Mechanics Report: Statics, Kinematics, Kinetics
advertisement

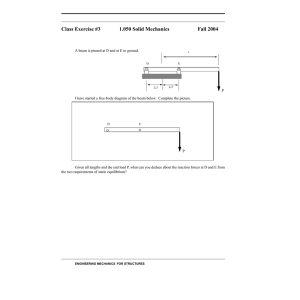
UNIVERSIDAD AUTÓNOMA DE NUEVO LEÓN FACULTAD DE INGENIERIA MECÁNICA Y ELÉCTRICA NOMBRE: Fabrizzio Salvador Guajardo Morales MATRICULA:1922249 CARRERA: Ingeniería Biomédica SEMESTRE: 3 Mecánica vectorial LUGAR: SAN NICOLAS DE LOS GARZA, NUEVO LEÓN “Mechanics may be divided into three branches: statics, which deals with forces acting on and in a body at rest; kinematics, which describes the possible motions of a body or system of bodies; and kinetics, which attempts to explain or predict the motion that will occur in a given situation. Alternatively, mechanics may be divided according to the kind of system studied. The simplest mechanical system is the particle, defined as a body so small that its shape and internal structure are of no consequence in the given problem. More complicated is the motion of a system of two or more particles that exert forces on one another and possibly undergo forces exerted by bodies outside of the system. The principles of mechanics have been applied to three general realms of phenomena. The motions of such celestial bodies as stars, planets, and satellites can be predicted with great accuracy thousands of years before they occur. (The theory of relativity predicts some deviations from the motion according to classical, or Newtonian, mechanics; however, these are so small as to be observable only with very accurate techniques, except in problems involving all or a large portion of the detectable universe.) As the second realm, ordinary objects on Earth down to microscopic size (moving at speeds much lower than that of light) are properly described by classical mechanics without significant corrections. The engineer who designs bridges or aircraft may use the Newtonian laws of classical mechanics with confidence, even though the forces may be very complicated, and the calculations lack the beautiful simplicity of celestial mechanics. The third realm of phenomena comprises the behaviour of matter and electromagnetic radiation on the atomic and subatomic scale. Although there were some limited early successes in describing the behaviour of atoms in terms of classical mechanics, these phenomena are properly treated in quantum mechanics.” (BRITANICA,2020)1 Importance of statics To determine the exact measurements needed for a structure to be secure To calculate the forces involved in a system To calculate if a rope is going to break when you use it in a pulley To calculate the equilibrium of a bar in a wall The principle of transmissibility “The principle of transmissibility states that the point of application of a force can be moved anywhere along its line of action without changing the external reaction forces on a rigid body. Any force that has the same magnitude and direction, and which has a point of application somewhere along the same line of action will cause the same acceleration and will result in the same moment. Therefore, the points of application of forces may be moved along the line of action to simplify the analysis of rigid bodies.”( moore, 2017)2 The line of action of a force “In physics, the line of action of a force F is a geometric representation of how the force is applied. It is the line through the point at which the force is applied in the same direction as the vector F→.[1][2] The concept is essential, for instance, for understanding the net effect of multiple forces applied to a body. For example, if two forces of equal magnitude act upon a rigid body along the same line of action but in opposite directions, they cancel and have no net effect. But if, instead, their lines of action are not identical, but merely parallel, then their effect is to create a moment on the body, which tends to rotate it.”(Wikipedia 2020) 3 The length of a line of action of a force is infinite I think myself of a 6 because I get really well the Pythagoras theorem but it has always been a challenge for me to use trigonometric functions. Bibliographies Contributor:David L. Goodstein Article Title:Mechanics Website Name:Encyclopædia Britannica Publisher:Encyclopædia Britannica, inc. Date Published:August 21, 2020 URL:https://www.britannica.com/science/mechanics Access Date:September 03, 2020 1 URLhttps://www.livescience.com/48001-biomedical-engineering.html Website Title: LiveScience Article Title: What Is Biomedical Engineering? Publication Day: 25 Publication Month: SEPTEMBER Publication Year: 2014 Author: Jim Lucas 2 URL:http://mechanicsmap.psu.edu/websites/2_equilibrium_concurrent/principle_of_ transmissibility/principleoftransmissibility.html#:~:text=The%20principle%20of%20tr ansmissibility%20states,forces%20on%20a%20rigid%20body.&text=Because%20o f%20the%20principle%20of,the%20above%20pairs%20is%20equivalent. Website Title: Mechanicsmap Article Title: Principle of transmissibility Publication Year: 2017 3 URL:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Line_of_action#:~:text=In%20physics%2C%20the %20line%20of,forces%20applied%20to%20a%20body. Website Title: wikipedia Article Title: Line of action Publication Day: 13 Publication Month: 03 Publication Year: 2019 4