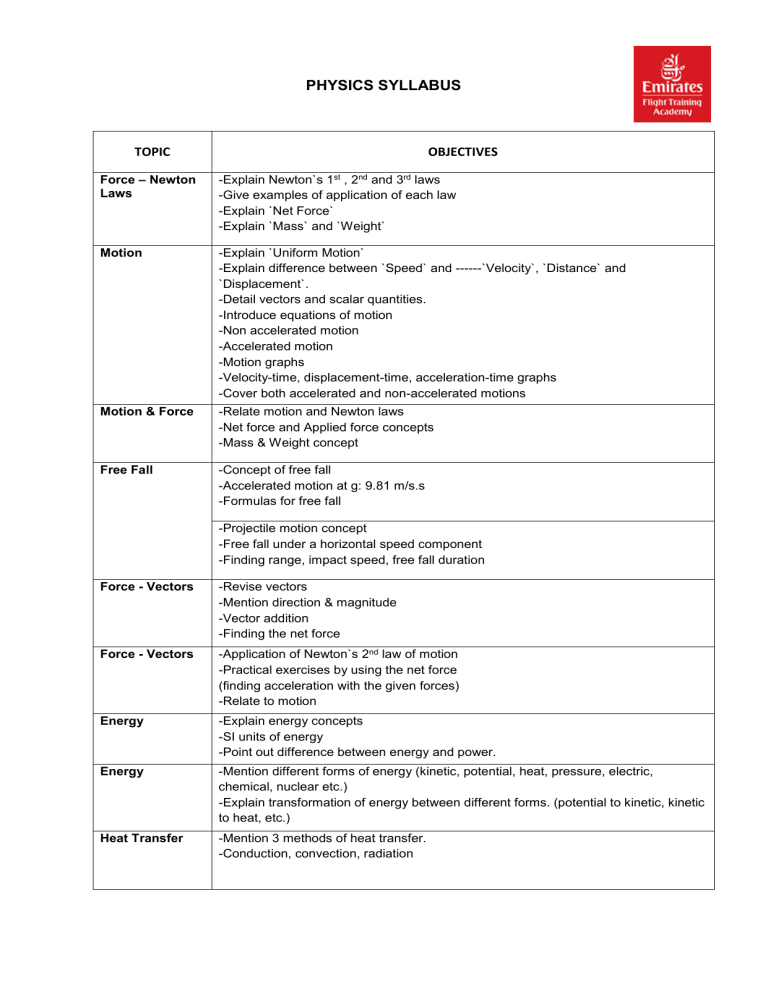
PHYSICS SYLLABUS TOPIC OBJECTIVES Force – Newton Laws -Explain Newton`s 1st , 2nd and 3rd laws -Give examples of application of each law -Explain `Net Force` -Explain `Mass` and `Weight` Motion -Explain `Uniform Motion` -Explain difference between `Speed` and ------`Velocity`, `Distance` and `Displacement`. -Detail vectors and scalar quantities. -Introduce equations of motion -Non accelerated motion -Accelerated motion -Motion graphs -Velocity-time, displacement-time, acceleration-time graphs -Cover both accelerated and non-accelerated motions Motion & Force -Relate motion and Newton laws -Net force and Applied force concepts -Mass & Weight concept Free Fall -Concept of free fall -Accelerated motion at g: 9.81 m/s.s -Formulas for free fall -Projectile motion concept -Free fall under a horizontal speed component -Finding range, impact speed, free fall duration Force - Vectors -Revise vectors -Mention direction & magnitude -Vector addition -Finding the net force Force - Vectors -Application of Newton`s 2nd law of motion -Practical exercises by using the net force (finding acceleration with the given forces) -Relate to motion Energy -Explain energy concepts -SI units of energy -Point out difference between energy and power. Energy -Mention different forms of energy (kinetic, potential, heat, pressure, electric, chemical, nuclear etc.) -Explain transformation of energy between different forms. (potential to kinetic, kinetic to heat, etc.) Heat Transfer -Mention 3 methods of heat transfer. -Conduction, convection, radiation Moment -Concept of moment -Mention moment is a vector. -Point out SI units of energy and moment and explain difference between them. (Nm) Moment -Balance scales and calculation of moment -Define centre of gravity Momentum -Revise mass and velocity -Momentum equation -Mention conservation of momentum -Concept of collisions Electricity & Magnetism -Describe Static electricity in terms of positive and negative charges -Describe the property of positive and negative charges to attract or repel -Describe the atom with particular reference to the electron -Describe charge as the unbalanced state of a material following the movement of electrons -Describe good and poor conductors according to the ease with which electrons move -Describe the use of poor conductors as insulators -Describe lightning as an extreme discharge of static electricity -Describe the use of bonding to protect from lightning strikes and special tires and wick dischargers to dissipate aircraft static build-up -Describe the movement of electrons as electric current and list some uses for current such as heating, lighting and magnetism -Recognize the symbols used for common circuit devices: Switch; Battery cell; Ammeter; Lamp -Define the unit of current [ampere] and state the associated symbol [(I] -Define the unit of charge [coulomb] and state the associated symbol [C] -Explain direct current [DC] -Define Potential Difference and state the unit of measurement [Volt] -Given a simple battery circuit diagram deduce the total voltage -Define electrical resistance and describe how the resistance of a conductor varies according to its conductivity, length and cross-sectional