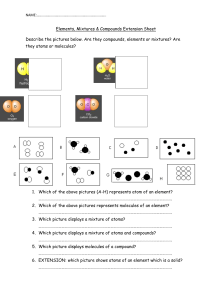
Physical and Chemical Properties of Matter Physical Properties • Something we can observe without changing the substance’s atoms or molecules. • Examples: • What state of matter is the substance? • Solid, liquid, or gas? • How hard or soft is the substance? • Is it shiny or dull? Physical Properties • Some changes in physical properties are reversible • If I melt an ice cube into water, I can refreeze it • Changing a state of matter is reversible • Some changes in physical properties are irreversible • If I crack an egg, I cannot put it back together • Shaving a piece of metal off a screw is irreversible Chemical Properties • The ability of a substance to undergo a change in chemical composition • Will change how the atoms or molecules interact • Chemical Change – Produces matter that looks different from the original matter • Burning is a good example Rust is an Example of Chemical Change Iron will chemically change when exposed to air Compounds • Two or more elements combined in a particular structure • They can be broken down into their parts • Individual elements! • Example Water! 𝐻2 0 • Made of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom • Most things in the world are made of compounds • More than one element Compounds • Dopamine - C8H11NO2 • Theobromine (Chocolate) - C7H8N4O2 • Caffeine - C8H10N4O2 • THC - C21H30O2 Molecules • When atom join together, they form molecules • Molecules can be made of all the same type of element • In the atmosphere, oxygen atoms pair up - 𝑂2 • Molecules can also be made of different elements • Example Water! 𝐻2 0 • This is a compound! Molecules and Bonding • Two or more atoms are joined by a covalent bond • Sulfuric Acid = H₂SO₄ Ionic Compounds • Ions – atoms that have a positive or negative charge • Postively charged ions are missing an electron • Negatively charged ions have an extra electron Ionic Compounds • Ionic compounds have: • 1 positive ion • 1 negative ion • No electrical charge – Why? Ionic Bonds • One atom takes or gives an electron to another • Ionic bond • Electron permanently moves to another atom • Different from covalent bond – they “share” electrons Ionic Compounds are Crystals • Positive and negative ions attract each other like magnets and form a pattern • Crystals!