Biochemistry Exam Questions & Answers: Glycolysis, Genetics, Oxidation
advertisement

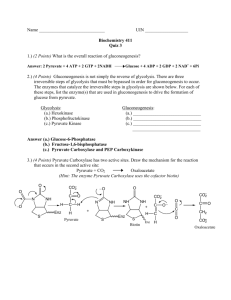
Group members o Question one Describe the significance of glycolysis pathway. o Answer It is important for the production of energy In skeletal muscle glycolysis provide ATP in the absence of oxygen, muscles survive under anaerobic conditions. It is used for synthesis of biomolecules. Example Phosphoglycerate is used for synthesis of serine.Glucose-6-phosphate is used for synthesis of glycogen. It may be considered as the preliminary step before complete oxidation. It provide carbon skeletons for the synthesis of nonessential Amino acids as well as glycerol as part of fat. Most of the reactions of glycolysis pathway are reversible which are also used for gluconeogenesis. It is the only pathway that is take part in all cells of the body. QUESTION 1B B . Explain why the reactions that is considered the main rate determine step of glycolysis is regulated? Answer o The rate determine steps of glycolysis are: Step (1). 2. Steps (3). 3. Step (9) But step (3) is the most important step in which the phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) is the most important rate limiting enzyme for glycolysis pathway. It convert fructose-6-phosphate to Fructose1,2-bisphoohate . ATP and citrate are the man at important inhibitors and AMP acts as an activator and fructose-1,2- bisphosphate. QUESTION IC C. Where does gluconeogenesis take place? Explain the first reaction in gluconeogenesis. Answer It take place in the Liver to leaser into the Kidney. The first step of gluconeogenesis take place in the mitochondria matrix. In this reaction, pyruvate is phosphorylate to Oxaloacetate, catalysed by pyruvate carboxylase. ATP is been phosphorylate to ADP with the help of H2O and Carbon dioxide. QUESTION 1d d. Name two gluconeogenesis Amino acids and explain how they are gluconeogenic. Answer o The two Amino acids are; Alanine and Aspartate. o Alanine: from pyruvate in the transamination reaction, pyruvate then undergoes the gluconeogenic pathway. In this reaction, alpha Ketoglutarate combined with the Alanine to form glutamate and pyruvate, with the help of enzyme called Alanine transaminase o Aspartate: forms Oxaloacetate in the transamination reaction. Oxaloacetate then undergoes the gluconeogenic pathway. Where the alpha Oxaloacetate combined with the aspartate to form glutamate and Oxaloacetate with the help of aspartate transaminase. Biochemistry 2016 by Alhaji Alpha Kamara Question 3 Using the Karyotype below Answer the following question [a] Outline the karyotype found in down syndromes Ans In down syndrome the karyotype shows can extra chromosome number 21 will present with; [1] Hypogonadism [2] Poor facial hair growth [3] Tall status and usually gynecomastia [4] Shyness [5] Infertility [6] Stress and behavioral [C] Describe four common chromosomal mutations and give examples Ans [1] AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE DISORDER; Individual requires two copies of defectives chromosome from both parents, to show symptom of the disease. Eg ALBINISM. [2] x-LINKED RECESSIVE DISORDERS; Transmitted by a defective X-chromosome, including to male children. Eg HEAMOPHILIA [3] AUTOSOMAL DOMININT DISORDER; Individual used only one copy of defective chromosomic from either parents to syndromes of the disease. Eg POLYDATYLE [4] X-LINKED DOMINANT DISSORDER; Transmitted by a defective X-chromosome especially to male and female child. Eg ALPORT SYNDROME QUESTION 3d b. How would you diagnose this patient? Klinefelter syndrome; the person has an extra sex chromosome’’ X’’ NOTE; A person with Klinefelter syndrome [D] WHAT ARE CHROMOSOMA ABERRATIONS? HOW CAN THEY CAUSED Ans These abnormalities in chromosome number or structure which may result in defective fractions individuals CAUSES OF CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS. NOVEMBER 2016 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS by ABDUL HAMID A teenage girl was brought to the medical center because of her complaints that she used to get too tired when asked to participate in gym classes. A consulting neurologist found muscle weakness in girl’s arms and legs. When no obvious diagnosis could be made, biopsies of her muscles were taken for tests. The tests revealed greatly elevated amounts of triglycerides esterified with primary long chain fatty acids. Pathology reported the presence of significant numbers of lipids vacuoles in the muscle biopsy. (a) What is the probable diagnosis? Ans: Carnitine deficiency (b) What is the cause for these observed symptoms? Explain your answer in detail including the process involved. Ans: Individuals have problem with the oxidation of fatty acids. When the fatty acids is in the cytosol of the adipose cells, it’s going to be activated by the enzyme thiokinase (fatty acyl synthase) to fatty acyl CoA. When it has been activated, it needs to be transported by a carnitine enzyme into the matrix of the mitochondria, however, if this enzyme is deficient, the activated fatty acyl CoA will not be transported into the mitochondria, and hence medical abnormalities may start to occur. QUESTION 5c & 5d 5c. Four (4) steps in beta-oxidation reactions Ans: Dehydrogenation Hydration Oxidation Thiolysis or cleavage QUESTIONS 5d (d) Outline the oxidation reactions for odd number fatty acids Ans: Synthesis of D-Methyl malonyl CoA Conversion of D-isomer to Lisomer Conversion of L-Methyl malonyl CoA into succinylCoA CoA