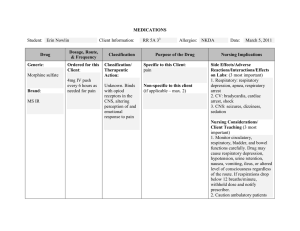
Risk Factors Pre-existing respiratory conditions (asthma, pneumonia) A previous anaphylactic reaction or pre-existing allergies Signs & Symptoms Neurological: headache, dizziness, paresthesia, feeling of impeding doom Skin: pruritis, angioedema, erythema, urticaria Respiratory: hoarseness, coughing, sensation of narrowed airway, wheezing, stridor, dyspnea, tachypnea, respiratory arrest Cardiovascular: hypotension, dysrhythmias, tachycardia, cardiac arrest Gastro-intestinal: abdominal pain, cramps, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea Etiology Respiratory failure from severe bronchospasm or laryngeal edema which may lead to brain damage Myocardial infarction Kidney failure Death Diagnosis Anaphylaxis Medical Management (Pharmacological/Surgical) Epinephrine Used in cases of anaphylaxis to produce bronchodilation Adverse effects: tremors, anxiety, headache, dizziness, palpitations, tachycardia, HTN, N&V. dyspnea o Assess lung sounds and monitor vitals especially BP and HR continuously o Paradoxical bronchospasms may occur and if they do medication should be stopped immediately Diphenhydramine Used to relieve allergy symptoms by competing with histamine for receptors and blocking histamine Adverse effects: dizziness, drowsiness, hypotension, urinary retention, thrombocytopenia, increased thick secretion o Assess respiratory rate and cough and provide fluids to decrease secretion thickness o Monitor I&O ratio and CBC o Caution patient to avoid hazardous activities due to drowsiness Methylprednisolone Decreases inflammation Adverse effects: flushing, sweating, HTN, embolism, tachycardia, diarrhea, pancreatitis o Monitor weight, monitory for infection o Caution patient to not discontinue abruptly o Teach patient signs of adrenal insufficiency: nausea, anorexia, fatigue, dizziness, dyspnea, weakness, joint pain Albuterol nebulizer Increases ability to breath by causing bronchodilation Adverse effects: tremors, headache, palpations, tachycardia, flushing, dry throat o Assess respiratory function o Advise patient to limit caffeine products Potential Complications Anaphylaxis is the most severe, life-threatening hypersensitivity reaction and it can occur when a patient is in contact with a foreign object. Medication is the most common cause of anaphylaxis. Other common causes include foods (milk, eggs, nuts), animal serums (snake venom, rabies), insect stings, and latex. Labs/Diagnostic Tests CBC with WBC differential (including absolute lymphocyte count and eosinophil count Total serum immunoglobulin E levels Plasma histamine Allergy skin test/blood test Cardiac monitoring Nursing Management/Care Nursing Diagnosis Assessment Findings Objective data: Vitals: BP, O2, HR, T, RR Chest X-rays Lab tests Respiratory assessment Physical assessment Comprehensive health/allergy history Diaphoresis Edema Redness Urticaria Laboured breathing Patient is panicked Subjective data: 27 year old male Pain Complain of coughing, chest tightness or difficulty breathing “I feel like my throat is swelling up” Abdominal cramping Health Teaching Teach patient about the medication that caused anaphylaxis Teach patient and family how to use auto-injector epinephrine in case of future exposure Teach patient and family about the signs and symptoms of anaphylactic reaction Ineffective airway clearing related to bronchospasms and laryngeal edema o Position patient in semi recumbent position with head of the bead at 30-to-45-degree angle o Monitor respiratory pattern including rate, depth, and effort as well as other vitals o Administer oxygen as ordered o Administer medication such as bronchodilators or inhaled steroids as ordered Impaired skin integrity related to improper circulation o Assess edema o Assess skin for pruritus as itching can result in disruption of skin integrity o Implement treatment plan for topical treatment of the site of skin impairment o Obtain precise history of allergies as well as medication and foods taken Anxiety related to threat of current status o Offer the client accurate information to help reduce irrational thoughts and fears o Recognize awareness of patient’s anxiety o Encourage controlled breathing o Teach client healthy anxiety managing techniques References Ackley, B. J., Ladwig, G. B., Makic, M. B., Martinez-Kratz, M. R., & Zanotti, M. (2020). Nursing diagnosis handbook: An evidence-based guide to planning care. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier. Hinkle, J. L., & Cheever, K. H. (2018). Brunner & Suddarths textbook of medical-surgical nursing. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Lewis, S. L., Bucher, L., MacLean Heitkemper, M., Harding, M. M., Barry, M., Lok, J., Tyerman, J., & Goldsworthy, S. (Eds.). (2019). MedicalSurgical Nursing in Canada: Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems (4th ed.). Elsevier Canada Skidmore-Roth, L. (2015). Mosbys Drug Guide for Nursing Students. Mosby.