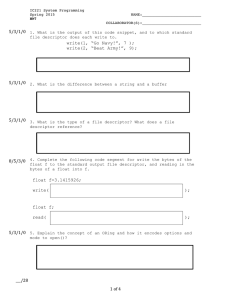
“Hello World” with an AVR
by Vijay Raju (vijay@unesols.com)
Universal Embedded Solutions
Introduction:
A simple program which puts the words “Hello World” on the screen is almost always
the starting point for programmers learning a new language. For an embedded systems
designer the equivalent to “Hello World” is a simple program to blink a set of LEDs
connected to a port of microcontroller. This simple program not only allows a designer to
get started with preprogramming a new controller but it also behaves as a simple check to
test if all the hardware is operational.
This document describes how to control a set of LEDs connected to a port of an AVR
microcontroller using an EVK01 microcontroller kit with code written in assembly and in
C. A section on how to achieve the same task with a bread board will be added later.
The EVK01:
The EVK01 is a complete microcontroller evaluation kit with all the hardware and
software necessary to try our “Hello Word” program. The following are the required tools
that the EVK01 provides:
Basic hardware with a microcontroller, power supply, crystal and LEDs.
A In-System Programmer
An assembler, a compiler and in-system programming software.
Assembling Assembly:
Atmel provides a free assembler and IDE for the AVR series called AVR Studio. AVR
Studio is can be found on the EVK01 CD under the “Software” tab or can be downloaded
from the Atmel website. Simply launch the installer and follow the simple on-screen
instructions to install AVR Studio on your PC.
Once the installation process has completed successfully, launch AVR Studio from the
“Start” menu. Create a new project by choosing “Project->New Project” if the new
project window is not already open.
Choose AVR Assembler in the project type and type in “Hello world” as your project
name and initial file name. Make sure the “Create Initial File” and “Create Folder” check
boxes are ticked. Choose a convenient location for you project and then click “Next”. In
the “Choose Debug Platform and Device” dialog box that appears next choose the debug
platform as AVR Simulator and the device as AT90S8515. Click the “Finish” button to
dismiss the dialog box and open the “Hello World” project with the “Hello World.asm”
file.
Now its time to fill in some code into “Hello World.asm”. Consider the following piece
of code:
;**********************************************************************
;*
;* Title
: AVR LEDs Upcount Sample Code
;* Version : 1.0
;* Last updated
: May 01 2003
;* Target
: AT90S8515
;* File
: LEDs Upcount.asm
;* Author(s)
: Vijay Raju
;*
Universal Embedded Solutions
;*
;*
;* DESCRIPTION
;*
Does an Upcount on the LEDs connected to PORTA
;**********************************************************************
;**** includes ****
.include "8515def.inc"
; This file provides definitions for the 8515 registers
;*******************************
;* Global Register Definitions *
;*******************************
.def
.def
.def
.def
temp
Delay
Delay2
Delay3
=
=
=
=
r16
r17
r18
r19
;**********************************************************************
;*
;* RESET routine.
;*
;**********************************************************************
RESET:
ser temp
out DDRA, temp
;Set a register
;Set Data Direction of PORTA to output
dec temp
out PORTA, temp
;Upcount register
;Send register to Port
loop:
;**********************************************************************
;*
;*
Provide a delay.
;*
;**********************************************************************
ldi Delay3, 0x05
DLY:
dec Delay
brne DLY
dec Delay2
brne DLY
dec Delay3
brne DLY
;**********************************************************************
;*
;*
Infinite Loop
;*
;**********************************************************************
rjmp loop
;**********************************************************************
Type out or copy this code into “Hello World.asm” and save it using “File->Save”.
Assemble (Build) this code by selecting “Project -> Build”. Once the build is complete
check the Output window for the build results. The output window will read as shown
below if the build was successful and “Hello World.hex” was created
The code can now be simulated by choosing “Project -> Build and Run”. Use the
“Debug” menu to control program execution and the I/O view to visualize the ports,
registers and other parameters.
Compiling C Code:
WINAVR is an open source installer which provides a variety of open source tools
including a C cross-compiler for the AVR. The WINAVR installer is available in the
software section of the EVK01 CD or can be downloaded from the WINAVR project
page. WINAVR makes setting up the AVR cross-compiler tool chain a breeze. Simply
launch the installer and answer a few simple questions and the installer will do the rest
and set up all the tools including the compiler, assemble linker, an IDE and much more.
