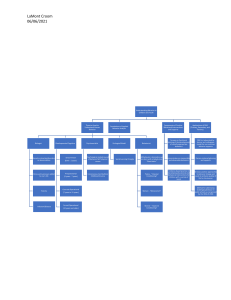
LaMont Croom 06/06/2021 Understanding Behavior in Children and Youth Biologist Developmental Cognitive Theories Used to Understand Human Behavior Foundations of Applied Behavior Analysis Psychosocialist Ecological Model Components of Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports focuses on functional training of the development of socially appropriate behaviors PBS first advocated by Horner and colleagues, model for non-aversive behavior supports All behavior is learned as we are born with a tabula rasa, "blank slate." concentrates on measurable and observable behaviors Person-centered planning and supports Pavlov - "Classical Conditioning" Evidence-based practice in developing educational and behavioral interventions for children with a variety of needs Stresses positive approaches to behavior change and seeks to enhance qulaity of life for the learner Behaviorist Genetics-inherited disorders or abnormalities Sensorimotor (birth - 2 years) Psychological-rooted caused of Behavior NOT physical causes Stress-extra pressure added to one's life Preoperational (2 years - 7 years) Unconscious mind battles/ Childhood trauma Toxicity Concrete Operational (7 years to 11 years) Watson - "Behaviorism" Infection/Disease Formal Operational (12 years and older) Skinner - "Operant Conditioning" Social Learning Triangle Applications of PBIS (Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary) Method for addressing challenging behavior in public schools as recognized by the IDEA of 2004