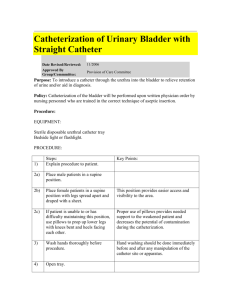
CATHETERIZATION OF THE URINARY BLADDER It is the introduction of A catheter thru the urethra into the bladder in order to remove urine. Purposes 1. To obtain sterile urine specimen for examination as in urine culture. 2. To relive urinary retention. 3. To ensure emptying of the bladder prior to surgery or delivery thereby preventing possible trauma. 4. To prevent bedwetting in an incontinent patient. 5. To remove urine when it is not advisable to for the patient to void. 6. To determine whether failure to void is due to urinary retention or suppression. 7. To determine residual urine. 8. To measure hourly urine output Special Considerations 1. Before starting the procedure, check the catheter for defects. 2. Insert the catheter GENTLY. 3. Observe strict surgical asepsis throughout the procedure. 4. See to it the patient is protected from unnecessary exposure and draft. 5. Provide adequate lighting in order to visualize well the urinary meatus and prevent contamination. 6. Use the correct size of catheter to prevent injury to the mucous membrane of the urethra or to cause the patient discomfort. 7. See to it that the patient is relaxed during the insertion of catheter. 8. In case of severe bladder distention observe, gradual decompression. 9. Ensure adequate cleanliness of the external genitalia before inserting the catheter. 10. If the specimen is to be collected for a needed examination, caution the patient not to void when being given with an external douche. Equipment: Catherization tray, Containing the following articles: Urethral catheter Fr. 8-10 for children Fr. 12-16 for female adults Fr. 16-20 for male adults Sterile pack of kidney basin Lubricant, preferably water soluble as KY Jelly. Antiseptic Cotton Pick- Balls up forceps Catheter to be kept in place Include also the following: adhesive plaster pair of scissors rubber tubing or disposable connecting tube urinary drainage system. Waterproof Syringe prefilled with sterile water Collection Bath drapes bag and tubing blanket or sheet for draping the client. Adequate lighting (Obtain a flashlight or lamp if necessary). 1. Explain to the client what you are going to do. 2. Wash hands and observe appropriate infection control procedures. 3. Provide for client privacy. 4. Place the client in the appropriate positions and drape all areas except the perineum. A. Female: supine with knee flexed and externally rotated. B. Male: supine, legs slightly abducted. 5. Established adequate lighting. Stand on the clients right if you are left handed. 6.If using a collecting bag and it is not contained in the catheterization kit, open the drainage package and place the end of the tubing within reach. 7. If agency policy permits, apply clean gloves and inject 10 to 15 ml xylocaine gel into the urethra. 8. Open the catheterization kit. Place a waterproof drape under the buttocks (female) penis (male) without contaminating the center of the drape with your hand. 9. Apply the sterile gloves. 10. Organize the remaining supplies -Saturate -Open the cleansing balls with the antiseptic solution. the lubricant package. -Remove the specimen container and place it nearby with the lid loosely on top. 11. Attached the prefilled syringe to the IC inflation hub and test the balloon. 12. Lubricate the catheter ( 1 to 2 inch for female and 6 to 7 for male) and place it with the drainage end inside the collection container. 13. Cleanse the meatus. 14.Insert the catheter until urine returns and continue insertion for 2.5 -5cm. 15. For IC inflate the retention balloon for with the designated balloon. 16.Collect a specimen if needed. Allow 20 to 30 ml to flow into the bottle. 17. Allow 18. the straight catheter to continue draining. Examine and measure the urine. 19. Remove the SC when urine flow stops, while for the IC ensure the bag is lower than the level of the patient and the tape the catheter to patients inner thigh for female. Hang bag below the level of the bladder. 20. Wipe the perineal area of any remaining antiseptic or lubricant. Return the client to a comfortable position 21. Document: size and type of catheter, volume of sterile water used to inflate the balloon the color, clarity and amount of urine drainage during the procedure. Added Info Catheters are made of rubber or plastic, some are latex, silicone or pvc. Types: A. straight catheter- single lumen with a small eye or opening, ½ inch from the insertion. B. Retention or Foley Catheter –double lumen catheter, the larger one drains urine from the bladder, the small one is used to inflate the balloon. C. Three way catheter for continuous or intermittent bladder irrigation the small lumen or third lumen through which the sterile irrigating fluid can flow into the bladder.