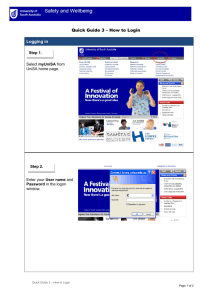
RAE3601/101/0/2021 Tutorial Letter 101/0/2021 Radio Engineering III (Theory) RAE3601 Year module Department of Electrical and Mining IMPORTANT INFORMATION Please register on myUnisa, activate your myLife e-mail address and make sure that you have regular access to the myUnisa module website, RAE3601-2021-Y, as well as your group website. Note: This is a fully online module and therefore it is only available on myUnisa. BARCODE CONTENTS Page 1 INTRODUCTION .......................................................................................................................... 4 1.1 Getting started … .......................................................................................................................... 4 2 OVERVIEW OF RAE3601 ............................................................................................................ 4 2.1 Purpose ........................................................................................................................................ 4 2.2 Outcomes ..................................................................................................................................... 4 3 LECTURER(S) AND CONTACT DETAILS................................................................................... 5 3.1 Lecturer(s) .................................................................................................................................... 5 3.2 Department ................................................................................................................................... 5 3.3 University ...................................................................................................................................... 5 4 RESOURCES ............................................................................................................................... 5 4.1 Prescribed book(s) ........................................................................................................................ 5 4.2 Recommended book(s) ................................................................................................................. 5 4.3 Joining myUnisa ........................................................................................................................... 6 4.3 Library services and resource information ..................................................................................... 6 5 HOW TO STUDY ONLINE ............................................................................................................ 6 5.1 What does it mean to study fully online? ....................................................................................... 6 5.2 The myUnisa tools you will use ..................................................................................................... 7 6 CONTINOUS ASSESSMENT AND GRADUATE ATTRIBUTES .................................................. 8 6.1 Assessment plan .......................................................................................................................... 8 6.2 Weighting of different continuous assessment options .................................................................. 8 6.3 Graduate attributes allocated to the continuous assessment ........................................................ 9 6.3.1 Graduate attributes ....................................................................................................................... 9 6.4. Assessment criteria ......................................................................................................................... 10 6.5 Assessment Guidelines .................................................................................................................... 10 6.5.1 TEST ............................................................................................................................................. 10 6.5.2 ASSIGNMENTS ............................................................................................................................ 10 6.5.2.1 UNIQUE ASSIGNMENT NUMBERS .......................................................................................... 10 6.5.2.2 DUE DATES FOR ASSIGNMENTS ........................................................................................... 