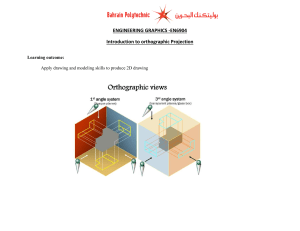
Name…………………………………………… Date………………………………. 1 Classroom rules! Be respectful and courteous to each other and staff. Attend 100% unless sick Observe agreed workshop rules Please write here the rules we have agreed on together as a group. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Learners signature…………………………………………………………………………… About this workbook. You will need to work through this book and complete all aspects of it. As you, work through you will gain the skills you need to achieve and complete the final assessment task. 2 Index 5. Solidworks 6. Basic concepts 7. Solidworks designing 8. User interface 10. Pinning the display / starting solidworks 11. Changing Units 12. Drawing a cube exercise 001 16. Self-assessment 17. Feature Manager Design tree / Feature-Based Modelling 20. Setting the part material 21. Checking the part mass to assess you have drawn it correctly / self –assessment 22. Producing an orthographic drawing from the part 23. Exercise 003 wooden block / self-assessment 24. Exercise 004 cross / self-assessment 25. Drawing exercise 005/ self-assessment 26-29. Drawing exercise 006/ self-assessment 30-31. Drawing exercise 007/ self-assessment 32. Drawing exercise 008/ self-assessment 33-35. Drawing exercise 009/ self-assessment 36-38. Drawing exercise 010/ self-assessment 39. Drawing exercise 0011/ self-assessment 40-42. Drawing exercise 012/ self-assessment 43. Drawing exercise 013/ self-assessment 44. Drawing exercise 014/ self-assessment 45-47. Drawing exercise 015/ self-assessment 48. Drawing exercise 016/ self-assessment 3 49-51. Drawing exercise 017/ self-assessment 52. Drawing exercise 018 / self-assessment 53. Drawing exercise 019/ self-assessment 54-55. Revolved cut 56. Revolved boss / base 57-58. Drawing exercise 020/ self-assessment 59-60. Drawing exercise 021 61-62. Drawing exercise 022 63-64. Drawing exercise 023 65. Assemblies 66-68. Constraints / Adding components 69-71. Screw jack assembly 72-73. CSWA 1 74-75. CSWA 2 4 More than 1,878,300 product designers and engineers worldwide, representing 165,900 organizations use SolidWorks If these companies design in SolidWorks…shouldn’t you? Microsoft, Samsung, Canon, HP, Intel, Hitachi, IBM, Panasonic , Seiko Epson Toshiba, Medtronic, 3M, Sony, Fujitsu, Pfizer, ExxonMobil, Apple, General Electric, Nokia 5 SolidWorks Basic Concepts ® • SolidWorks is a 3D solid modelling package, which allows users to develop full solid models in a simulated environment for both design and analysis. ® • SolidWorks you sketch ideas and experiment with different designs to create 3D models. ® • SolidWorks is used by students, designers, engineers, and other professionals to produce simple and complex parts, assemblies, and drawings. ® • Designing in a modelling package such as SolidWorks is beneficial because it saves time, effort, and money that would otherwise be spent prototyping the design. ® • SolidWorks is a mechanical design automation software package (tool) used to build parts, assemblies and drawings that take’s advantage of the familiar ® Microsoft Windows graphical user interface. • SolidWorks provides various analysis tools, (SolidWorks Simulation, SolidWorks Motion, SolidWorks Flow Simulation, Sustainability, etc.) • Associativity. Model dimensions between parts, assemblies and drawings ensure that changes made to one document are automatically made to all other documents. • Sketches are the foundation for creating features. SolidWorks provides the ability to create either 2D or 3D sketches. 6 3D Designing – SolidWorks You will need to be able to draw the types of shapes below. 7 SolidWorks User Interface is straightforward. There is 6 main area of interface you normally work with. 1) Menu Bar – Top most of the application, executing New File, Open File, Save, Print, Undo, Select, Rebuild, File Properties and Options. 2) Command Manager – Access to part, assembly and drawing editing tools. 3) Feature Manager Design tree – Outline overview how your part, assembly and drawing constructed. Continued on next page 8 4) Status bar – Provide an information about your part, assembly and drawing. 5) Head up view toolbar – View tools such as zoom, pan, zoom plane and section view. 6) Graphics area – Workspace for your part, assembly and drawing. 9 Settings: Pinning the Display Original Display Click on ‘SOLIDWORKS’ Select the ‘Pin’ Display stays Starting SolidWorks The new file icon will bring up the following dialog box 10 Getting started- Select part modelling Part modeling Assembly modeling 2D drawing Helpful Hints - Changing Units Specifications (inch/mm) Under Options select Document and then click on Units Click on appropriate Units specification (MMGS) and then select OK 11 Drawing exercise 001 (cube) Select the sketch button and select a plane to draw on. Select the rectangle and using the origin draw a rectangle of ANY SIZE. Use the smart dimension tab to dimension the object. Making all lines black, to show the object is fully defined. Continued on the next page 12 3D Part Creation The 3D command manger, shows the tools available for creating 3D parts from 2D sketches Once the square is fully defined (black lines), you can then use the features tab. In the