Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
advertisement

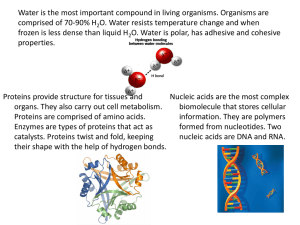
Macromolecules __________________________: large organic molecules (carbon-containing) that make up all living things - Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids We can’t live without them!! They run our body, hold information for how to run our body, and provide the energy to do so EVERYTHING we will learn for the rest of the semester will relate back to macromolecules!!! Structurally, most macromolecules are polymers made out of monomers Structure Overview ____________________________: small, basic sub-units Think about a brick or a word ____________________________: larger more complex structures made of monomers Think about a brick wall or a sentence Carbohydrates Main function = ___________________ storage (short-term) Other uses = ___________________________, transport, and signaling Found in = ____________________ and _______________________________ Monomer = monosaccharides = _______________________sugar molecules Ex. Glucose (main fuel for cell), galactose (in milk), fructose (in fruit) Polymer = polysaccharides = ______________________sugar molecules Ex. Starch (how plants store sugar), glycogen (how animals store sugar), cellulose (structural support in plant cell walls) Energy storage = 4 calories/gram Body can access and break it down easily, thus it is typically the first thing your body will break down to get energy when you need it! Lipids Main function = ___________________ storage (long-term) Other uses = ____________________________, protection, and structure Found in = ________________, oils, phospholipids (in the cell membrane), steroids Monomer = fatty acids Polymer = triglycerides Energy storage = 9 calories/gram When your body runs out of easy-to-access carbs, it will break down lipids next for energy Phospholipids - Structure = 2 fatty acids + 1 phosphate o Hydrophilic head = phosphate group o Hydrophobic tail = fatty acids Phospholipid bilayer = 2 layers make up the plasma membrane of our cells Makes membrane selectively permeable Proteins - Main function = no “_______________________function” because proteins do SO MUCH! They run your body! o ______________ that control the rate of biochemical reactions o Hormones that regulate cell processes (Ex. Insulin) o ____________________________ make up bones and muscles (Ex. Collagen) o Transport substances in and out of cell (Ex. Hemoglobin) o ____________________________________ help immune system fight diseases o Movement (Ex. Contractile proteins) o Receptors aid in cell signaling o _________________________ source in the food we eat (Ex. Casein) Found in = _____________________, nuts, and dairy products, but many are made by your body Monomer = ___________________________ acids Polymer = Polypeptide Amino acids linked together by a peptide bond Energy storage = 4 calories/gram Proteins do SO MUCH besides for the body that they are usually the last resort if energy is needed Proteins are the most ____________________ macromolecule in terms of structure AND function 4 levels to their structure Form dictates function The __________________________________ of the protein determines what it does! Nucleic Acid Main function = informational molecules that store, transmit, and express our genetic information; instructions for making proteins Found in = _________________ and RNA You get them from your parents not your food!! Monomer = Nucleotides ___________________, Guanine, _______________________, Cytosine, and Uracil These are made up of: _________________________________________ Phosphate group ________________________________________ Polymer = Nucleic acid = DNA or RNA Energy storage = 0 calories/gram They are NEVER broken down as a source of energy!!