11 6.5.2.3. SUBMISSION OF ASSIGNMENTS ........................................................................................... 11 7 CONCLUSION............................................................................................................................ 11 ASSIGNMENT 1..................................................................................................................................... 12 2 RAE3601/101/1/2021 ASSIGNMENT 2..................................................................................................................................... 16 ASSIGNMENT 3..................................................................................................................................... 18 ASSIGNMENT 4..................................................................................................................................... 22 ANNEXURE 1: FORMULAR SHEET ..................................................................................................... 23 ANNEXURE 2: CONSTANTS LIST ........................................................................................................ 24 3 1 INTRODUCTION Dear Student Welcome to Radio Engineering III. Because this is a fully online module, you will need to use myUnisa to study and complete the learning activities for this module. Visit the website for [module code] on myUnisa frequently. The website for your module is RAE3601-21-Y Getting started … 1.1 Owing to the nature of this module, you can read about the module and find your study material online. Go to the website at https://my.unisa.ac.za and log in using your student number and password. You will see RAE3601-21-Y in the row of modules displayed in the orange blocks at the top of the webpage. Select the More tab if you cannot find the module you require in the orange blocks. Then click on the module you want to open. We wish you much success in your studies! 2 OVERVIEW OF RAE3601 2.1 Purpose The purpose of this module is to equip students with knowledge that will enable them to apply analytical and practical techniques and knowledge related to Radio Engineering III. Communicate in a professional way using the language concepts, models, techniques and equipment encountered in the engineering working environment. Apply mathematical techniques and interpret results of mathematical calculations to assist in solving engineering problems. 2.2 Outcomes For this module, you will have to master several outcomes: • Identify, design and build different types of amplifiers for either transmitting or receiving radio frequencies. • Understand the working of oscillators from low to ultra high frequencies (UHF). • Know the importance of RF amplifiers and mixers and how these circuits are integrated in a simple receiver. • 4 Understand the concept of modulation and demodulation in radio circuits. RAE3601/101/1/2021 • Design a balanced modulator and have a better understanding of single-sideband principles. • Have a broader view of FM transmitters and receivers. Be able to design a FM transmission and receiving circuits on a small scale. • Understand digital transmission and reception. • Understand the transmission of signals and the factors that influence signals as they are being propagated. • Know antenna terminology and the construction of different types of antenna arrays. 3 LECTURER(S) AND CONTACT DETAILS 3.1 Lecturer(s) The primary lecturer for this module is Mrs L.B. Rabaza: Department: Electrical and Engineering E-mail: 3.2 rabazlb@unisa.ac.za Department You can contact the Department of Electrical and Mining as follows: E-mail: electrical&mining@unisa.ac.za 3.3 University To contact the University, follow the instructions in the brochure Study @ Unisa. Remember to have your student number available whenever you contact the University. Whenever you contact a lecturer, please include your student number to enable the lecturer to help you more effectively. 4 RESOURCES 4.1 Prescribed book(s) Modern Electronic Communication / Jeffrey S. Beasley, Gary M. Miller. 9/e or latest. 4.2 Recommended book(s) There are no recommended books for this module. 