features tab use the extruded boss base button. Using the dimension of the square add this into the boss extrude tab. 13 You should now have a 3D cube. Select one face and start a new sketch using sketch tab. Using the head up view toolbar, view the sketch you have selected. Using “normal to”. “Normal to” view option orients to a selected plane or surface Continued on next page 14 Draw a circle and smart dimension it. Go back into the feature tab and select extruded cut Select through all and ok. You should now have a cube with a hole in. 15 Feature Manager Design tree The FMDT keeps track of the model creation by showing the sketches or features used in order from top to bottom Notice that the sketches are no longer shown once used for a feature but can be accessed by clicking the plus sign next to that feature Feature-Based Modelling • Final parts are created using a series of steps • The first step to creating a part is to create the “Base” feature • This base feature takes into account the overall shape of the object and tries to account for as many features as possible in one extrusion • Once a base feature is created the shape can be modified by adding or subtracting material to create form features • Special features that would be too complex to add by extrusion or revolving are built-in to 3D parametric programs 16 Continued on next page Breaking it Down into Features Feature Modelling Example 1 Objects can be thought of in terms of features • Shapes • Holes • Rounds • Etc. • Determines design strategy We can think of the block in terms of 2 “L” shapes and then cut out the hole 17 Example Construction 2 We can think of the block in terms of a “C” shape and then add the plank with a hole Example Construction 3 Finally, we could draw the overall shape from the top view and remove unwanted material 18 Drawing exercise 002 20DIA Centre of block 50 60 25 25 50 20 Material 1060 Alloy Setting the part material Right click on material in the design tree, click edit material, select aluminium alloy, and select 1060. Continued on the next page 19 Checking the part mass to assess you have drawn it correctly Select Evaluate tab, mass properties. Your block should weight= 370.98 grams 20 Producing an orthographic drawing from the part Using the drop down menu on the part icon, select make drawing Select paper size (A4 ANSI Landscape) Drag you views into the sheet Right click to edit sheet 21 Exercise 003 wooden block Draw the block using minimum extrusions / Select the correct material (check the mass of the part) / from the part create an orthographic drawing 22 Drawing exercise 004 Draw the cross using minimum extrusions / Select the correct material (check the mass of the part) / from the part create an orthographic drawing Material: Brass Mass: 143.44 grams 23 Drawing exercise 005 Draw this camera (using your own sizes). With positive and negative extrusions. From the part, create an orthographic drawing 24 Drawing exercise 006 Draw the block using minimum extrusions / Select the correct material (check the mass of the part) / from the part create an orthographic drawing Material: Cast alloy steel Mass: 256.96 grams See suggested layout on the next page 25 Drawing exercise 006 Think about the best way to start the sketch. I decided to use the top plane and start to sketch the two circles on the origin. As below. (smart dimension) Then draw a line, creating a rectangle off the tangent of the outside circle, as below. (smart dimension) Add the chamfers using the Sketch chamfer Add the size you require in the sketch chamfer box Continued on next page 26 Drawing exercise 006 Using trim entities and power trim, remove the unwanted lines. You can now extrude the sketch. Sketch the two rectangles on the top face and smart dimension. You can now use extruded cut. Down to 21mm. You should now have something like this Continued on next page 27 Drawing exercise 006 Sketch a triangle using the line command on the shown face Use the extruded cut command to cut out the triangle. You should now have something like this. Finished 28 Drawing exercise 007 Draw the bracket using minimum extrusions / Select the correct material (check the mass of the part) / from the part create an orthographic drawing Material: PVC rigid Mass: 57.52 grams See suggested layout on the next page 29 Drawing exercise 007 1. Sketch on the front plane, using the origin as the centre position and smart dimension. 3. Using the feature tab and extrude boss. Select mid plane and extrude out 40mm 2. Use the trim function to remove unwanted lines 4. Use the front plane to sketch on, rather than a face. Do not forget to use the normal 2 button when you select a new face / plane to sketch on. Use the extruded cut, again from the mid plane to produce the cut out 5. Sketch the profile of the shape, on the front plane and smart dimension it 11mm back. Sketch the boss on the back face and extrude out. Finished, check the mass of the part 30 Drawing exercise 008 Draw the foot using minimum extrusions / Select the correct material (check the mass of the part) / from the part create an orthographic drawing Material: Titanium TI-5AI-2.5Sn Mass: 753.07 grams 31 Drawing exercise 009 Draw the angled bracket using minimum