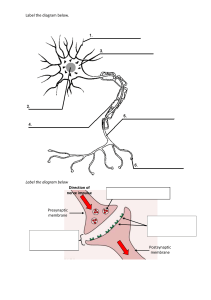
This is a compilation of some homework/classwork questions that I have used over the course of the semester. This is a worksheet to help you understand whether you can recall information you learned during the semester. Try to answer these questions without using your notes or books. Use your textbook and notes only if you are not able to answer them. This is not comprehensive or all inclusive. This document does not in any way infer that this information will be directly on test or that this is all that will be on test. It is strictly for your use to test recall of some facts covered during the semester. You should rely on the information given in the study summary sheet, textbook, and notes to help you prepare for your final exam. Unit 1 Review Questions (Chapters 1 and 2) 1. ________________ is the tendency of the body to maintain a stable constant environment. 2. ORGANIC COMPOUNDS Proteins Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids SUBUNITS FUNCTION 3. ________________ is the process by which amino acids link together to form proteins. 4. ________________ is the science that studies functional changes due to diseases. 5. ________________makes up matter. 6. ________________ are electrolytes that release hydrogen ions in water. 7. ________________ is a bond where atoms gain or lose electrons. 8. ________________ is the most complex level of organization. 9. ________________ is the basic unit of life. 10. ________________ is the study of the structure of body parts. 11. ________________ is the study of the function of body parts. 12. ________________ is the subatomic particle with a negative charge. 13. ________________ is the smallest complete portion of an element. 14. ________________ is a charged atom. ORGAN Skeletal SYSTEM Muscular Nervous Digestive Reproductive Respiratory Integumentary Cardiovascular ORGANS FUNCTION(S) Unit 2 Review Questions (Chapters 3 and 4) NAME OF ORGANELLE NICKNAME OF ORGANELLE FUNCTION OF ORGANELLE Smooth Endoplasmic Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria Nucleus Cell membrane Lysosome Ribosome Golgi apparatus Cell membrane 1. ________________ are the types of lipids that makeup the framework of the cell membrane. 2. ________________ is the major energy molecule used in the body. 3. ________________ is a process that breaks down complex substances into smaller ones. 4. ________________ is the movement of substances from a place of higher concentration to a place of lower concentration. TYPES OF CELLULAR DESCRIPTION TRANSPORT Passive transport Mechanisms (Do NOT require energy) Osmosis Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion Filtration Active Transport (Requires energy) Active transport Phagocytosis Pinocytosis 5. ________________ is the first stage of protein synthesis where an RNA copy of DNA is made, and ________________ is the process of codons being translated into amino acids. 6. ________________ is the part of the cell cycle where DNA is replicated and the cell is preparing for cell division. 7. ________________ means the splitting of the cytoplasm. 8. ________________ is cellular transport where substances move from a place of low concentration to a place of high concentration and requires energy. PHASES OF MITOSIS Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase EVENTS OCCURING IN PHASE Unit 3 Review Questions (Chapters 5 and 6) TYPE OF TISSUE Epithelial Connective Nervous Muscle (know 3 types and be able to describe each type) FUNCTION(S) 1. ________________ means one layer. 2. ________________ is the most rigid type of connective tissue. 3. ________________ is striated voluntary muscle that moves the skeleton. 4. ________________ is the outermost layer of the skin. 5. ________________ are specialized junctions in cardiac muscle tissue. 6. ________________ is the type of membrane that lines cavities that open to the outside of the body. 7. ________________ is the type of membrane that lines cavities that do not open to the outside of the body. 8. ________________ is the layer of the skin that contains the accessory organs. 9. ________________ is the protein that waterproofs the skin. 10. ________________ is another name for sudoriferous glands that function in body temperature regulation and excretion. 11. ________________ are glands that secrete oil. 12. ________________ is the worst degree of burns. 13. ________________ is the primary way heat is lost from the body. 14. ________________ means many layers. 15. ________________ is a special type of epithelial tissue only found in the urinary bladder, ureters, and urethra. 16. ________________ are strong, thick white fibers. 17. ________________ are yellow fibers that are very elastic. 18. ________________ are glands that secrete substances into ducts. 19. ________________ are glands that dump their secretions into tissue fluids and the blood. 20. ________________ are cube shaped cells. 21. ________________ are flattened squashed cells. 22. ________________ are cells that are longer than they are wide. 23. ________________ is the type of tissue that makes up the epidermis. 24. ________________ connects epithelial tissue to connective tissue underneath it. 25. ________________ is a compound released by mast cells that prevents blood clotting. 