Launch Programmer’s Notepad, the IDE provided by WINAVR from the start menu
when the installation is complete. Create a new project by choosing “File->New>Project” and specifying a project name in the “Project Location” dialog box. Let’s call
the project “HelloWorld” in the folder “Hello World in C”. Next create a new file using
“File->New->C/C++ file”. Copy or rewrite the following code into the new file you just
created.
//*********************************************************************
//
// File Name
: 'HelloWorld.C'
// Title
: LED Upcount
// Author
: Vijay Raju
// Created
: 22/3/2004
// Revised
:
// Version
: 1.0
// Target MCU
: Atmel AVR series
// Editor Tabs
: 4
//
//
Description : Code to do an Upcount on LEDs connected to PORTA
//
// This code is distributed under the GNU Public License
//
which can be found at http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.txt
//
//*********************************************************************
#include <avr/io.h>
int main(void)
{
unsigned char x = 0;
unsigned char a,b,c,d;
//Set PortA to output
DDRA = 0xFF;
//infinite loop
for(;;)
{
//Send x to PORTA
PORTA = x;
//Increment x
x++;
//Provide a delay
//The optimizer may decide that this loop is useless
//because it seems to do nothing. Disable the optimizer in
//the makefile. i.e. dont have -O flag.
for(a=0;a<20;a++)
{
for(b=0;b<256;b++)
{
for(c=0; c< 256; c++)
{
//just to fool the optimizer into
//thinking that this is a useful loop.
d++;
}
}
}
}
}
Save this file using “File->Save” and specifying the name “HelloWorld.c” for the file.
Add this file to the project in Programmers notepad by right-clicking “HelloWorld” in the
project manager and choosing “Add Files” in the context menu that appears.
The easiest way to compile this is file is using a tool called make and a makefile.
WINAVR provides a sample make file which is in the “[WINAVR directory]\sample”
directory. Copy this sample makefile into the “Hello World in C” folder and add this file
to the project in Programmers notepad by right-clicking “HelloWorld” in the project
manager and choosing “Add Files” in the context menu that appears.
Open the makefile by double-clicking on it and make the following changes to it:
Set the name of the microcontroller to 8515. To do this find the line which reads
“MCU = ******” in the makefile and modify it to read:
MCU = at90s8515
Set the target filename to HelloWorld. Find the line which reads “TARGET =
*****” and modify it to read:
TARGET = HelloWorld
We do not need any optimization for this program, so set the optimization level to
zero by modifying the line reading “OPT = *” to:
OPT = 0
If you have not installed WINAVR in the default location i.e. “c:\WinAVR” then
specify the new directory by replacing the line “DIRAVR = c:/WINAVR” with
the directory where you installed WINAVR. (Note the forward slash)
Save the modified makefile by selecting “File->Save”. Now the code is all set to be
compiled. Choose the “[WINAVR] Make All” option from the tools menu to compile the
code.
The output window will show the following when the code compiles successfully and a
“HelloWorld.hex” will be created.
-------- begin -------avr-gcc (GCC) 3.3.2
Copyright (C) 2003 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. There is
NO
warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE.
Compiling: HelloWorld.c
avr-gcc -c -mmcu=at90s8515 -I. -g -O0 -funsigned-char -funsignedbitfields -fpack-struct -fshort-enums -Wall -Wstrict-prototypes -Wa,adhlns=HelloWorld.lst -std=gnu99 -Wp,-M,-MP,-MT,HelloWorld.o,MF,.dep/HelloWorld.o.d HelloWorld.c -o HelloWorld.o
HelloWorld.c: In function `main':
HelloWorld.c:25: warning: unused variable `a'
Linking: HelloWorld.elf
avr-gcc -mmcu=at90s8515 -I. -g -O0 -funsigned-char -funsigned-bitfields
-fpack-struct -fshort-enums -Wall -Wstrict-prototypes -Wa,adhlns=HelloWorld.o -std=gnu99 -Wp,-M,-MP,-MT,HelloWorld.o,MF,.dep/HelloWorld.elf.d HelloWorld.o
--output HelloWorld.elf -Wl,Map=HelloWorld.map,--cref -lm
Creating load file for Flash: HelloWorld.hex
avr-objcopy -O ihex -R .eeprom HelloWorld.elf HelloWorld.hex
Creating load file for EEPROM: HelloWorld.eep
avr-objcopy -j .eeprom --set-section-flags=.eeprom="alloc,load" \
--change-section-lma .eeprom=0 -O ihex HelloWorld.elf HelloWorld.eep
Creating Extended Listing: HelloWorld.lss
avr-objdump -h -S HelloWorld.elf > HelloWorld.lss
Creating Symbol Table: HelloWorld.sym
avr-nm -n HelloWorld.elf > HelloWorld.sym
Size after:
HelloWorld.elf :
section
size
addr
.text
152
0
.data
0
8388704
.bss
0
8388704
.noinit
0
8388704
.eeprom
0
8454144
.stab
804
0
.stabstr
1400
0
Total
2356
Errors: none
-------- end -------> Process Exit Code: 0
AVR Studio 4.08 can be used to simulate the compiled code. To do this an Extended
COFF (Common Object File Format) file has to be created. WINAVR provides a utility
produce an ExtCoff file and this utility can be called on from Programmer’s Notepad
using the makefile. To do this, open the options window using “Tools->Options”. Move
to the “Tools” section using the navigation pane of the window. In the “Scheme” dropdown box choose “(None – Global Tools)”. Click the “Add” button to bring up the “New
Tool” dialog box. Fill in the following parameters to create a new “[WINAVR] Make
ExtCoff” tool:
Click the “OK” button to create the new tool and dismiss the “New Tool” dialog box and
then click “OK” again to dismiss the “Options” window. To run the ExtCoff utility
choose the “[WINAVR] Make ExtCoff” from the “Tools” menu.
