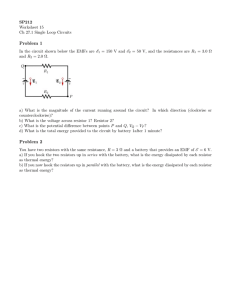
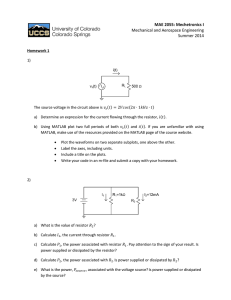
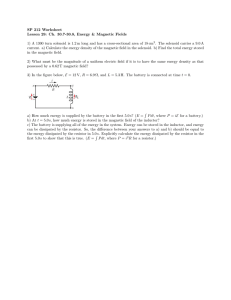
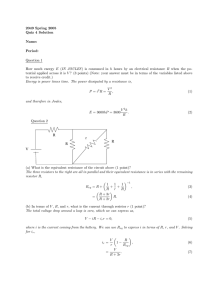
1. D [1] 2. C [1] 3. B [1] 4. C [1] 5. (a) (b) (i) the work done per unit charge in moving a quantity of charge completely around a circuit / the power delivered per unit current / work done per unit charge made available by a source; 1 (ii) the ratio of the voltage (across) to the current in the conductor; 1 (i) emf × current; 1 (ii) total power is V1I + V2I; equating with EI to get result; or total energy delivered by battery is EQ; equate with energy in each resistor V1Q + V2Q; IB Questionbank Physics 2 1 (c) graph X: horizontal straight line; graph Y: starts lower than graph X; rises (as straight line or curve) and intersects at 4.0 V; 3 Do not pay attention to numbers on the vertical axis. (d) (i) (ii) realization that the voltage must be 4.0 V across each resistor; and so emf is 8.0 V; 2 power in each resistor = 3.2 W; and so total power is 6.4 W; or current is 0.80 A; so total power is 8.0×0.80 = 6.4 W; 2 [12] 6. (a) (i) (ii) æ pl ö 1.1´ 10 -6 ´ 4.5 use of R ç = ; =÷ -8 è A ø 6.8 ´ 10 72.8 Ω (73 Ω) 240 2 / shows appropriate alternative equation; 72.8 790 W; IB Questionbank Physics 1 2 2 (iii) one-third length so E2 has one-third resistance of E1 / evaluates R (24 Ω); (same V so) 3 × power of E1; so total power = 4 × E1 = 3.2 kW; 3 or numerical method 728 = 3 A; 240 current in R2 = 9 A; total current = 12 A and total power = 3.2kW; Award [3] for correct alternative working. current in R1 = (iv) (b) (i) (ii) the power output will be less; because the total resistance is greater in the series case; hence the current is less and power depends on I2; V2 P= ; R 3 max concentric circles (by eye); a minimum of three circles required; correct direction; 3 current in one turn produces magnetic field in region of adjacent turn; this gives rise to force in adjacent turn which also has electric current; they attract; 3 [15] 7. (a) (i) ratio of potential difference to current / (ii) resistance = IB Questionbank Physics V with terms defined; I 1 230 2 ; 980 3 = 54 Ω; Award [2] for bald correct answer. (iii) L= = RA r ; 54 ´ π ´ [1.75 ´ 10 -4 ] 2 ; 1.3 ´ 10 - 6 (L ≈ 4 m) Must see re-arrangement of data booklet equation or completely correct substitution as shown in second line for first mark. (b) 2 2 e.g. switch connected so that P can be achieved; another switch connected so that 2P and 3P can be achieved; Award [0] if three or more switches used. Allow any correct alternative including case where single resistor is permanently connected to supply. There are many variants, this diagram is only one example. 2 [7] 8. (a) (i) (ii) (b) uniform field equal spacing of lines; edge effect; direction; 3 as shown; 1 combine F = qE and F = ma; ma to get E = ; q E = 5.0 × 103 N C–1/V m–1; IB Questionbank Physics 3 4 (c) (d) V= 1.9 ´ 10 -17 1.6 ´ 10 -19 = 120 V ; 1 (i) 3.0 W; 1 (ii) power dissipated in battery = (0.252 × 4.0) = 0.25 W; power dissipated in circuit = (3.0 – 0.25) = 2.8 (2.75) W; 2 (iii) power dissipated in lamp = (3.0 × 0.25) = 0.75 W; power dissipated in resistor = (2.75 – 0.75) = 2.0 W; 2.0 ö æ resistance ç = ÷ = 32 Ω; è 0.25 2 ø 3 or resistance of lamp =12 Ω; 12 = 0.25 (R + 16); R = 32 Ω; or V across R = 8.0V; 0 .8 R= ; 0.25 = 32 Ω; 3 [16] IB Questionbank Physics 5