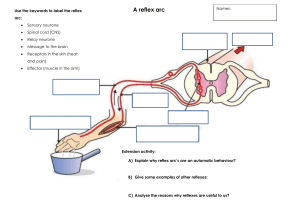
Neurologic Quarter Screening A neurological quarter screening exam is designed to assess symptoms extending below the gluteal folds, below the upper trapezius or quarter symptoms of an unknown origin. The results of the neurological examination will assist with differential diagnosis, and prognosis. Sensory (Dermatomes) Evaluation for sensory loss is performed during the quarter screen by lightly brushing the hand over key dermatomal regions. Any deficit noted should be tested further with the use of a pin to clearly map out the area of sensory deficit. General sensory loss may indicate either serious pathology or possibly symptom magnification. Considerable overlap and individual variations in dermatomal patterns are known to exist. The results of sensory testing should be collaborated with the results of reflex and resisted testing to determine the presence and extent of nerve root compression. Grading: Normal, Diminished or Absent Motor (Resisted isometric testing) Evaluation of key muscles to each myotome is performed. Myotomal weakness may be indicative of lower motor neuron lesions, while more generalized weakness may indicate more serious pathology or simply generalized disuse atrophy of the lower limb Grading: Normal or Diminished Reflex Reflex assessment is used to evaluate the reflex pathway. Diminished or absent reflexes may be indicative of nerve root impingement and subsequent lower motor neuron disturbance. Confirming evidence that accompanies a diminished reflex would be myotomal weakness or sensation loss or abnormality in a particular dermatome. Hyperactive reflexes in tendon reflexes can represent upper motor neuron disturbances (e.g., myelopathy). At the same time, hyperactive reflexes can be a normal variant. If encountered, the clinician should at least suspect a myelopathic process or an upper motor neuron pathology. Confirming evidence for upper motor neuron involvement that accompanies hyperactive reflexes would be pathological reflexes. Grading: 0 Absent, 1+ Minimal response, 2+ Normal response, 3+ Brisk response, 4+ Hyperactive reflex (Grades 0 and 4+ are indicative of pathology, 1+ and 3+ are normal unless asymmetric or associated with other abnormalities) Pathological reflexes are graded as positive or negative. Upper Quarter Screen Nerve Root C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 Dermatome No Dermatome Back of head/occipital region Back of neck Clavicle, AC joint Lateral upper arm Lateral forearm, palmar tip of thumb or index finger C7 Palmar tip of middle finger C8 Palmar tip of little finger T1 Medial forearm T2 Medial upper arm Myotome Reflex Pathological reflexes Cervical rotation Hoffman reflex Cervical flexion, shoulder shrug Shoulder shrug Shoulder shrug Shoulder abduction Biceps Elbow flexion or wrist Brachioradialis extension Elbow extension or Triceps wrist flexion Thumb extension Finger adduction or little finger abduction Lower Quarter Screen Nerve Root L1 L2 L3 L4 Dermatome Inguinal ligament Anterior proximal thigh Anterior distal thigh and medial knee Medial lower leg L5 Lateral lower leg, dorsum of foot S1 Lateral foot, heel S2 Posterior knee –popliteal fossa Myotome Hip flexion Hip flexion Knee extension (2° hip adduction) Dorsiflexion Great toe extension (2° hip abduction) Functional heel walking Eversion , plantarflexion (2° knee flexion, hip extension) Functional toe walking Bowel/bladder problems Reflex Pathological reflexes Ankle clonus Babinski Patellar tendon Achilles’ tendon