Macromolecules Flash Cards
advertisement

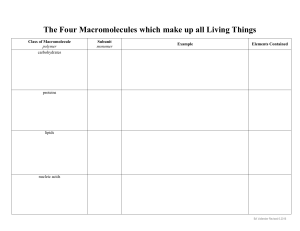
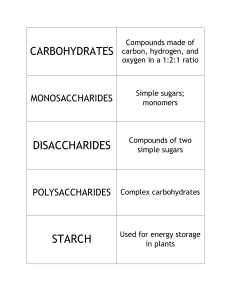
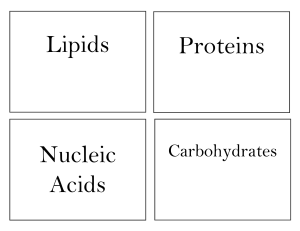
CARBOHYDRATES Compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio MONOSACCHARIDES Simple sugars; monomers DISACCHARIDES Compounds of two simple sugars POLYSACCHARIDES Complex carbohydrates STARCH Used for energy storage in plants GLYCOGEN Used for energy storage in animals CELLULOSE A structural component of plants CHITIN A structural component of animals LIPIDS Insoluble polymers made of C and H SATURATED LIPIDS Lipids that are solid at room temperature and contain only single bonds UNSATURATED LIPIDS Lipids that are liquid at room temperature and contain one double bond POLYSATURATED LIPIDS Lipids that are liquid at room temperature and contain multiple double bonds FATS (TRIGLYCERIDES) Lipids that contain one glycerol and three fatty acid chains; used for energy storage PHOSPHOLIPIDS Lipids that are used in cell membranes and contain one glycerol, one phosphate group, and two fatty acid chains STEROIDS Lipids with four fused carbon rings that are used to mediate physiological reactions NUCLEIC ACIDS Polymers made of H, O, C, P, and N; used for storing genetic material NUCLEOTIDE Monomer of nucleic acids DNA Nucleic acid that controls its own replication; contains deoxyribose and is double stranded RNA Nucleic acid that is synthesized from DNA; contains ribose and is single stranded PROTEINS Polymers with various functions that are composed of amino acids AMINO ACIDS Compounds with an amine group, a carboxyl group, and an R group PEPTIDE BONDS Bonds found in proteins PRIMARY STRUCTURE Simplest level of protein structure; sequence of amino acids SECONDARY STRUCTURE Describes the folding of a polypeptide chain TERTIARY STRUCTURE Describes the overall shape of a functional protein QUATERNARY STRUCTURE Describes the position of a protein in relation to other proteins ACTIVATION ENERGY The amount of energy needed to start a reaction EXOTHERMIC REACTION A reaction that releases energy and occurs spontaneously ENDOTHERMIC REACTION A reaction that absorbs energy and requires an energy source in order to begin CATALYST A substance that speeds up a chemical reaction by lowering its activation energy ENZYME A protein that acts as a biological catalyst SUBSTRATE The reactant in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction ENZYMESUBSTRATE COMPLEX An enzyme and its respective substrate ACTIVE SITE The location on an enzyme where substrates bind to undergo reactions and form new products LOCK AND KEY MODEL Model depicting the specificity of enzymes and their substrates