5 4.3 Joining myUnisa The myUnisa learning management system is the University's online campus that will help you communicate with your lecturers, with other students and with the administrative departments at Unisa. To go to the myUnisa website directly, go to https://my.unisa.ac.za. Click on the Claim UNISA Login on the top of the screen on the myUnisa website. You will then be prompted to give your student number in order to claim your initial myUnisa details as well as your myLife e-mail login details. For more information on myUnisa, consult the brochure Study @ Unisa, which you received with your study material. 4.3 Library services and resource information For brief information, go to www.unisa.ac.za/brochures/studies For detailed information, go to the Unisa website at http://www.unisa.ac.za/ and click on Library. For research support and services of personal librarians, go to http://www.unisa.ac.za/Default.asp?Cmd=ViewContent&ContentID=7102 The Library has compiled numerous library guides: • finding recommended reading in the print collection and e-reserves – http://libguides.unisa.ac.za/request/undergrad • requesting material – http://libguides.unisa.ac.za/request/request • postgraduate information services – http://libguides.unisa.ac.za/request/postgrad • finding, obtaining and using library resources and tools to assist in research – http://libguides.unisa.ac.za/Research_Skills • contacting the Library/finding us on social media/frequently asked questions – http://libguides.unisa.ac.za/ask 5 HOW TO STUDY ONLINE 5.1 What does it mean to study fully online? Studying fully online modules differs completely from studying some of your other modules at Unisa. 6 RAE3601/101/1/2021 • All your study material and learning activities for online modules are designed to be delivered online on myUnisa. • All of your assignments must be submitted online. This means that you do all your activities and submit all your assignments on myUnisa. In other words, you may NOT post your assignments to Unisa using the South African Post Office. • All of the communication between you and the University happens online. Lecturers will communicate to you by e-mail, sms and using the Announcements, the Discussion Forums and the Questions and Answers tools. You can also use all of these ways to ask questions and contact your lecturers. 5.2 The myUnisa tools you will use The main tool that we will use is the Lessons tool. The content and assessments of your module will be provided in this tool. At times you will be directed to join discussions with fellow students and complete activities and assessments before you can continue with the content of the module. It is very important that you log in to myUnisa regularly. We recommend that you log in at least once a week to do the following: • Check for new announcements. You can also set your myLife e-mail account to receive the announcement e-mails on your cell phone. • Do Discussion Forum activities. When you do the activities for each learning unit, we want you to share your answers with the other students in your group. You can read the instructions and even prepare your answers offline, but you will need to go online to post your messages. We have also provided the Social Cafe where you can socialise with the other students in the module. • Do other online activities. For some of the learning unit activities you might need to post something on the Blog tool, take a quiz or complete a survey under the Self-Assessment tool. Do not skip these activities because they will help you complete the assignments and the activities for the module. We hope that by giving you extra ways to study the material and practise all of the activities, this system will help you succeed in the online module. To get the most out of the online module you MUST go online regularly to complete the activities and assignments on time. 7 6 CONTINOUS ASSESSMENT AND GRADUATE ATTRIBUTES 6.1 Assessment plan Because this is a continuous assessment (CA) and online module, the assignments are provided in this tutorial letter and on myUNISA. Assessment Nr 6.2 Group Format Unique Nr Due Date Weight 1 Formative MCQ 803140 20210515 2% 2 Formative SAmigo 660972 20210524 15 % 3 Formative Written 877265 20210611 3% 4 Formative SAmigo 631421 20210705 30 % 5 Formative MCQ 783315 20210813 2% 6 Formative SAmigo 626766 20210830 15 % 7 Formative Written 881398 20210917 3% 8 Formative SAmigo 725097 20211011 30 % 9 Formative SAmigo 644899 20210726 10 Formative SAmigo 645633 20211101 Weighting of different continuous assessment options In continuous assessment the principles of a year mark and examination