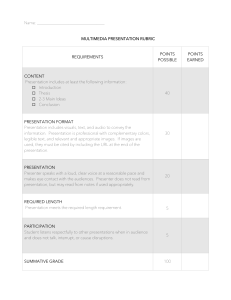
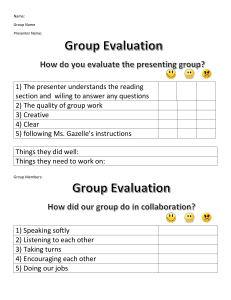
BSBCMM401 Make A Presentation Assessment 2 Student Name: Roger Yee Wei Tzeng Student ID No: CI 160373 Questions / Activities Answer Q1 – Describe when you Verbal presentation would use the following Verbal presentation refers to direct speaking engagements where a presentation methods. presenter may talk but there may be little or no interaction from the participants. A verbal presentation may be useful when wanting to showcase a product as an introductory talk or session. Video presentation Video presentation refers to presenting with the aid of power point slides, video making or other multimedia tools. Presenter will talk with interactions from the participants. A video presentation may be useful when wanting to showcase a product or presenting a report. Storyboards Storyboard refers to presenting with the aid of power point slides, video making or other multimedia tools. Presenter will talk with interactions from the participants. A storyboard may be useful when wanting to showcase a product in more details. Q2 – Detail 5 different Objects presentation aids, and Physical things can be very useful and create a very visceral impact as how they can benefit you use them as direct examples or as metaphors for points you want your presentation. to make. Charts Non-numeric charts can show a number of different things, in particular where individual items have distinct relationships with one another. Flowcharts show the relationships between different activities. Organizational charts show who reports to who. Network diagrams show many-to-many relationships. Diagrams Diagrams illustrate concepts and ideas by using shapes rather than words. Shapes can have different internal angles and use color with specific effect, such as using red to make something stand out or imply danger. They can be positioned relative to one another for subtle effect, for example higher up or more central often means 'more important'. Photographs Photographs provide a picture of reality and are easily included in slides where they can be used illustrate a point or just provide a background. They are good for illustrating action, evoking emotion and more. When you show a person doing something, your audience may well empathize with the image, putting themselves in the place of that person. Graphs Graphs and charts are diagrams that interpret data, visually. They include line graph, bar charts, pie charts, radar diagrams and so on. Q3 – Describe 2 different Surveys and questionnaires evaluation techniques Surverys and questionnaires can be given to the audiences straight after you could use to evaluate or a short time after the presentation. A list of questions can be lined your presentation. State out for the audiences to answer. The feedback from the audiences can the benefits of each generally give a picture of how the presentation is done. The presenter technique detailed. is able to analyze how well the presentation goes, does the information deliver clearly to the audience and so on. Focus group interviews Focus group interviews can be conducted in groups of audience with target questions. This is an unstructured group interview technique where generally 8 to 12 people are brought together, under the guidance of a trained interviewer, to focus on a specific concept, product, or subject. The group dynamics generate ideas and provide insights into audience reactions and perceptions. The feedback from the audiences gives a closer picture of how well the presentation is done. The presenter is able to get the idea of how well the presentation goes, does the information deliver clearly to the audience and so on. Q4 – Describe the Case studies benefits and limitations Benefits – Both the participants and the presenter can observe skills of the following being utilized. Case studies give a ‘real life’ feel to the presentation that presentation strategies. extends and tests understanding of the concepts presented. Limitations – Some participants can be too quiet to fully participate. Can be time consuming to prepare. If a case study lacks substance some participants will become bored. Demonstration Benefits – Visual aids can be used to demonstrate and illustrate material or skills. They can provide accurate information. Use of equipment for demonstrations can break up the learning environment. They can assist with the kinesthetic and visual participants. Limitations – Material can be out of date. Over-copying can result in poor quality. If using a data projector it can be difficult for all the participants to see. Can result in passive learning – the participants may not be taking in any information. A trainer may rely too heavily on the resources and create less interaction with the group. Discussions Benefits – The participants can easily express their ideas. It promotes a bit more interest. The participants can support each other in their learning. It provides a change of focus away from the presenter and allows the participants to focus on each other and work together. Limitations – One or two participants can dominate the discussion. Some of the quieter participants may not want get involved. Discussion can often move away from the desired topic. Some participants may argue which could create a negative environment. Group and/or pair work Benefits – The participants can easily express their ideas. It promotes a bit more interest. Group