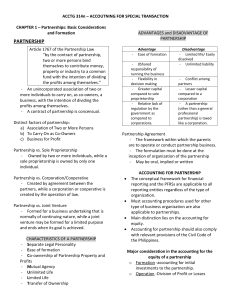
CHAPTER 7 TYPES OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP A type business is owned and controlled by one person. • These are usually small businesses in which the enterprises require a small amount of capital. • There is one person in charge of overseeing every business operation. ADVANTAGES OF SOLE PROPRIETORSHIPS • Ease of start-up • Full control over the company • Exclusive rights to profits DISADVANTAGES OF SOLE PROPRIETORSHIPS Unlimited liability • Sole proprietors are responsible for all business debts • Liability- responsible for debt Sole Responsibility • Owner has a plethora of responsibilities Limited growth potential • When a business is started out small, it is difficult to get enough revenue to vastly expand • Collateral- anything a borrower gives up if he or she is not able to repay a loan Lack of longevity (or life of business operation) • If the sole proprietor is unable to work or loses interest in the business then the business might fail PARTNERSHIPSSECTION 2 Business that is controlled by two or more people is a partnership • Two or more people work together and oversee the entire business. • “General Partnership”partners enjoy equal decision making powers between them • “limited partnership”partners join as investors who provide financial capital in exchange for a share of the profits while another partner oversees the operations ADVANTAGES OF PARTNERSHIPS Ease of start-up • Easy to start up with more people Specialization • Each person can contribute to the company with a specialized task • This allows for people to work in areas that they are most comfortable. Shared decision making • Help make smart decisions together • With more than one mind on an issue, better solutions can be discovered for problems or conflicts Shared business losses • When the business fails, the partnership can work together to bring the business back up. • The debt or losses can be divided over several people instead of just one person DISADVANTAGES OF PARTNERSHIPS Unlimited liability • Partners are responsible for all debt of the company, similar to a sole proprietorship Potential for conflict • With more than one mind working on the business, there is the possibility of conflict between partners Lack of longevity • If partners disband or lose interest, the company will either need to be sold or will dissolve CORPORATIONSSECTION 3 A business in which a group of owners, called stockholders, share in the profits and losses is a corporation. • Owned by shareholders • A share is a piece of stock in the company • The person who owns the most stock is the majority shareholder • Dividends- profits paid to you as a shareholder STOCKS AND BONDS Common Stock- provides shareholders with a voice in how the company is run and a share in any potential dividends Preferred Stock- provides guaranteed dividends, but does not grant shareholders a voice in running the corporation A BOND is a certificate issued by the corporation in exchange for money borrowed from an investor • Indicates that the corporation owes you money Principal is the amount of money that was borrowed from you • Interest is the money that the corporation must pay for the use of your money OTHER FORMS OF ORGANIZATIONSECTION 4 Corporate Combinations • Merger-when one company joins with or absorbs another • Horizontal- when two or more companies producing the same good or service merge • Vertical- two or more companies in different production phases merge • Conglomerate- merger of companies producing unrelated product OTHER COMPANIES Franchises • One company agrees to let another person or group open up a branch in the company name, for a fee Cooperatives (CO-OP) • Businesses that are owned collectively by their members Nonprofit organizations • Works like a business to provide goods and services while pursuing goals