mark is not used. With CA the compilation of the module mark represents the allocation of various weightings to several assessments during the module bringing the total to 100%. All assessments, which include the assessment that replace the examination paper, adds to the continuous assessment. A weighting is determined for each assignment / assessment which will determine the module mark. Your continuous assessment mark allocation for this module is as follows: 8 RAE3601/101/1/2021 (i) weighting of the course: combined formative and summative assessment Learning Unit Assessment Weight Introductory Topics Assignment 1 2% Introductory Topics Minor Online Test 1 15% AM and FM (Transmission and Receive), Single Assignment 2 3% side bands AM and FM (Transmission and Receive), Single Major Online Test 1 30% side bands Wave propagation, Waveguide and radar Assignment 3 2% Wave propagation, Waveguide and radar Minor online 2 15% Transmission lines and Antennas Assignment 4 3% Transmission lines and Antennas Major online Test 2 30% Transmission lines and Antennas Minor Online Test: Repeat AM and FM (Transmission and Receive), Single Major Online Test: Repeat side bands microwave application 6.3 Graduate attributes allocated to the continuous assessment 6.3.1 Graduate attributes To maintain our programme/qualification accreditation, each programme must provide evidence that our students are attaining key “attributes” as defined by the ENGINEERING COUNCIL of SOUTH AFRICA (ECSA). Moreover, our programs need to also be performing “continuous improvement” – i.e., finding evidence-driven actions and processes to improve curriculum and student learning. As such it is important as a student that you are familiar with the ECSA assessment criteria (graduate attributes). Please see link: https://www.ecsa.co.za/education/EducationDocs/120710SPGraduateAttributes.pdf 9 6.4. Assessment criteria Assignments are seen as part of the learning material for this module. As you do the assignments, study the reading texts, consult other resources, discuss the work with fellow students or e-tutors or do research, you are actively engaged in learning. Looking at the assessment criteria given for each assignment will help you to understand what is required of you more clearly. 6.5 Assessment Guidelines Unisa is following a continuous assessment system. So, you will be able to accumulate marks throughout the semester/Year. Your promotion mark comprises of quizzes or tutorials mark of Your mark will be compiled as follows: 6.5.1 TEST Test Number Assessment Tool Unique Number Date Minor Online Test 1 SAmigo 660972 24 May 2021 Major Online Test 1 SAmigo 631421 05 July 2021 Minor Online Test 2 SAmigo 626766 30 August 2021 Major online Test 2 SAmigo 725097 11 October 2021 Minor Online Test: Repeat SAmigo 644899 26 July 2021 Major Online Test: Repeat SAmigo 645633 01 November 2021 6.5.2 ASSIGNMENTS Assignments are numbered consecutively per module, starting from 01. 6.5.2.1 UNIQUE ASSIGNMENT NUMBERS 10 Assignment 1: 803140 Assignment 2: 877265 Assignment 3: 783315 Assignment 4: 881398 RAE3601/101/1/2021 6.5.2.2 DUE DATES FOR ASSIGNMENTS THE DUE DATES FOR THE ASSIGNMENTS ARE: Assignment 1: 15 May 2021 Assignment 2: 11 June 2021 Assignment 3: 13 August 2021 Assignment 4: 17 September 2021 6.5.2.3. SUBMISSION OF ASSIGNMENTS ALL ASSIGNMENTS HAVE TO BE ATTEMPTED!!!!!!! THE SUBMISSION OF AN EMPTY ASSIGNMENT COVER IS UNACCEPTABLE. IT IS VERY IMPORTANT TO CONSIDER THE FOLLOWING POINTS: • No Late Assignment Submissions Will Be Accepted. • Keep A Clear Copy of The Assignment for Your Own Reference. This Is Important, As Assignments Do Get Lost. Submissions of Assignments Must Be in Accordance With “My Studies @ Unisa”. 7 CONCLUSION Do not hesitate to contact us by e-mail if you are experiencing problems with the content of this tutorial letter or with any academic aspect of the module. We wish you a fascinating and satisfying journey through the learning material and trust that you will complete the module successfully. Enjoy the journey! Mrs L.B. Rabaza – lecturer for RAE3601 DEPARTMENT OF EELECTRICAL AND MINING 11 ASSIGNMENT 1 Introductory topics 1 2 3 What is the process of removing intelligence from high frequency in the receiver? 