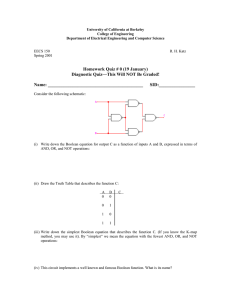
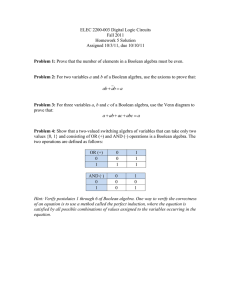
Boolean algebra EE2315 What is Boolean algebra? It is a mathematical operation that works with the binary numbers. Boolean algebra is used to analyze and simplify the digital circuits. Boolean algebra and the Boolean operations are the basis for computer logic. Rules Variables used can have only two values either 1(True) or 0 (false). Overbar represents a complement of a variable, where the complement of A can be represented as 𝐴. A OR B A+B A AND B A.B Boolean laws Commutative law A+B = B+A A.B = B.A Associative law (A+B)+C = A+(B+C) (A.B).C = A.(B.C) Distributive law A.(B+C) = A.B + A.C Boolean laws Annulment 𝐴. 0 = 0 𝐴 + 1 = 1 Identity law 𝐴 + 0 = 𝐴 𝐴. 1 = 𝐴 Complement 𝐴 + 𝐴 = 1 𝐴. 𝐴 = 0 Boolean laws Idempotent law 𝐴. 𝐴 = 𝐴 𝐴 + 𝐴 = 𝐴 Inversion law 𝐴 = 𝐴 Absorption law 𝐴 + 𝐴𝐵 = 𝐴 𝐴. 𝐴 + 𝐵 = 𝐴 𝐴 + 𝐴𝐵 = 𝐴 + 𝐵 𝐴. 𝐴 + 𝐵 = 𝐴𝐵 DE Morgan's Theorem Compliment of a product is equal to the sum of the compliments. 𝐴𝐵 = 𝐴 + 𝐵 Compliment of a sum is equal to the product of the compliments. 𝐴 + 𝐵 = 𝐴. 𝐵 Thank you.