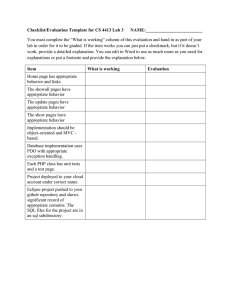
SQL SERVER 2012 Lecturer: Abdiaziz Ali Hassan (M.Sc. IS, India) E-mail: azuzsom@gmail.com 1 CHAPTER 5 DEFINING TABLES, CONT.. CONSTRAINTS OBJECTIVES After completing this lecture, you should be able to answer the following questions: What are the different types of SQL commands What are constraints and how to create constraints in SQL Server 2012 3 SQL COMMANDS The standard SQL commands to interact with relational databases can be classified into groups based on their nature; and they are: DDL DML DCL DQL SQL COMMANDS CONT.. DDL -Data Definition Language CREATE ALTER DROP DML -Data Manipulation Language INSERT UPDATE DELETE SQL COMMANDS CONT.. DCL -Data Control Language GRANT REVOKE DQL -Data Query Language SELECT SQL CONSTRAINTS Constraints are the rules enforced on data columns in a table. These are used to limit the type of data that can go into a table. This ensures the accuracy and reliability of the data in the database. In SQL, we have the following constraints: SQL CONSTRAINTS CONT.. NOT NULL - Indicates that a column cannot store NULL value UNIQUE - Ensures that each row for a column must have a unique value PRIMARY KEY - A combination of a NOT NULL and UNIQUE. Ensures that a column (or combination of two or more columns) have a unique identity which helps to find a particular record in a table more easily and quickly FOREIGN KEY - Ensure the referential integrity of the data in one table to match values in another table CHECK - Ensures that the value in a column meets a specific condition DEFAULT - Specifies a default value when specified none for this column NOT NULL CONSTRAINT Example: UNIQUE CONSTRAINT Example: PRIMARY KEY A primary key is a field in a table which uniquely identifies each row/record in a database table. Primary keys must contain unique values. A primary key column cannot have NULL values. A table can have only one primary key, which may consist of single or multiple fields. When multiple fields are used as a primary key, they are called a composite key. PRIMARY KEY Create Primary Key Example: SETTING A FOREIGN KEY Primary keys uniquely identify a single row of a table Foreign keys link/relate a row of data from a second table to the primary key of the first table TWO RELATED TABLES CREATING THE PRIMARY KEY CREATING THE FOREIGN KEY DEFAULT CONSTRAINT Example: ANOTHER EXAMPLE CHECK CONSTRAINT ANOTHER EXAMPLE IDENTITY MORE THAN ONE CONSTRAINT QUESTIONS AND DISCUSSION Thank You!!!