single substance. 4) Decomposition: Single substance is broken down into two or more substances 6) Neutralization: When an acid and base react to produce a salt and water. - When kerosene reacts w/ oxygen to light a lamp: Combustion reaction. - PH SCALE: Shows the acidity of a substance. Goes from 1-14, 7=neutral (ex. Water). LITMUS PAPER: Measures PH. ACIDS: Compounds that contribute to a hydrogen ion (H+) when in solution. Have PH < 7. BASE: Compounds that contribute a hydroxide ion (OH-) in solution. Have PH>7. FORCES & MOTION: VARIABLES THAT MEASURE MOTION: 1) Speed: How quickly something moves. Speed= distance/time. 2) Displacement: Shortest distance btwn. initial and final locations of a moving point. 3) Velocity: The rate at which an object changes position (speed with direction). Velocity=displacement/time. 4) Acceleration: How quickly an object moves. Acceleration= change in velocity/time. FORCES: Work is the force to move mass over a distance. 1) Gravity. 2) Tension: Pulling or holding an object (ex. Ropes) 3) Friction: Created when two objects move against each other. 4) Normal force: When an object is resting. LAWS OF MOTION: Isaac Newton. 1st LAW: A n object at rest, stays at rest/ object in motion, stays in motion unless acted on by force. 2nd LAW: Force=mass x acceleration (F=ma) 3rd LAW: Every action= equal or opposite reaction. LAWS OF MOTION=SIMPLE MACHINES: Inclined plane, wheel & axel, pulley, screw, wedge, &lever. ENERGY & MATTER: - HEAT: Movement of energy from one substance to another. ENERGY: How an object does work (movement or change) 2 KINDS: 1) K INETIC (named Temperature): Objects in motion. EX: Moving car. 2 POTENTIAL: Objects that have the potential to be in motion due to their position. Both Kinetic and Potential energies can be turned into one another. - TYPES OF POTENTIAL ENERGY: 1) ELECTRIC: Interaction btwn. positive/negative charges. 2) GRAVITATIONAL: Pull of Earth’s gravity on an object. 3) ELASTIC: When compressed energy is released to form kinetic energy Ex. Pressing & releasing a spring. 4) CHEMICAL: Energy is stored in chemical bonds. - Energy can be transferred by 1) R ADIATION: Does not need a medium. Sun radiates energy to Earth through the vacuum of space. 2) CONDUCTION: When two substances are in contact w/ each other. Ex. When a pan is placed on a stove, the heat energy is conducted from the stove to the pan & then food to plan. 3) CONVECTION: Transfers energy through circular motion of air or liquids. Ex. A convection oven transfers heat through circular movement caused by hot air rising & cold air sinking. WAVES: A way to transfer energy - TYPES OF WAVES: 1) MECHANICAL: Travel faster through denser mediums. Sound waves move faster in water than air. 2) TRANSVERSE: Waves that move up and down (like ripples). 3) L ONGITUDINAL: Travel through compression (like a slinky). Sound is longitudinal (created by vibrations) - PROPERTIES OF WAVES: 1) AMPLITUDE: A wave’s displacement form resting position. Can create a sound’s loudness/height of a sound wave. 3) WAVELENGTH: Distance btwn. crests of waves 3) FREQUENCY: # of times per sec on the wave cycles. Determines sound’s pitch. 4) PERIOD: Time btwn. wave crests. 5) PHASE: The position on a wave cycle at a given time. -DOPPLER EFFECT: How one hears sound in a resting position. EX. Standing while hearing a siren move away/towards you. ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES: Vibrations that fluctuate btwn. an electric & magnetic field. Include: Radio waves, microwave, X-rays, and visible light. - OPTICS: Study of light. When light srikes an object it can be: 1) REFLECTED: Bounce of surfaces (flashlight in mirror)2) REFRACTED/TRANSMITTED: Bending light. (holding pencil upright in water, observing it bend). 3) ABSORBED: Light stored as heat energy. LENSES: Curved pieces of glass. Can be used to bend light (microscopes) COLOR: Red/Orange=lower frequency; Blue/Violet=High. ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM ELECTRIC CHARGE: Difference in the balance btwn. protons & electrons= pos. or neg. charge. STATIC ELECTRICITY: Build-up of charge. ELECTRICITY: Movement of electrons through a conductor, an electrical-closed loop circuit. VOLTAGE: Powers the movement of electrons (current). -MAGNETS: Alignment of spinning electrons. Ex. Iron, nickel, & cobalt. MAGNETIC FIELD: When the alignment of electrons acts on other objects. Always has N or S poles, even when cut in half. (opposite poles attract/ same repel). - If you wrap a wire around a nail, put nail on battery, will cause magnetic field. MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY: Used to diagnose/ TECH. & ENV’T: -Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Uses strong magnetic fields to take pictures of organs. Can detect cancerous tumors. ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (EKG): Records electrical signal of heart. DEFIBRILLATORS: Reestablish heart rhythm. - Technology has helped to revise the food pyramid. - FOSSIL FUELS: Oil, natural gas, and coal. Nonrenewable resources. Carbon based fuels. When burned, emit pollutants that damage environment. GREENHOUSE GASES: Pollutants such as carbon dioxide and methane which tray heat = global warming. As nonrenewable resources become depleted, scientists look to use RENEWABLE RESOURCES: Nuclear energy, hydropower, wind energy (windmills), solar energy, biomass (plant-based fuel), & geothermal power. BIOFUELS: Can be burned to produce heat, steam, or electricity. -Fertilizers and pesticides can cause water pollution. Large amount of lands can damage the diversity and stability of ecosystems. GMOs contain genes from other organisms and is inserted in its DNA (corn, potatoes) -Succession: most likely to happen after a forest fire. . INQUIRY-BASED LEARNING: Provides the strongest foundation for scientific thinking. Steps of Inquiry-based learning (first to last): Question, Research, Hypothesize, Experiment, Collect Data, Conclusion (Queen Rachel Hopes Every Coward G ains Courage) .INDEPENDENT VARIABLES: Controlled by experimenter. DEPENDENT VARIABLES: Influenced by I.V. CONTROL GROUP: Does not receive treatment. - A graduated cylinder measures volume. A balance measure mass. A barometer measures atmospheric pressure. OTHER INFO: - Mammals keep warm by: Shivering, fluffing out coat, & contracting certain blood vessels. - A metric ruler= determines volume of a large block of wood of unknown density. - Some traits are on genes of the Y chromosome. A man will carry these traits to all male offspring. - If a nail is put into a potato wrapped by aluminum foil, it will cook faster b/c the nail conducts heat. - In a vacuum (no air resistance), all objects will fall at the same rate. -LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY: Energy can change form. It has to go somewhere/be from somewhere. - Carbon dioxide is a chemical element. -HETEROTROPHS: Fed off a host. Can only consume food, can’t produce it. MOON PHASES: IN ORDER 3) FIRST QUARTER MOON: half of the lit portion of the Moon is visible after the waxing crescent phase. 4) WAXING GIBBEOUS MOON: More than half of the lit portion of the Moon can be seen, shape increases ("waxes") in size from one day to the next 5) FULL MOON: It’s Lit! Moon is on the opposite side of the Earth from the Sun. Lunar eclipse can only happen at full moon. 6) WANING GIBBEOUS MOON: more than half of the lit portion of the Moon can be seen, shape decreases ("wanes") in size from one day to the next. The waning gibbous phase occurs between the full moon and third quarter phases. 7) LAST QUARTER MOON: ½ moon is visible. 8) WANING CRESCENT MOON: Moon looks like crescent. Moon decreases in size from one day to next.