Hydraulic Hammer Structure & Function: Service Training
advertisement

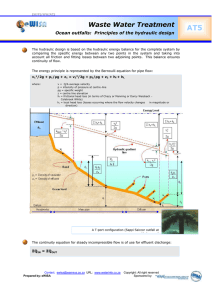
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Contents: • • • • • What is a Hydraulic Hammer? How does a hydraulic hammer work? What are the parts of a Hydraulic Hammer? How install a Hydraulic Hammer? How to maintain a Hydraulic Hammer NIPPON - PNUEMATIC – KOGYO – NIPPON - PNUEMATIC – KOGYO – “JAPANESE” NIPPON - PNUEMATIC – KOGYO – “JAPANESE” A system or equipment that utilizes air as a medium. NIPPON - “JAPANESE” PNUEMATIC – A system or equipment that utilizes air as a medium. KOGYO – “MANUFACTURER” NIPPON - “JAPANESE” PNUEMATIC – A system or equipment that utilizes air as a medium. KOGYO – “MANUFACTURER” What is a Hydraulic Hammer? What is a Hydraulic Hammer? It is an “attachment” used in a Hydraulic Excavator to change its main purpose. What is a Hydraulic Hammer? It is an “attachment” used in a Hydraulic Excavator to change its main purpose. Which is most commonly and popularly known as What is a Hydraulic Hammer? It is an “attachment” used in a Hydraulic Excavator to change its main purpose. Which is most commonly and popularly known as BREAKER What is a Hydraulic Hammer? It is an “attachment” used in a Hydraulic Excavator to change its main purpose. Which is most commonly and popularly known as BREAKER Parts of an Breaker Hydraulic Oil pressure is fed in the “IN” Port then goes to C2 chamber. The pressure causes the piston to move upwards. (As the piston moves upward, the Precharged Nitrogen is being compressed) As the piston has been travelling upward by the Hydraulic Oil pressure fed in the “IN” port. Soon, pressure will be initiated to the sensing port ( the small oil port), this pressure will be acting in the surface area of the main valve. That signal pressure will initiate movement of the main valve to go upward. Since the MAIN VALVE has been pushed upward by the signal pressure, this causes hydraulic pressure in the chambers: C2 and C1 to equalized. Equalization takes place in the opening of the main valve, allowing oil from C2 going to C1. Since the compressed NITROGEN counteracts the pressure, it pushes the piston DOWN. Since the piston is moving DOWNWARD, the pressure in the SIGNAL PORT weakens, causing the MAIN VALVE to begin to LOWER The pressure in the chambers : C1 and C2 becomes equal, the piston is now pushed DOWNWARD by the NITROGEN pressure. Since the piston is moving DOWNWARD, the pressure in the SIGNAL PORT weakens, causing the MAIN VALVE to begin to LOWER The pressure in the chambers : C1 and C2 becomes equal, the piston is now pushed DOWNWARD by the NITROGEN pressure. * note: 00:50 – 2:35 When the Hammering Force is Weak Relation between Pre-charge Pressure of Nitrogen Gas and Impact Energy. Relation between Pre-charge Pressure of Nitrogen Gas and Impact Energy Relation between Pre-charge Pressure of Nitrogen Gas and Impact Energy Relation between the charged pressure of nitrogen gas and hammering frequency 1.-1 The oil flow of the carrier determines frequency. 1.-2 Change in the gas pressure influences frequency, due to change in the oil volume. Relation between Pre-charge Pressure of Nitrogen Gas and Impact energy and Frequency Relation between Pre-charge Pressure of Nitrogen Gas and Impact energy and Frequency The gas pressure is too low. Relation between Pre-charge Pressure of Nitrogen Gas and Impact energy and Frequency Weak impact The gas pressure is too low. Relation between Pre-charge Pressure of Nitrogen Gas and Impact energy and Frequency Weak impact The gas pressure is too low. No hammering Relation between Pre-charge Pressure of Nitrogen Gas and Impact energy and Frequency Weak impact The gas pressure is too low. No hammering The gas pressure is too high. Relation between Pre-charge Pressure of Nitrogen Gas and Impact energy and Frequency Weak impact The gas pressure is too low. No hammering The gas pressure is too high. Relation between Pre-charge Pressure of Nitrogen Gas and Impact energy and Frequency Weak impact The gas pressure is too low. No hammering The gas pressure is too high. Low frequency Tools NITROGEN Tank/ Barrel 4) Rotate the cap to the arrow direction so that to be locked. Cap 4) Rotate the cap to the arrow direction so that to be locked. Cap 5) While rotating the handle, once the rotation should get tight. Keep rotating, then the charged pressure will be indicated on the pressure measure. 4) Rotate the cap to the arrow direction so that to be locked. 5) While rotating the handle, once the rotation should get tight. Keep rotating, then the charged pressure will be indicated on the pressure measure. Cap OK! • Check Items before Installation Stop valve (OUT) Stop valve (IN) Hose Hose Valve Set-up