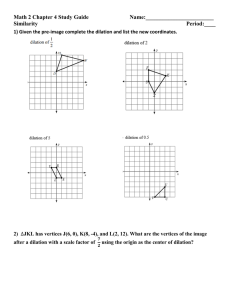
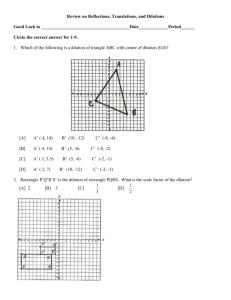
LESSON 13.2 Algebraic Representations of Dilations How can you describe the effect of a dilation on coordinates using an algebraic representation? ADDITIONAL EXAMPLE 1 Graph the image of rectangle JKLM after a dilation with the origin as its center and a scale factor of 2. What are the vertices of the image? The vertices of the dilated image are J' (2, 2), K' (6, 2), L' (6, 8), and M' (2, 8). 13.2 LESSON QUIZ 8.3.C 1. A rectangle has vertices at P(6, 6), Q(6, –6), R(–6, –6), and S(–6, 6). The origin is the center of dilation, and . What are the vertices of the dilated image? P'(2, 2), Q'(2, –2), R'(–2, –2), S'(–2, 2) 2. Write an algebraic representation of a dilation that has a scale factor of 0.45. (x, y) (0.45x, 0.45y) 3. Triangle JKL is the preimage. Write two algebraic representations, one for the dilation to triangle J’K’L’ and one for the dilation to triangle J’’K’’L’’. Triangle J’K’L’: (x, y) (0.5x, 0.5y) Triangle J’’K’’L’’: (x, y) (1.5x, 1.5y) How can you describe the effect of a dilation on coordinates using an algebraic representation? Sample answer: For scale factor k, the algebraic representation of the dilation, with center at the origin, is (x, y) (kx, ky).