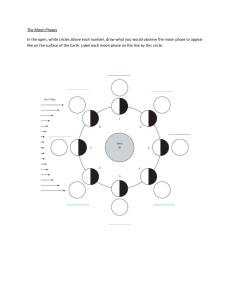
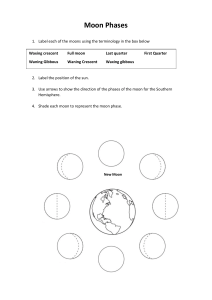
DETAILED LESSON PLAN SCIENCE V I. OBJECTIVES At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to: a. Describe the changes of the moon’s light as seen from night to night; b. Identify the phases of the moon; c. Draw and arrange the phases of the moon orderly. II. Subject Matter Topic: Topic: Phases of the Moon References: Science in our World, K to 12 5 WORKTEXT Materials: Instructional materials, activity sheets, Oreo cookies, model of a Moon and Earth, flashlight, paper plate and spoon Science Processes: Observing, Describing, Inferring and Manipulating Value: Appreciation, Cooperativeness III. Procedure Teacher’s Activity Pupil’s Activity Preparation (Prayer) Good morning class... Good morning sir. How are you today? We’re good sir. Nice to hear that class. Motivation (Post different shapes of the Moon as seen each night) What can you say about the pictures? It shows the different shapes of the moon at night time. Nice answer! (The pupils will be ask) How do you feel when there is no moon at night time? How does the appearance and non-appearance of the moon at night affect your way of life? Presentation Now, the different shapes of the moon that you see are what we called the “The Phases of the Moon”, and that is our topic for today. Let’s have this diagram… The diagram shows the different positions of the moon around the Earth with reference to the Sun. Have you noticed that the moon keeps changing shape? It starts as a thin crescent which grows bigger every night until it is a bright ball in the sky. What makes it seems to change like this? Just like the Earth, the moon does not have its own light. It reflects light from the sun. The phases of the moon you see depend on its position in relation to the sun and earth. And in fact, the shape of the moon does not change, only its lighted part. Then we see less and less of its lighted part. That is why its shape appears to change, this is what we call, “Phases of the Moon”. (I will introduce and explain the characteristics of the moon phases) Now, let’s find out and discover why and how the moon shows different phases through this improvised model of the moon and earth. (I will use an improvised model in showing how the moon revolves and forms the different phases while revolving around the earth in relation to the sun)… Alright, I have questions for you, if the moon is in between the Earth and Sun, we can see total darkness, what do you call this phase? The phase is called “New Moon”. Correct answer! Then, how about if the earth is in between the moon and sun, we can see the whole bright or lighted moon. What do you call this phase? The phase is called “Full Moon”. Nice answer! Next, it is between the quarter and new moon and looks like a “banca”; sometimes it is waxing and waning. What do you call this main phase of the moon? The phase is called “Crescent Moon”. Very Good! Another question, this phase is frequently named the half moon, it is between the gibbous and crescent moon. What phase of the moon it is? It is the “Quarter Moon” Correct Answer! Finally, this phase is between the quarter and full moon stages, more than half of the moon can be seen; it is sometimes waxing or waning. What do you call this main phase of the moon? The phase is called “Gibbous Moon”. Excellent Answer! Group Activities (The class will be divided into 4 groups) (I will set standards in doing group activity) All groups will perform the: OREO COCKIE MOON PHASES ACTIVITY PROCEDURES 1. Gently separate the Oreos so all filling is on one side. (Be careful as you separate your Oreos, full moon and new moon are already done when you pull apart your Oreo). 2. Scrape off filling to resemble each phase of the moon. 3. Place Oreo phases in the plate (correct order) in relation to the earth and sun. 4. Label the Oreo phases starting with the new moon. 5. Once you finished your work, clap 5 times. (In order for your teacher to know whose group finished first? 6. Finally, think a good way in presenting your work in front of the class. (After the presentation of the group works, the students will be ask) Were you able to follow the instructions correctly? Is it very important that you follow the instructions correctly? Generalization Now let’s go back, what do you call the changes of the It is called the Phases of the Moon. moonlight’s shape as the moon revolves around the earth? Very Good Answer! Alright, what are the five main phases of the moon? The five main phases of the moon are: New Moon, Crescent Moon, Quarter Moon, Gibbous Moon and Full Moon. Excellent Answer! Then, how about the 8 phases of the moon within a month, The eight phases of the moon within a month are the; New what are those phases? moon, Waxing Crescent, First Quarter, Waxing Gibbous, Full Moon, Waning Gibbous, Last Quarter and Waning Crescent. Nice Answer! Class, always remember that; = Phases of the Moon/Lunar Phases – are the different moonlight shapes of the moon during a month. = New Moon – is when the moon is all dark and located between the Earth and Sun. = Crescent Moon – is when the moon is in between new moon and quarter moon stages, appears to be partly but less than one-half illuminated. If the moon’s light is increasing, it is called waxing crescent, if it is decreasing, it is waning crescent. = Quarter Moon – is when half of the moon is visible. If the moon’s light is waxing, it is called first quarter, if it is waning; it is called the last quarter. = Gibbous Moon – is between the quarter and full moon stages, appears to be more than one-half but not full illuminated. If the moon's light is increasing, it is called waxing gibbous. And if it is decreasing, it is called the waning gibbous. = Full moon - if the moon appears brightly and completely illuminated by direct sunlight. The earth is in between the moon and sun during this phase. = Waxing - means to increase gradually in size and is used to describe the moon's light as it grows from the new to full moon. = Waning - means to decrease gradually in size and is used to describe the moon's light as it gets smaller from full moon to new moon. Application Draw the different phases of the moon shown below then arrange them in their order of appearance around the earth. EARTH Full Moon Waxing Crescent First Quarter Waning Gibbous New Moon Waning Crescent Waning Crescent Last Quarter IV. EVALUATION Match Moon Phases Assessment Match the description with the corresponding moon phase and features. Write the correct letter of your answer at the space provided before the number. ______ 1. The moon decreasing in light, it is between a full moon and a last quarter. ______ 2. The moon is almost directly between the Earth and Sun, we cannot see the moon at this phase. (Start of Cycle) ______ 3. The different moonlight shapes of the moon as it revolves around the Earth within a month. ______ 4. A bit of the sunlit side of the moon shows, with the sunlit side being on the right (forms like a banca). ______ 5. Two weeks have passed since the new moon. We see the entire or complete face of the moon shining brightly. ______ 6. The moon is three-quarters of its way around the earth. ______ 7. The moon is quarter of its way around the earth. ______ 8. A bit of the sunlit side of the moon shows the light side being on the left (forms like a banca). ______ 9. The moon is increasing in light; it is between a first quarter and a full moon. ______ 10. The estimated days of a complete revolution of the moon around the Earth. V. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. Waning Gibbous Moon First Quarter Moon New Moon Waxing Crescent Moon Waxing Gibbous Moon Full Moon Waning Crescent Moon Third or Last Quarter Lunar Phases/Phases of the Moon 29 ½ Days Sun Earth ASSIGNMENT Observe the shape of the moon every night for two weeks, then draw the moon’s shape each night in a chart similar to the one shown below and write your observation. WEEK 1 Week 1 Week 2 Observation: 2 3 NIGHT 4 5 6 7