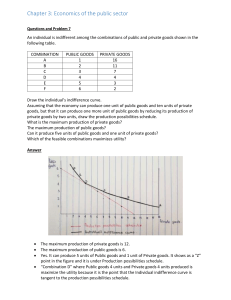
© VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS Chapter 1: What economics is all about Scarcity, choice and opportunity cost Wants- Human desires for goods and services Wants are unlimited –we all want everything. Needs-Are necessities, the things that are essential for survival. Needs are not absolute unlimited, it is possible to calculate basic needs which have to be met if a person or household is to survive Demand-There is demand for a good or service only if those who want to purchase it have the necessary means to do so. Demand has to be backed by purchasing power © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS • Some wants will be satisfied but many will be left unsatisfied, difficult choices have to be made • When resources are used to produce a certain good, they are not available to produce other goods • A decision to produce more of one good therefore also means that less of another good can be produced • Resources are scarce the use of resources can be costless • There are always costs involved in any use of scarce resources • We are all faced with difficulty choices between different alternative • We can measure the cost of the alternative we have chosen in terms of the alternative that we have sacrificed. This is called opportunity cost that is the best alternative that has to be sacrificed • Opportunity cost of a choice is the value of the decision maker of the best alternative that could have been chosen but was not chosen. The opportunity cost of a choice is the value of the best forgone opportunity • Every time a choice is made, opportunity costs are incurred Illustrating scarcity, choice and opportunity cost: the production possibilities curve Table 1-1 Production possibilities for the Wild Coast community (Textbook page 6) © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS The production possibilities curve indicates the combinations of any two goods or services that are attainable when the community’s resources are fully and efficiently employed Illustrating scarcity, choice and opportunity cost: the production possibilities curve Figure 1-1 A production possibilities curve for the Wild Coast community (Textbook page 6) © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS Further applications of the production possibilities curve See Box 1-2 Goods and services (Textbook page 7) Figure 1-2 Improved technique for producing capital goods (Textbook page 9) © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS Further applications of the production possibilities curve Figure 1-3 Improved technique for producing consumer goods (Textbook page 10) © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS Further applications of the production possibilities curve Figure 1-4 Increase in the quantity or productivity of the available resources (Textbook page 10) © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS Further applications of the production possibilities curve Table 1-2 The production possibilities curve (PPC): a summary (Textbook page 10) © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS Microeconomics and macroeconomics © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS