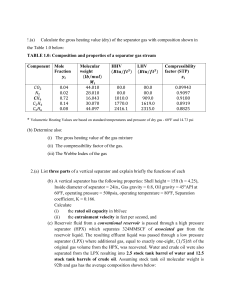
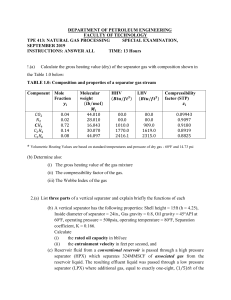
PVT Experiments: Separator Test production-technology.org/pvt-experiments-separator-test/ By Islam Fetoui October 13, 2017 Separator Test experiments are carried out for both oil and gas condensate mixtures. A sample of reservoir liquid is placed in the laboratory cell and brought to reservoir temperature and bubble-point pressure. Then the liquid is expelled from the cell through a number of stages of separation. Usually, two or three stages of separation are used, with the last stage at atmospheric pressure and near-ambient temperature (60 to 80°F). The gas is let out of the separator through the top and is transferred to standard conditions, where its volume is measured. As for the differential liberation experiment, liquid dropping out from the gas is converted to an equivalent gas volume at standard conditions. The liquid from the rst separator is let into a second separator at a lower pressure and temperature than the rst one. At which conditions, more gas will be liberated as sketched in the figure below. As with the gas from the rst separator, this gas is transferred to standard conditions. The oil remaining after gas removal is brought to the conditions of the next separator stage. The gas is removed again and quantified by moles and specific gravity. Oil volume is noted, and the process is repeated until stock-tank conditions are reached. Final oil volume, Vo, and specific gravity, SGo, are measured at 60°F. NB: Often the composition of the separator gas and stock tank gas are measured. Example: The separator test experiment results are presented in the following table. It includes a Bo-factor for the reservoir uid at the saturation point (199.7 bar) and reservoir temperature (97.8°C). This Bo-factor expresses how much saturated-oil at the reservoir temperature will shrink through a four-stage separation with separator temperatures and pressures as presented in Table. The remaining Bo-factors in the Table express the shrinkage of the oil from the current stage of the separation down to stock tank conditions. The separator gas/oil ratio equals the ratio between the volume of the gas liberated from the current stage taken to standard conditions and the volume of the oil from the last separator stage, which is at standard conditions. 1/2 * This example is from the book “Phase Behavior of Petroleum Reservoir Fluids”. Using the separator test data, for a given set of separator conditions, in conjunction with the differential liberation data, will provide a means of obtaining the PVT parameters required for field use. It is considered that the differential liberation data can be used to describe the separation in the reservoir while the separator flash data account for the volume changes between reservoir and stock tank. You May Also Like… PVT Sampling Methods: Downhole, Wellhead & Surface Recombination PVT Experiments: Constant Composition Expansion PVT Experiments: Differential Liberation PVT Properties and Correlations 2/2