extrusions / Select the correct material (check the mass of the part) / from the part create an orthographic drawing See suggested layout on the next page 32 Drawing exercise 009 Start the sketch on the right plane, 40 x 60 rectangle. This time when you extrude the sketch, extrude it from the mid plane. This time when you start the sketch, start it on the right plane, rather than a face. Sketch the triangle and smart dimension. Use the extruded cut, again from the mid plane. Once this stage is completed, sketch on the bottom of the block and add the two lugs. Continued on the next page 33 Drawing exercise 009 Sketch one lug, with the hole and add a centre line. Use the (1) mirror function to mirror the lug over. (1) (2) select the entities to mirror (lug and hole). (3) Then select mirror about (centre line) (2) 34 Drawing exercise 010 Draw the bearing housing, using minimum extrusions / Select the correct material (check the mass of the part) / from the part create an orthographic drawing Material: Phosphor Bronze Mass: 532.24 grams See suggested layout on the next page 35 Drawing exercise 010 Start by sketching a centre point arc from the origin on the front face. Draw a centre line down from the origin Using the offset entities and bi-direction, select 3.5mm and then select the centre line. You should now have a line either side of your centre line. Roughly, sketch the base and smart dimension. Continued on the next page 36 Drawing exercise 010 Smart dimension the base around a centre line You should have something like the above picture Using trim entities and power trim remove unwanted lines, as above. Then extrude boss base from the mid plane (56mm) Sketch the 34OD & the 22ID again on the front plane, using the origin. Extruded it again from the mid plane @ 58mm. Finished. 37 Drawing exercise 011 Draw the clamp using minimum extrusions / Select the correct material (check the mass of the part) / from the part create an orthographic drawing Material: AISI 316 Annealed Stainless Steel bar Mass: 5922.43 grams 38 Drawing exercise 012 Draw the fixture using minimum extrusions / Select the correct material (check the mass of the part) / from the part create an orthographic drawing Material: Plain carbon steel- Mass: 990.6 Grams See suggested layout on the next page 39 Drawing exercise 012 Roughly sketch the base shape on the top plane. Smart dimension using the aid of a centre line. Extrude the sketch Sketch a rectangle on the top plane and smart dimension. Then extrude the feature. You should have a shape that resembles the view to the left Continued on next page Continued on next page 40 Drawing exercise 012 Sketch another rectangle on top of the last extrusion. This time use the extruded cut to cut out the rectangle. Use the through all command. Sketch another rectangle on the face shown Again, use the extruded cut to cut out the rectangle. Use the through all command. Complete 41 Drawing exercise 013 Draw the shaft support using minimum extrusions / Select the correct material (check the mass of the part) / from the part create an orthographic drawing Material: Aluminium Bronze Mass: 2422.05 Grams 42 Drawing exercise 014 Draw the clamp bracket using minimum extrusions / Select the correct material (check the mass of the part) / from the part create an orthographic drawing 12 64 61 85 Material: Cast stainless steel Mass: 1057.59 Grams 43 Exercise 015 (Using swept boss/base) How to create allen key (convert to metric) In this solidworks tutorial, you will create simple allen key. 1. Click New. Click Part, OK. 2. Click Front Plane and click on Sketch. 3. Click Line, skecth a L shape . 4. Click Smart Dimension, and dimension sketch as 2.5″ and 1″. Continued on the next page 44 5. Click Sketch Fillet, add 0.3″ fillet at L corner. 6. Exit sketch, click on Top Plane and click Sketch. 7. Click on Sketch2 and click Normal To. 8. Click Polygon, sketch a polygon at origin. 9. Click Smart Dimension, and dimension sketch diameter to 0.15″. Continued on the next page 45 10. Exit sketch, click on Isometric view. 11. Click Features>Swept Boss/Base, For profile click on Sketch2 and for path click on Sketch1 and OK. You are done! 46 Drawing exercise 016 Draw the shaft seat using minimum extrusions / Select the correct material (check the mass of the part) / from the part create an orthographic drawing 4 holes @ 10mm Material: Copper Mass: 2141.65 Grams 47 Drawing exercise 017 Draw the bracket using minimum extrusions / Select the correct material (check the mass of the part) / from the part create an orthographic drawing Material: Grey cast iron / Mass: 767 Grams See suggested layout on the next page 48 Drawing exercise 017 Sketch the key shape on the front plane and extrude it out 50mm 1. Open a new sketch on the front plane and draw the two other circles and smart dimension. 