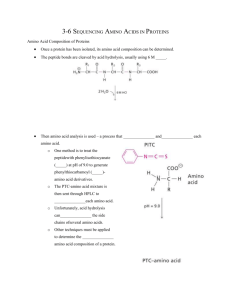
ASSIGNMENT On . Subject: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Course Name: Protein Technology Course no.: BMB-305 Submitted By: Name: MD. Shakil Ahmed Submitted To: Roll: 1810425117 Name: Md Nuruzzaman Session: 2017-18 (Assistant professor) Year: Third Department of. Biochemistry and Department of. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Molecular Biology Rajshahi University, Rajshahi University, Rajshahi Rajshahi. Edman degradation Edman degradation, developed by Pehr Edman, is a method of sequencing amino acids in a peptide. In this method, the amino-terminal residue is labeled and cleaved from the peptide without disrupting the peptide bonds between other amino acid residues. The Edman degradation sequentially removes one residue at a time from the amino end of a peptide. The Edman degradation process are as follows, Suppose that the protein is: Ala-Gly-Asp-Phe-Arg-Gly We expose the peptide to phenyl isothiocyanate. This molecule reacts with the uncharged terminal α- amino group of the peptide to form a phenylthiocarbamoyl derivative. Then, under mildly acidic conditions, a cyclic derivative of the terminal amino acid is liberated, which leaves an intact peptide shortened by one amino acid, which can be identified by chromatographic procedures. Furthermore, the amino acid composition of the shortened peptide: (Arg , Asp, Gly2, Phe) can be compared with that of the original peptide: (Ala, Arg, Asp, Gly2, phe). The difference between these analyses is one alanine residue, which shows that alanine is the amino-terminal residue the original peptide. The Edman procedure can then be repeated on the shortened peptide. The amino acid analysis after the second round of degradation is, (Arg, Asp, Gly, Phe) showing that the second residue from the amino end is glycine. This conclusion can be confirmed by chromatographic identification of PTH-glycine obtained in the second round of the Edman degradation. Three more rounds of the Edman degradation will reveal the complete sequence of the original peptide.