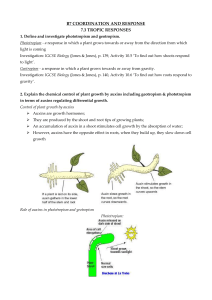
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Biology 7.2 & 7.3 - Hormones Endocrine (Hormone) Control in Humans You need to know that hormones are: - chemicals that are transported in the blood plasma - secreted by glands and affect the target organ(s) - By altering the activity of the target organ(s) - destroyed by the liver Glands produce hormones and then secrete them into the blood. - Major glands include: - Pancreas (from Unit B4.3) - Produces : Insulin, glucagon... - Reproductive organs (Unit B8.3) - Produces : Oestrogen, testosterone… - Adrenal gland - Produces : Adrenaline You need to know the effects of one specific hormone in particular, adrenaline. Adrenaline is produced in the adrenal gland: - ad- meaning ‘next to’, and renal meaning ‘relating to the kidneys’. The adrenal gland is next to the kidneys. Adrenaline is often called the “fight or flight” hormone because it is produced when the body is preparing for action (fighting or running away). The effects of adrenaline allow the body to be active more efficiently: - - Increased heart rate, breathing rate, blood sugar concentration: for increased respiration - These allow the body to produce more energy to the active muscles. Vasodilation in the brain (blood vessels expand for more flow) - Provides more blood to the brain, and might feel slightly dizzy Blood diverted away from digestive system - This might feel as “butterflies in the stomach” - Because blood flow is focused into muscles and away from “unnecessary” organs for action Masks pain You need to know the similarities and comparison between the endocrine system and the nervous system: Endocrine System Nervous System Functions Control the body functions Control the body functions Method Special chemicals produced in glands Electrical Impulses from neurons Time Slower and depends on the stimulation of glands Rapid and is constantly occurring Tropic Control in Plants You need to know that plants grow in response to the environment, controlled by plant hormones called auxins. Auxins are a type of plant hormone which speed up or slow down growth of cells affected. - Normally auxins are used in growing stems, - They are also used to grow in different directions as responses. - If auxins are distributed to only one side of the stem - Side with auxins are made to grow faster than the other side - And the stem will bend. You need to know two types of plant responses: Geotropism - Is the response of a plant to grow towards or away from gravity. (Geo- for earth) - Positive geotropism is growing towards gravity (down) - Negative geotropism is growing against gravity (up) Phototropism - Is the response of a plant to grow towards or away from light. (photo- for light) - Positive phototropism is growing towards away from light - Negative phototropism is growing away f rom light The syllabus says you should be able to, (SO check if you can): - Define a hormone as a chemical substance, produced by a gland, carried by the blood, which alters the activity of one or more specific target organs and is then destroyed by the liver. - State the role of the hormone adrenaline in the chemical control of metabolic activity, including increasing the blood glucose concentration and pulse rate. - Give examples of situations in which adrenaline secretion increases. - Compare nervous and hormonal control systems. - Define and investigate geotropism (as a response in which a plant grows towards or away from gravity) and phototropism (as a response in which a plant grows towards or away from the direction from which light is coming) Explain the chemical control of plant growth by auxins including geotropism and phototropism in terms of auxins regulating differential growth.