The following output will appear in the output window and a “HelloWorld.cof” file will
be created:
> "make.exe" extcoff
Converting to AVR Extended COFF: HelloWorld.cof
avr-objcopy --debugging --change-section-address .data-0x800000 -change-section-address .bss-0x800000 --change-section-address .noinit0x800000 --change-section-address .eeprom-0x810000 -O coff-ext-avr
HelloWorld.elf HelloWorld.cof
Discarding local symbol outside any compilation unit:
.do_copy_data_start
Discarding local symbol outside any compilation unit:
.do_copy_data_loop
Discarding local symbol outside any compilation unit:
.do_clear_bss_start
Discarding local symbol outside any compilation unit:
.do_clear_bss_loop
> Process Exit Code: 0
Now that the Extended COFF file is created, launch AVR Studio using the windows
“Start” Menu. Choose “File->Open File…” to bring up the “Open’ Dialog box. Navigate
to the “Hello World in C” directory and open the “HelloWorld.cof” file that you just
created. AVR Studio will automatically create a new project with the object files and the
sources and open an I/O view. Use the “Debug” menu to control the program execution
and simulate the code.
Programming the chip
Once you have verified that the code is running correctly with the simulator, it is now
ready to be burnt into the FLASH memory of the chip.
Connect the dongle provided with the kit to the parallel port and connect the
programming cable (long 10-core ribbon cable) between the dongle and the connector
marked ISP on the EVK01 board. Next connect the adapter provided with the kit to the
socket marked POWER and plug it into a normal wall socket. Power on the EVK01 by
pressing the switch marked POWER. The red POWER LED should now glow.
Begin by installing PonyProg, the programming software on the CD. You can find the
PonyProg installer in the software section of the EVK01 CD or on the PonyProg Website.
To install PonyProg simply launch the installer and follow the simple on screen
instructions. When the installation is complete, launch PonyProg from the windows
“Start” menu.
When you run PonyProg for the first time you will be prompted to run the “Interface
setup” and “Calibration”. To calibrate PonyProg© choose “Setup->Calibration” and
follow the on-screen instructions. To setup PonyProg© for programming, choose “Setup>Interface Setup” and select the following options in the dialog box that appears:
Select “Parallel”, “Avr ISP I/O” and “LPT1”
•
Make sure that all the check boxes in the “Polarity of Control lines” section are
not ticked, so that none of the control lines are inverted.
•
Press the “Probe” button at the bottom of the dialog box. PonyProg© will check
for the dongle and should display a “Test Ok” message.
•
Select Ok to close the “Interface Setup” dialog box.
On the toolbar in the main window choose “AVR Micro” and “AT90S8515” in the
device selection drop boxes.
Use “File->Open Device File” to load your assembled Intel Hex file “Hello World.hex”
into the PonyProg buffer. Use the “Command->Erase” first to erase any existing
program on the chip. Now program the FLASH on the chip with “Command -> Write
Program (FLASH)”. An automatic verification of the data is performed by PonyProg.
Executing the code:
The code begins executing immediately after the programming is done and PonyProg
releases the RESET pin of the processor. To see the LEDs blink simply connect one of
the I/O cables (shorter 10-core ribbon cable) between connectors marked PORTA and
LEDS on the EVK.
EEKS! I don’t own an EVK01:
Coming Soon…