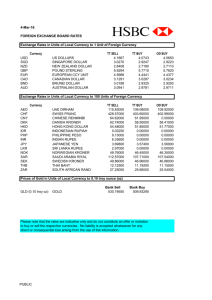
Currency Subtitle History of currency The first region of the world to use an industrial facility to manufacture coins that could be used as currency was in Europe, in the region called Lydia (modern-day Western Turkey), in approximately 600 B.C. The Chinese were the first to devise a system of paper money, in approximately 770 B.C. Exchange rates International currency exchange rates display how much one unit of a currency can be exchanged for another currency. Currency exchange rates can be floating, in which case they change continually based on a multitude of factors A floating exchange rate doesn't mean countries don't try to intervene and manipulate their currency's price, since governments and central banks regularly attempt to keep their currency price favorable for international trade. Rupee Rupee is the common name for the currencies of India, Indonesia, the Maldives, Mauritius, Nepal, Pakistan, Seychelles, and Sri Lanka, and of former currencies of Afghanistan, Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, and the UAE (as the Gulf rupee), British East Africa, Burma, German East Africa, and Tibet. The rupee sign ₨ is a currency sign used to represent the monetary unit United States dollar The United States dollar is the official currency of the United States and its territories. The Coinage Act of 1792 introduced the U.S. dollar at par with the Spanish silver dollar The U.S. dollar became an important international reserve currency after the First World War, and displaced the pound sterling as the world's primary reserve currency by the Bretton Wood Agreement towards the end of the Second World War. The dollar is the most widely used currency in international transactions. It is also the official currency in several countries and the de facto currency in many others Euro The euro is the official currency of 19 of the 27 member state of the European Union. This group of states is known as the eurozone or euro area and includes about 343 million citizens as of 2019. The name euro was officially adopted on 16 December 1995 in Madrid. The euro was introduced to world financial markets as an accounting currency on 1 January 1999, replacing the former European Currency Unit (ECU) at a ratio of 1:1 (US$1.1743). Kuwaiti Dinar The Kuwaiti dinar is the currency of Kuwait. As of May 2021, the Kuwaiti dinar is the strongest circulating currency, with one Kuwaiti dinar equalling 3.32 United States dollars, which is just in front of the Bahraini dinar with one Bahraini dinar equalling 2.65 United States dollars. The dinar was introduced in 1960 to replace the Gulf rupee, equal to the Indian rupee. It was initially equivalent to one pound sterling. Kuwaiti Dinar When Iraq invaded Kuwait in 1990, the Iraqi dinar replaced the Kuwaiti dinar as the currency and large quantities of banknotes were stolen by the invading forces. After liberation, the Kuwaiti dinar was restored as the country's currency and a new banknote series was introduced, allowing the previous notes, including those stolen, to be demonetized. Japanese Yen The yen is the official currency of Japan. It is the third most traded currency in the foreign exchange market after the United States dollar and the Euro. It is also widely used as a third reserve currency after the U.S. dollar and the euro. Following World War II the yen lost much of its prewar value. The Japanese government focused on a competitive export market, and tried to ensure a low exchange rate for the yen through a trade surplus. Currency Currency is a medium of exchange for goods and services. In short, it's money, in the form of paper or coins, usually issued by a government and generally accepted at its face value as a method of payment. In general, the eight most traded currencies (in no specific order) are the U.S. dollar (USD), the Canadian dollar (CAD), the euro (EUR), the British pound (GBP), the Swiss franc (CHF), the New Zealand dollar (NZD), the Australian dollar (AUD) and the Japanese yen (JPY). 1 United States Dollar = 74.23 Indian Rupee 1 Euro = 88.60 Indian Rupee 1 Kuwaiti Dinar = 246.33 Indian Rupee 1 Japanese Yen = 0.67 Indian Rupee Barter system The history of bartering dates all the way back to 6000 BC. Introduced by Mesopotamia tribes, bartering was adopted by Phoenicians. When money was invented, bartering did not end, it become more organized. Due to lack of money, bartering became popular in the 1930s during the Great Depression. A barter system is an old method of exchange. The is system has been used for centuries and long before money was invented. People exchanged services and goods for other services and goods in return. The value of bartering items can be negotiated with the other party. Thankyou