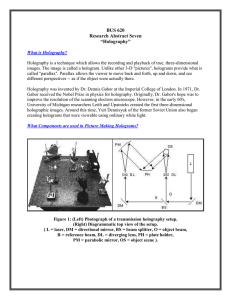
THERMOGRAPHY & HOLOGRAPHY 1 Non Destructive Testing and Evaluation B.Tech 4TH SEMESTER METALLURGICAL AND MATERIAL ENGINEERING NIT SRINAGAR THERMOGRAPHY Thermography is a technique of obtaining image of heat distribution over the surface. Special television camera with infrared sensitive detector and a lens which transmits radiation . Such camera operates at normal video rates. Temperature variation in the object are then displayed as the shades of the grey or can be converted into the pseudo colour image . Bodies which have the temperature above 0 kelvin radiates infrared waves. 2 3 PRINCIPLES OF THERMOGRAPHY : Bodies give out infrared radiations . The infrared energy is dependent on absolute surface temperature . The infrared energy is dependent on surface emissivity. Semiconductor's are used to measure the infrared energy . 4 Basic thermal science’s: Heat Temperature Basic heat transfer: Conduction Convection Radiation Stefan's Boltzmann law: It states that total energy radiated per unit surface area of a black body in unit time is directly proportional to fourth power of black bodies absolute temperature T. WBB=ρx𝑇 4 5 6 Types of infrared camera: Single sensor. Focal plane array. 7 Thermographic approach: Active Passive Detectors: Uncooled microbolometric detector. Cooled detectors. Uses: Detects different disease and disorders . Detects tumors and cancer cells. In electronic industry. Aerospace applications ,electrical inspections ,mechanical inspections Advantages of thermography: Non-contact method with low thermal stress. Effective prevention of test scrap. Simple analysis of large and uneven surface. Meaningful analysis of the defects. Disadvantages : Need skilled and trained person. Interpretation of thermal images also challenged. Cost of equipment's is also high. Image contrast is high so that ability to distinguish the detail is poor, We cannot inspect transparent material. 8 HOLOGRAPHY Holography : it is method of producing a visual threedimensional (3-D) image of the object by means of light wave patterns recorded on a photographic plate. Its an advanced form of photography that allows an image to be recorded in three dimensions. Holography from the Greek (whole+write) is the science of producing holograms. A photograph of an interference pattern which, when suitably illuminated by laser light, produces a three dimensional image. 9 Working of Holography: Laser light….usually helium-neon =(HeNe) laser is used. Beam splitter ….device that use mirrors and prisms to split laser into two beams. 1.object beam 2.reference beam. Mirrors …direct the beams of light to correct locations Holographic film….to record image very high resolution. Can be seen through naked eye. Hologram properties: If you look at these holograms from different angles,you see objects from different perspectives . It shows divisible property i.e if you cut one in half,each half contains whole views if the entire holographic image 10 How to create a hologram: To create hologram, a laser beam (coherent light) is split in two beams Reference beam: That stays undisturbed Object beam: strikes the objects and then bounces onto the plate. Working of holography is divided into two phases 1.Recording 2.Reconstruction 11 Applications of holography: Optical computers Bio-medical applications Compact disk Grocery store Holographic interferometery Holographic scanners Holostores Reconstruction: when a hologram is later illuminated with coherent light of the same frequency that created it,a three dimensional image of the image of the subject appears. 12 13 Photography vs Holography: PHOTOGRAPHY 2-D recording process Ordinary light can be used Lens system Image has poor resolution HOLOGRAPHY 3-D recording process Only laser light can be used Lens less system Very high resolution Advantages: Cost effective High storage capacity Increased feasibility of objects(depth) Enables the achievement of multiple image on a single plate and give 3-D images Ability to combine with other technologies Disadvantages: Provide static images Do nit produce images of complex movement Require complicated precise machinery to produce and view an image Reference illumination beams are collinear 14 conclusions: Holographic technology has endless applications as far as the human mind can imagine Holographic technologies are not just about art or business communication, they are about safety,security,education,planning and the strength of our civilization here and beyond Holographic technology will become a very integral part of human scoieties and civilizations in future 15 16 THANK YOU