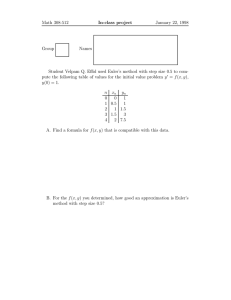
Euler’s Method Lesson 2.1 Objective • Apply Euler’s method to approximate differential equations Definitions Euler’s Method – A way to approximate differential equations using successive linear approximations. Euler’s Method The method is based on the idea of linear approximation. 𝑓 𝑥 ≈ 𝑓′ 𝑐 𝑥 − 𝑐 + 𝑓 𝑐 Or 𝑦 = 𝑚 𝑥 − 𝑥1 + 𝑦1 However, with Euler’s method we don’t stay on the same line. We reformulate the tangent line as we take steps 𝑑𝑥 . Euler’s Method To help apply Euler’s method we will use the following table: 1) Applying Euler’s Method 𝑑𝑦 Consider the differential equation = 𝑥 + 𝑥𝑦. Let 𝑦 = 𝑓(𝑥) be the 𝑑𝑥 function that satisfies the given differential equation with the initial condition 𝑓(1) = 2. Use Euler’s method, starting at 𝑥 = 1 with a step size of 0.5, to approximate 𝑓(2). 𝒙 𝒚 𝒎= 𝒅𝒚 𝒅𝒙 𝑑𝑦 = 𝑚 ∙ 𝑑𝑥 𝑦𝑛𝑒𝑤 = 𝑦 + 𝑑𝑦 2) Applying Euler’s Method 𝑑𝑦 Consider the differential equation = 𝑦 + 𝑥 2 . Let 𝑦 = 𝑓(𝑥) be the 𝑑𝑥 function that satisfies the given differential equation with the initial condition 𝑓(0) = 1. Use Euler’s method, starting at 𝑥 = 0 and using 2 steps, to approximate 𝑓(2). 𝒙 𝒚 𝒎= 𝒅𝒚 𝒅𝒙 𝑑𝑦 = 𝑚 ∙ 𝑑𝑥 𝑦𝑛𝑒𝑤 = 𝑦 + 𝑑𝑦 3) Applying Euler’s Method 𝑑𝑦 Consider the differential equation = 𝑥 2 + 𝑥 − 1. Let 𝑦 = 𝑓(𝑥) be the 𝑑𝑥 function that satisfies the given differential equation with the initial condition 𝑓(0) = 1. Use Euler’s method, starting at 𝑥 = 0 with a step size of 0.5, to approximate 𝑓(1). 𝒅𝒚 𝒙 𝒚 𝑑𝑦 = 𝑚 ∙ 𝑑𝑥 𝑦𝑛𝑒𝑤 = 𝑦 + 𝑑𝑦 𝒎= 𝒅𝒙 4) Applying Euler’s Method The rate at which the flu spreads through a community is modeled by the 𝑑𝑃 logistic differential equation = 0.001𝑃 3000 − 𝑃 , where 𝑡 is measured 𝑑𝑡 in days and 𝑡 ≥ 0. Using Euler’s method with 3 steps, approximate the population infected after 3 days if the initial population infected is 50. 𝒙 𝒚 𝒎= 𝒅𝒚 𝒅𝒙 𝑑𝑦 = 𝑚 ∙ 𝑑𝑥 𝑦𝑛𝑒𝑤 = 𝑦 + 𝑑𝑦 5) Applying Euler’s Method 5) Applying Euler’s Method