1. Using the shift key and the tangent button move the 40mm circle in line with the edge. 2. Using the shift and the tangent once again, select the two circles. Continued on next page 49 Drawing exercise 017 You will need to convert entities on this line Add detail and crop out unwanted lines Extruded out 15mm Add cut-off to finish 50 Drawing exercise 018 Draw the lower foot support using minimum extrusions / Select the correct material (check the mass of the part) / from the part create an orthographic drawing 15mm THRO HOLE Plate is 6mm thick (not 9) Material: Galvanized steel Mass: 330.83 Grams 51 Drawing exercise 019 Draw the bearing bracket using minimum extrusions / Select the correct material (check the mass of the part) / from the part create an orthographic drawing Material: Monel(R) 400 Mass: 478.92 Grams 52 How to use Revolved Cut In this tutorial, you will create this part using revolved feature tools. 1. Draw the cube 2. Click Circle, and sketch a circle on front face. 7. Click Smart Dimension, dimension sketch as below sketched. Continued on the next page 53 8. Click Features>Revolved Cut of revolution, and click on right side edge as axis . 9. You are done! 54 How to use Revolved Boss/Base In this tutorial, you will create this part. 1. Click New. Click Part, OK. 2. Click Front Plane and click on Sketch. 3. Select centreline, sketch vertical line start from origin, roughly 35mm and OK. 4. Click circle and sketch a circle on left side of the centreline. 5. Click Smart Dimension, click sketched circle and set it diameter to 20mm and add dimension for its location, as above sketch and OK. 6. You just completed your sketch, let us build feature from it. Click Feature>Revolved Boss/Base 7. Click centreline as axis OK. 8. You are done! 55 Exercise 020 (ball) Draw the object below, using revolve boss / bass and revolved cut Material: Brass Mass: 389.47 Grams See suggested layout on the next page 56 Exercise 020 1. Sketch a circle on the front plane and smart dimension 50mm Draw two centre lines through 2. Use offset entities tool, to offset a line 18mm as show. 4. In the feature tab select revolve boss base. The centre line will be the axis of revolution. 3. Trim out unwanted lines You can now add the detail. 57 Drawing exercise 021 Draw the pulley wheel bracket using minimum extrusions / Select the correct material (check the mass of the part) / from the part create an orthographic drawing Material: Phosphor Bronze Mass: 8290.32 Grams 58 Drawing exercise 022 Draw the block using minimum extrusions / Select the correct material (check the mass of the part) / from the part create an orthographic drawing Convert dimension into millimetres Material: Polyetherketone (PEEK) 59 Mass: 1.12 Drawing exercise 023 Draw the bottle open using minimum extrusions / Select the correct material (check the mass of the part) / from the part create an orthographic drawing 60 Assemblies Assemblies are c collections of 3D parts that form one engineering system 1. Modeled to Fit Together 2. Location defined by 6 degrees of freedom • 3 translational (x,y,z) • 3 rotational (about x,y,z axes) 3. Assembly Constraints • • • • Concentric Mating Surfaces Coincident Distance 61 Concentric Constraints Mating Surfaces 2D surfaces can be mated to become flush with one another but the correct direction must be given to the computer 62 Additional Constraints Coincident Lines or Vertices Distance between entities if not flush Adding Components In the Assembly tab (similar to the Features tab of a Part file), use the Insert Components button to add part files to this assembly Select from the open parts listed or use the Browse to find saved files Continued on next page 63 The first part inserted will become fixed in space and should be placed at the origin as a base for the assembly. This is done by selecting the part and then clicking the green check mark to default to the origin instead of just clicking in space. Select the pin to keep the Insert Component dialog box open after a component is added Constraints In SolidWorks these are the Standard Constraints used in Assemblies Change Direction 64 In the figure window, it will show a preview of the mating and a smaller dialog box will appear Confirm Mate Drawing exercise 024 Draw the four components of the screw jack to create a part assembly 65 66 SolidWorks 2010 CSWA Exam Preparation Overview This document contains practice questions that can be used to prepare for the Certified SolidWorks Associate (CSWA) exam. The questions are intended to help you become familiar with the types of questions featured on the CSWA exam. Additional information about the CSWA exam is available on the student Web site (www.g-wlearning.com/CAD). CSWA Exam Practice Questions Part Modelling Model the part shown in the figures provided. Use the following information. Unit system: MMGS (millimetre, gram, second) Decimal places: 2 Part origin: Arbitrary A = 50 B = 70 Material: AISI 1020 What is the overall mass of the part in grams? A. 878.62 B. 998.54 C. 1098.32 D. 1127.72 Practice question 1A 67 Practice question 1B Practice question 1C 68 SolidWorks 2010 CSWA Exam Preparation Advanced Part Modelling Model the part shown in the figures provided. Use the following information. Unit system: MMGS (millimeter, gram, second) Decimal places: 2 Part origin: Arbitrary A = 66 B = 56 Material: Cast Carbon Steel What is the overall mass of the part in grams? A. 205.19 B. 237.10 C. 305.66 Practice question 2A D. 442.33 69 Practice question 2B 70 Well done you have completed the workbook Learners comments: Date: Learners signature: Assessors comments: Date: Assessors signature: 71