work can be contextualized easily. The participants can support each other in their learning. Limitations – Some of the quieter participants may not want get involved. Group discussion can be time consuming. There could be personality clashes in the group causing some participants to withdraw. Some participants may argue which could create a negative environment. Questioning Benefits – Both participants and presenter can easily interact. The participants can easily express their ideas. Limitations – Passive participants will not take part as the active ones will always give responses. Simulations and role-play Benefits – Role plays give a ‘real life’ feel to the presentation. It allows the participants to practice in an experimental environment without repercussions and demonstrates how things happen with consequences. Sessions can become active and meaningful. Participants can feel as though they are working on real problems. Limitations – Role plays can be dominated by louder personalities, causing the quieter ones to be more withdrawn. If more than one role play is taking place at once, it can become difficult for the presenter to focus on each one individually. They can get out of control if not watched correctly. Can be time consuming to prepare. Q5 – What is meant by Facilitation refers to the process of designing and running a facilitation? successful meeting. Facilitation concerns itself with all the tasks needed to run a productive and impartial meeting. Facilitation serves the needs of any group who are meeting with a common purpose, whether it be making a decision, solving a problem, or simply exchanging ideas and information. It does not lead the group, nor does it try to distract or to entertain. A slightly different interpretation focuses more specifically on a group that is engaged in experiential learning. Q6 – In your own words, how does the following legislation affect business operations? Anti-discrimination Anti-discrimination legislation allows employees and customers to be legislation treated with respect without discrimination in terms of sex, age, race, ethnicity, nationality, disability, mental illness or ability, gender, sex characteristics, religious, creed or individual political opinions. Ethical principles Ethical issues are a set of moral values that need to be addressed while carrying out business. Businesses operate in a society that is structured around moral values. Therefore, when conducting its operations, a business has certain responsibilities which are to provide the society with quality goods and services that will improve the people’s living standards. Codes of practice Codes of practice set out industry standards of conduct. These are guidelines for fair dealing between the business owner and customers, and let customers know what the business agrees to do when dealing with them. Privacy laws Privacy laws prevent a business from disclosing personal information of the employee and customers to the third parties. This will limits the business owner from knowing the employees past employment and the characteristics of their customers. On the other hand, privacy laws will protect their privacy from disclosure to other people. Occupational health and OHS involves the assessment and migration of risks that may impact the safety health, safety or welfare of customers, employees, visitors, contractors, volunteers and suppliers. OHS help to retain staff, maximise employee productivity, minimise injury and illness in the workplace, reduce the costs of injury and workers’ compensation and ensure you meet your legal obligations and employee responsibilities. Q7 – Describe the Seven principles of effective communication requires the following: principles of effective 1. Completeness: communication The message or the context of the communication should contain all facts required for proper reaction by the recipient. A complete communication clarifies all possible questions and helps to take proper decision. 2. Conciseness: The subject-matter of the communication should be brief and short in nature. No unnecessary elaboration is to be made in a communication. Words used in a communication should be appropriate and expression should be precise. Repetition should be avoided. 3. Consideration: While making communication the sender should consider the social and cultural background, education, age, emotions, etc. of the recipient and modify language, change attitude and approach accordingly. 4. Concreteness: Concrete communication refers to exchange of specific, definite and exact information instead of vague and general information. It is convincing and acceptable to the recipient as there is no ambiguity in it. 5. Courtesy: The sender of the message should be alert in respect of dignity, respect and honour of the receiver. Care should be taken so that the communication may not hurt, injure, belittle or irritate the receiver in any way. Sender will also be respected in turn as honour begets honour. 6. Clarity: The idea contained in the message should be expressed clearly. There will remain no confusion in respect of the meaning of the message. The sender and the receiver of the message will understand it identically. 7. Correctness: Effective communication should be correct in spelling, construction of sentence and use of language. Grammatical mistakes must be avoided. A correct message creates good impact on the receiver and enhances prestige of the sender.