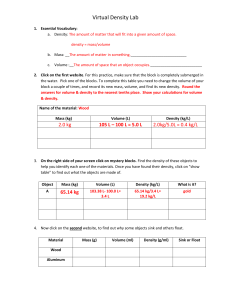
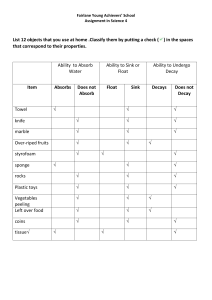
Measuring USING MEASURING TOOLS TO MAKE QUANTITATIVE OBSERVATIONS We already learned how to measure: MASS the measure of the amount of matter in an object VOLUME the measure of the space occupied by an object mass of 3 oranges = 300 g mass of the bag of apples = 3 kg What is the volume of this rectangular solid? Don't forget to write the unit of measurement. Volume of Rectangular Solid = length x width x height 3 Volume = 45 cm x 25 cm x 15 cm = 16,875 cm What is the volume of the stone in the graduated cylinder? Don't forget to write the unit of measurement. Water Displacement Method: Volume of stone = Final volume - Starting volume Starting volume of water = 150 ml Final volume (water + stone) = 180 ml Volume of stone = 180 ml - 150 ml = 30 ml Now let's study DENSITY The density of a substance is its mass per unit volume. It describes how closely packed the particles are in that substance. Density determines if an object will sink or float in water. Float or Sink? Remember: density of water = 1 g/ml density of object < 1 FLOAT density = 1 NEITHER FLOAT NOR SINK density > 1 SINK Bouyant Force is the upward force exerted on objects submerged in fluids depends on the density of the fluid in which the object is submerged, If the mass of the stone is 50 g and its volume is 30ml, what is its density? Don't forget to write the unit of measurement. density = mass volume mass = 50 g volume = 30 ml density = 50 g = 1.67 g 30 ml ml