area -State the unit of resistance and the formula that links resistance with potential difference and rate of current flow [V = IR] -Explain alternating current [AC] -State the purpose of a diode -Define Capacitance and state its unit of measurement [Farad] -Define Electrical Power and state its unit of measurement [Watt] -State the formula that links Watts with Amperes and Volts. [W = I V] -Describe the properties of magnets, list magnetic materials and define permanent and temporary magnetism -Describe the earth’s magnetic field with reference to: a) Lines of force b) North and south magnetic poles c) Magnetic variation & Angle of dip -Describe the use of electricity to create magnetism with particular reference to the right hand screw rule to predict the direction of the magnetic field -Describe the use of electricity to create temporary magnetism and state how the strength of the resulting magnetic field varies with the current in the coil; the number of turns; the proximity of the poles -Describe a simple AC generator Properties of Matter -Review definitions of atoms; molecules; compounds and mixtures -Describe molecules and their properties of attraction and repulsion -Explain the kinetic theory of matter with reference to solids, liquids and gases -Discuss the ideal gas laws: Pressure law Charles’ law Boyle’s law Combined gas law -Calculate different variables based on the ideal gas law equations -Describe the following properties of matter: Diffusion Surface tension Adhesion and cohesion Capillarity Mechanical properties Density -Define density. -Apply the formula for density to calculate [for example] mass given volume and density. -Describe how the density of solids, liquids and gases can be measured. -Define Relative Density [specific gravity] and state that it has no units. -State that relative density can be greater, less than or equal to 1. -Describe how density is affected by: -The compression or expansion of an object -Change of volume due to change of temperature -Apply knowledge of density to deduce how the loading of cold fuel affects the relative density, the weight of full tanks and the available range Pressure -Define pressure and state the unit used for the measurement of pressure -Calculate pressure given mass and surface area -Describe pressure within a liquid and explain why pressure increases with depth -State Pascal’s principle i.e. that pressure acts equally in all directions and acts on equal areas with equal force -Apply Pascal’s principle to explain the operation of simple hydraulic machines -Describe the operation of car brakes in terms of hydraulic principles -Explain how hydraulic machines can be used as force multipliers -Describe pressure within the earth’s atmosphere -Explain why the pressure of the atmosphere is not normally noticeable to humans and why it puts no stress on to un-pressurized aircraft -Describe the pressure difference that exists between the inside and the outside of a pressurized aircraft and why this must be limited -Describe the following devices for measuring pressure: Bourdon tube U-tube manometer Mercury barometer Aneroid barometer -Describe some of the implications of unusually low or high pressure: In aviation In space