1 Demodulation 2 Demultiplexing 3 Decoupling 4 Modulation A measurement made using a 1 W reference is called…… 1 dWm 2 dbW 3 dB 4 dBi Noise defined as any undesired voltages or currents that end up appearing in circuit is...... 4 12 1 Thermal noise 2 Cosmic noise 3 Electrical noise 4 White noise Chokes which are used at RF frequencies and above have…… 1 Minimum current rating 2 Maximum current rating 3 Minimum voltage rating 4 Both current and voltage rating equal to zero RAE3601/101/1/2021 5 6 Data points generated by time to frequency conversion using FFT is……... 1 Frequency domain record 2 Time domain record 3 Fast Fourier transform 4 Fourier analysis The output power for the audio amplifier is specified to be 38 dBm. Convert the value to watts. 7 1 6.3 W 2 38 W 3 8W 4 2.45 W The output power for an audio amplifier is specified as to be 38 dBm. Convert the value to dBw. 8 1 38 dBw 2 15.7 dBw 3 1.5 dBw 4 8 dBw Which of the following equations is not correct about resonance circuits? 1 2 3 4 9 A receiver has the noise power bandwidth of 10 kHz. The resistor that matches the receiver input impedance is connected across its antenna terminals. What is the noise power contributed by that resistor in the bandwidth, if the resistor has a temperature of 27 C? 13 10 11 1 15.71 kW 2 4.14 x 10-17 W 3 0.14 x 10-17 W 4 4.14 kW Using the information from question 9, determine the effective noise bandwidth? 1 5 kHz 2 31.4 kHz 3 15.71 MHz 4 15.71 kHz One of the reasons for electronic circuit to fail is characterised by sporadic circuit where the works for a while and then quits working and this is referred to……. 12 13 14 1 Poor system performance 2 Intermittent faults 3 Complete failures 4 Induced failures The oscillator that is often used when the greater frequency stability is required is…. 1 Crystal 2 Hartley 3 Clap 4 Colpitts A filter whose capacitive and inductive reactance are equal to constant value 1 Poles 2 Roll off 3 Constant-k filter 4 m-derived filter RAE3601/101/1/2021 14 15 The human voice ranges from about …. 1 30-300 Hz 2 20-3000 Hz 3 3 – 30 MHz 4 30-300 kHz Thermal noise is also known as...... 1 Shot noise 2 White noise 3 Johnston noise 4 Excess noise TOTAL: 15X1 = 15 15 ASSIGNMENT 2 Question 1: Amplitude Modulation 1.1 What is the difference between low level modulation and high-level modulation? (2) 1.2 An SABC transmitter generates a carrier of 25 MHz and is modulated by a picture signal that has frequency components ranging from 70 Hz to 80 kHz. 1.2.1 Determine the range of frequencies generated to the upper and lower sidebands. (2) 1.2.2 Draw the frequency spectrum of the AM modulator output. 1.3 (1) A transmitter with a 10-kW carrier transmits 15 kW when modulated with the single sine wave. 1.3.1 Calculate the modulation index (3) 1.3.2 If the carrier is simultaneously modulated with another sine wave at 50 percent, 1.4 calculate the total transmitted power. (3) List three major benefits of using RF amplifiers in AM broadcast receivers. (3) [14] Question 2: Single side band communication 2.1 Calculate a filter`s required Q to convert DSB to SSB, given that the two sidebands are separated by 200 Hz. The suppressed carrier (40 dB) is 2.9 MHz. (3) [3] Question 3: Frequency Modulation 3.1 An FM transmitter with the signal is represented by the voltage waveform of v= sin (6 X108t + 5sin 1250t). 3.2 3.1.1 Calculate the carrier and modulating frequency . (2) 3.1.2 Determine the modulation index and maximum deviation. (2) 3.1.3 Calculate the power that will be dissipated in 10Ω resistor. (2) A broadcasting radio station produces a 5 kHz audio tone that is used to modulate a 50 MHz carrier and cause frequency deviation of 20kHz. 16 RAE3601/101/1/2021 3.2.1 Calculate the modulation index. (2) 3.2.2 Use the Bessel table to determine the relative total power of the carrier and the side frequencies (4) [12] Question 4: Digital Communication 4.1 4.2 Define the following terms 4.1.1 Nyquist rate (1) 4.1.2 Block check character (1) 4.1.3 Cyclic redundancy check (1) 4.1.4 Parity (1) 4.1.5 Dynamic range (1) What is the difference between bipolar code and unipolar code? (1) [6] TOTAL = 35 17 ASSIGNMENT 3 Wave Propagation, Waveguide and radar 1 2 What is the most popular waveguide shape? 1 Circular 2 Rectangular 3 Flexible 4 Ridged A metallic post inserted in the broad wall of a waveguide provides a lumped reactance at that point. This is referred to… 3 4 1 Tuner 2 Tee 3 Attenuator 4 Coupler The ratio of output power and incident power is known as… 1 Tuning 2 Coupling 3 Bridging 4 Bending What is the name given to the number of radar pulses (waveforms) transmitted per second? 