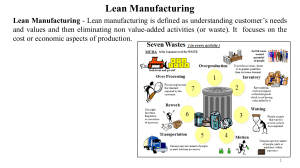
Business Studies: Operations Management Production of goods and services Tangible meaning something that you can touch like wood but intangible is something that you can’t touch like ideas. The meaning of production has some form of the word “process” or “method” in it. Labour intensive needing a large workforce or a large amount of work in relation to output. Capital intensive – needing a large amount of financial assets to invest in order to create The meaning of production: - - Production is process of transforming tangible inputs (raw materials) and intangible inputs (idea) into goods or services. Resources used is to create an output that has an exchange value. It is the process of adding value to a product (using four factors of production – land, labour, capital and enterprise) to satisfy customer needs and wants. Productivity => Is how a business measure its efficiency. - - Productivity could mean using fewer inputs or workforce to create the same amount of output. Or using the same amount of input but produce a greater amount of output. The rate a company produce goods is correlate to the number of people and the number of materials necessary to produce the goods: Equation for productivity: Quantity of output: The amount of something produced by a person, machine, or industry. Quantity of input: Resources such as people, raw materials, energy, information, or finance that are put into a system (manufacturing plant, computer system) to obtain a desired output. Business Studies: Operations Management Production of goods and services Fixed costs – costs that does not change with the level of output. Variable costs – costs that varies with the output. Ways to improve productivity - - Improving layout of factory so production becomes faster and more efficient Training workers so they can be more productive Using automation – introduction of automatic equipment in a manufacturing or other process or facility. Robots or machines to do the job. Review employee performance to measure whether workers are meeting industry standards. Communicate openly to foster a positive workplace environment. Match tasks to skills Keep goals clear and focused Benefits of increasing efficiency/productivity - Lower cost per unit (Cost Per Unit = (Total Fixed Costs + Total Variable Costs) / Total Units Produced) Less employees needed (reduce labour cost) Increasing engagement, (more productive worker tends to be more engaged in their work) Reduce overall costs Increasing profitability Improves competitiveness (anything that gives you an edge to be better than your competitors). Why business hold inventories Example reasons: - Factories hold inventories mainly to make sure that there are enough materials for production Business Studies: Operations Management Production of goods and services - Shops hold stock to ensure that products are constantly available to customers Overall, business hold inventories for these reasons: 1. Meet variations in customer demand: - Meet unexpected demand - Smooth seasonal or cyclical demand 2. Price advantages - Temporary price discounts - Advantage of scale of economy (quantity discounts) - Hedge against price increases (in case the cost of stock increases in the future, sell for more profit) 3. Process & supply surprises - Internal – upsets in parts of our own processes - External – delays in incoming goods Why holding too much stocks is bad - Money wasted on storage cost/ warehouse costs Product life (the product expires before selling it) Opportunity cost (money could’ve been used somewhere else) Insurance costs Handling costs Why holding too little stocks is bad - Unsatisfied customers and loss of customer loyalty Missed sales Loss of profit Giving the opportunity for the competitor to take over the market Business Studies: Operations Management Production of goods and services Buffer stock (Extra stock) What is it? - Extra products, supplies, etc that a company keeps, so it always has enough available to sell or use: Why? - Safety stock – inventory to deal with sudden customer demands for a product or in case supplies doesn’t get delivered on time Lean production - - It is a term for technique used by business to cut down waste and increase efficiency. An approach to management to cut down waste, while ensuring quality. This can be applied to all aspects of a business, for example design, to production to distribution. Lean production aims to cut down costs by making the business more efficient and become more responsive to markets. Lean production originated in Japan but it has now been adopted by many businesses. Lean production cuts out or minimizes activities that do not add value to the production process, such as holding stocks, repairing faculty product and unnecessary movement of people and product around the business. The lean approach to managing operations is really about: - Doing the simple things well Doing things better Involving employees in the continuous process of improvement Business Studies: Operations Management Production of goods and services - And as a result, avoiding waste. The concept of lean production is an incredibly powerful for any business that wants to become or remain competitive. Common wastes in businesses Overproduction – producing too many products which then costs the business money to keep the product in storage, which can become damaged or expires. Waiting – goods not being processed on time. Transporting – materials being moved around the factory inefficiently. Over-processing – Using advanced machine to do simple tasks, hiring a skilled employee to do basic tasks. Defects – production of faulty products which can’t be sold. Business Studies: Operations Management Production of goods and services - Reduced space – as part of the waste reduction process, space will be created. 3 common lean production techniques - Kaizen Just-in-time production Cell production Kaizen Kaizen means continuous improvement by eliminating waste. - Workers meet regularly to discuss problems and possible solutions. In this way, wastage is reduced and efficiency is improved. Factory floors are usually rearranged so that the flow of production from one activity to the next is improved. Just-in-time production Items are created to meet demand, not created in surplus or in advance of need. - Focus on reducing the need to hold stocks of raw material or parts that are needed (this reduces storage costs) Raw materials are delivered just in time by suppliers for production Reliable suppliers are needed for this to work Example: Milk gets delivered to milkshake factory 30 minutes before production starts, this means that the milkshake factory won’t have to spend money on expensive refrigerators to store milk before it gets produced. Business Studies: Operations Management Production of goods and services Cell production Cell production is a form team working and helps ensure worker commitment, as each cell is responsible for a complete unit of work, which Herzberg would view as part of job enrichment. - The production line is divided into separate teams of workers, each makers a part of the finished production Motivation is improved due to the variety of tasks and the worker belonging to a team Quality improves because each cell has ‘ownership’ over production Improved customer response time