Obligations & Suspensive Conditions: Loss, Deterioration, Improvement
advertisement

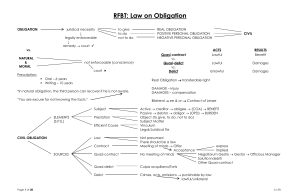
Article 1189. When the conditions have been imposed with the intention of suspending the efficacy of an obligation to give, the following rules shall be observed in case of the improvement, loss or deterioration of the thing during the pendency of the condition: (1) If the thing is lost without the fault of the debtor the obligation shall be extinguished; (2) If the thing is lost through the fault of the debtor he shall be obliged to pay damages; it is understood that the thing is lost when it perishes, or goes out of commerce, or disappears in such a way that its existence is unknown or it cannot be recovered; (3) When the thing that deteriorates without the fault of the debtor, the impairment is to be borne by the creditor; (4) If it deteriorates through the fault of the debtor, the creditor may choose between the rescission of the obligation and its fulfillment, with indemnity for damages in either case; (5) If the thing is improved by its nature, or by time, the improvement shall inure to the benefit of the creditor; (6) If it is improved at the expense of the debtor, he shall have no other right than that granted to the usufructuary. Requisites: (1) The obligation is REAL OBLIGATION. (2) The object is SPECIFIC/DETERMINATE THING. (3) The obligation is subject to SUSPENSIVE CONDITION. (4) The condition is FULFILLED; and (5) There is LOSS, DETERIORATION, IMPROVEMENT of the thing during the pendency of the condition. Kinds of Loss (1) Physical Loss - the thing perishes (burned house to ashes). (2) Legal Loss - the thing goes out of commerce or thing legal becomes illegal. (3) Civil Loss - thing disappear that its existence is unknown; or even known, it cannot be recovered. Rules in case of Loss, Deterioration, or Improvement during pendency of Suspensive Condition (1) Loss of thing without debtor’s fault. - obligation is extinguished. (2) Loss of thing through debtor’s fault. - obligation to pay damages. (3) Deterioration of thing without debtor’s fault. - when its value is reduced or impaired (4) Deterioration of thing through debtor’s fault. (1) Rescission or cancelation of the obligation with damages. (2) Fulfillment of the obligation also with damages. (5) Improvement of thing by nature or by time. - when its value is increased or enhanced by nature or by time or at the expense of the debtor or creditor. (6) Improvement of thing at the expense of debtor. - debtor have right granted to a usufructuary. Usufruct The right to enjoy the use and fruits of a thing belonging to another.








![6obligations-and-contracts[1]](http://s1.studylib.net/store/data/025863945_1-d5c48764c4a3018d637d8c1f47d48e5d-300x300.png)