18 1 Pulse repetition rate 2 Pulse repetition frequency 3 Pulse repetition time 4 Rest time RAE3601/101/1/2021 5 What is the phenomenon whereby the frequency of a reflected signal is shifted if there is a relation motion between the source and the reflecting object? 6 7 1 Radar 2 Double range echoes 3 RFDI 4 Doppler The velocity with which wave appears to more pass the guide side wall is termed…... 1 Light velocity 2 Group velocity 3 Phase velocity 4 Wave velocity When testing VSWR using power meter the reflected power should be very low and the VSWR should be …... 8 9 1 Nearly 1 2 Exactly 1 3 Much greater than 1 4 Much lesser than 1 The contender for wiring of miniature millimetre wavelength circuit is …... 1 Waveguide 2 Dielectric filled waveguide 3 Dielectric waveguide 4 Flexible waveguide Which tags are suitable are suitable for animal identification and typically use frequency shift keying (FSK)? 1 Low frequency tags 2 High frequency tags 19 10 11 3 Very high frequency tags 4 Ultra high frequency tags A plane jointing all points of equal phase in a wave is…… 1 Ground waves 2 Surface waves 3 Wavefront 4 Isotropic point source Determine the ghost width on a TV screen 15 in wide when a reflected wave results from an object 0.5 mi “behind” a receiver 12 1 5.38 µs 2 1.51 in 3 53.5 µs 4 1 mi What is the best frequency for the optimum communication between any points at any specific condition of the ionosphere? 13 20 1 Maximum usable frequency 2 Optimum waking frequency 3 Critical frequency 4 Center frequency What is the typical HF band that moves outward and upward into ionosphere? 1 Ground wave 2 Sky wave 3 Surface wave 4 Space wave RAE3601/101/1/2021 14 15 Line of sight is also known as …... 1 Radiated wave 2 Reflected wave 3 Refracted wave 4 Direct wave What is the value of electromagnetic waves in vacuum? 1 8.85 x 10-12 F/m 2 300 x 106 m/s 3 4 x 10-7 H/m 4 6.626 x 10-34 J.s TOTAL: 15 x 1 = 15 21 ASSIGNMENT 4 Question 1: Transmission lines 4.1 What it is the primary reason for terminating a transmission line in an impedance equal to the characteristic impedance of the line? 4.1 (2) Briefly explain what a standing wave ratio (SWR) is and discuss what happens in a line when the reflection coefficient is equal to zero and when reflection coefficient is equal to one. 4.1 (3) A citizen band transmitter operating at 27 MHz with a 4W out is connected through a 10 m RG-8A/U cable to an antenna that has an input resistance of 300 Ω. Determine the: 4.1.1 The reflection coefficient (2) 4.1.2 The electrical length of cable in wavelength (2) 4.1.3 VSWR (2) 4.1.4 The amount of transmitter`s 4-W output absorbed by the antenna (4) 4.1.5 What happened to the rest of the power? (1) 4.1.6 What can be done to increase power absorbed by the antenna? (2) [18] Question 2: Antennas 2.1 Two /2 dipoles are separated by 50 km. They are aligned for optimum reception. The transmitter feed antenna with 10 W at 144 MHz. Calculate the power received. 2.2 Define a collinear array and driven array? 2.3 An antenna has a gain of 14 dB. It is fed by an RG-8/U transmission line 25 m long (4) (2) whose attenuation is 3 dB/10 m at 220 MHz. The transmitter output is 50 W. Calculate: 2.4 22 2.3.1 A transmission line loss (5) 2.3.2 The effective radiated power (3) Define radiation resistance and its significance (3) RAE3601/101/1/2021 [17] TOTAL= 35 ANNEXURE 1: FORMULAR SHEET Modulation index Thermal noise generated by the resistor is P = V2/R PR = PT + GT- Lp+ GR 23 ANNEXURE 2: CONSTANTS LIST Speed of light = 3 x 108 m/s Boltzmann constant = 1.38064852(79) x 10-23 J/K Table 1: Bessel Functions of the First Kind, Jn(mf) 24 mf J0 (Carrier) J1 J2 J3 J4 J5 J6 J7 J8 J9 J10 0.00 0.25 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0 10.0 1.00 0.98 0.94 0.77 0.51 0.22 -0.05 -0.26 -0.40 -0.18 0.15 0.30 0.17 -0.09 -0.25 0.12 0.24 0.44 0.56 0.58 0.50 0.34 -0.07 -0.33 -0.28 0.00 0.23 0.24 0.04 0.03 0.11 0.23 0.35 0.45 0.49 0.36 0.05 -0.24 -0.30 -0.11 0.14 0.25 0.02 0.06 0.13 0.22 0.31 0.43 0.36 0.11 -0.17 -0.29 -0.18 0.06 0.01 0.03 0.07 0.13 0.28 0.39 0.36 0.16 -0.10 -0.27 -0.22 0.02 0.04 0.13 0.26 0.36 0.35 0.19 -0.06 -0.23 0.01 0.05 0.13 0.25 0.34 0.34 0.20 -0.01 0.02 0.05 0.13 0.23 0.32 0.33 0.22 0.02 0.06 0.13 0.22 0.30 0.31 0.02 0.06 0.13 0.21 0.29 0.02 0.06 0.12 0.20