26. ________________ is a substance that promotes inflammation and allergic reactions and is also produced by the mast cells. 27. ________________ is a form of connective tissue also called fat. 28. ________________ is the pigment that produces skin color. 29. ________________ is the layer of the skin that contains fat and blood vessels. 30. ________________ are sweat glands that become active during puberty. Unit 4 Review Questions (Chapters 7 and 8) 1. ________________ is the end of a long bone. 2. ________________ are bone cells that destroy or break down bone. 3. ________________ are bone cells that produce bone. 4. ________________ is a space in compact bone occupied by osteocytes. 5. ________________ is the joint where the humerus and scapula meet. 6. ________________ is the type of joint with the most movement found in the hip. 7. ________________ is the type of bone that makes up the ends of long bones. 8. ________________ is a place where 2 or more bones meet. 9. ________________ are slightly movable joints. 10. ________________ is the shaft of a long bone. 11. ________________ are types of bones that begin as hyaline cartilage and become bone. 12. ________________ is the term that means blood cell formation. 13. ________________ are soft spots in an infant’s skull. 14. ________________ is the place of growth in long bones that remains until about age 25. 15. ________________ is the fibrous covering of bones. 16. ________________ is turning the palm upward 17. ________________ means pointing foot downward. 18. ________________ are transverse channels w/ large blood vessels that connect the surface to the medullary cavity. DISORDER Gigantism Rickets Acromegaly Osteoarthritis Rheumatoid arthritis Greenstick fracture Comminuted fracture Transverse fracture Osteoporosis Lordosis Kyphosis DESCRIPTION Unit 5 Review Questions (Chapters 10 and 11) Be able to define these terms: neuron, neuroglial cell, axon, dendrite, collateral, synapse, neurotransmitter, nissl bodies, cell body 1. ________________ is the nervous system that contains the brain and spinal cord. 2. ________________ is made up of the nerves found all over the body. 3. ________________ is the division of the ANS that is active under normal circumstances. 4. ________________ is the division of the PNS that controls conscious or voluntary activities. 5. ________________ is the type of migraine that occurs in about 15% of people with an aura of light. 6. ________________ are afferent neurons that carry impulses to the CNS. 7. List and describe the 3 types of structural neurons. 8. ________________ is the largest part of the brain. 9. ________________ is the part of the brain that controls the coordination of skeletal muscles. 11. ________________ is the lobe of the cerebrum that handles higher level intellectual processes and is fully developed at age 25. 12. ________________ are protective layers that cover the brain and spinal cord. 13. ________________ is the part of the brain below the occipital lobe of the cerebrum. 14. ________________ is the enlargement that extends from the pons to the foramen magnum. 15. ________________ is located below the thalamus and regulates heart rate, body weight, and many other body functions. 16. ________________ is also known as a stroke and involves a sudden interruption of blood flow. 17. ________________ is the lobe of the cerebrum that functions in hearing, and remembering visual and music patterns. 18. ________________ is the part of the spinal cord that conducts impulses from the body to the brain. 19. ________________ is the thin covering that attaches directly to the brain and spinal cord. 20. ________________ is the space between the vertebral column and the spinal cord where pain medication may be injected in women during the last stages of giving birth. 21. ________________ are ridges or convoluted folds in the cerebrum. 22. ________________ is the persistence of learning. 23. ________________ are masses of gray matter deep in cerebral hemispheres that function to control motor activities. 24. ________________ secretes cerebrospinal fluid. 25. ________________ are interconnected cavities in the cerebral hemispheres and brain stem that contain cerebrospinal fluid. 26. ________________ is a disorder that involves headache, light sensitivity, nausea, and vomiting. 27. ________________ works with the medulla oblongata to regulate rate and depth of breathing. 28. ________________ is the white matter found in side the cerebellum. 29. ________________ is an injury to the motor system that affects the ability to speak. 30. ________________ is a disorder also called smooth brain that involves profound retardation and seizures. 31. ________________ is part of the diencephalons that produces feelings, motivation, and is significantly affected by substance abuse. 32. ________________is an inflammation of the meninges caused by bacteria or viruses. 33. __________________ is the neurotransmitter that stimulates skeletal muscle contraction. 34. __________________ is what the membrane is said to be when sodium begins to move inside the axon’s membrane. 35. __________________ is what the membrane is said to be when potassium begins to move outside the axon’s membrane. NEUROGLIAL CELL Oligodendrocyte Microglia Ependymal Schwann cell Astrocyte ***Study all notes for chapter 9*** FUNCTION/LOCATION