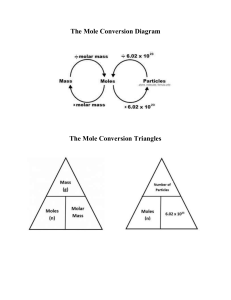
NOTE-TAKING GUIDE Unit 6, SEGMENT B Main Ideas, Key Points, Questions: After watching the video segment, write down key points, main ideas and big questions. Continue to learn about dimensional analysis and THE MOLE. Name: Date: Objective(s): • • To relate Avogadro’s number to both mass and volume of a substance. To use dimensional analysis to solve mole conversions. Notes: During the video segment, use words, phrases or drawings to take notes. 1 mole = 6.02 x 10^23 0.5 moles of helium = 3.01 x 10^23 Mass of a typical hydrogen atom = 1.66 c 10^-24 grams The SI unit that measures the amount of matter a substance has - abbreviated as moI - 6.02 x 10^23 representative particles - representative particles: atoms, molecules, or formula units Atomic Mass unit = one atomic mass unit equals 1/12 the mass of a carbon atom - the average mass of a single atom of that type of element in amu - the mass in grams of a mole of the particular element, i.e. the element molar mass Molar Mass = the mass in grams of a mole of a substance Stochiometry = the calculation of the quantities of reactants and products involved in a chemical reaction Summary: After watching the video segment, write at least three sentences explaining what you learned. You can ask yourself: “If I was going to explain this to someone else, what would I say?” Dimensional Analysis Steps 1. Identify starting and ending units 2. Place the number that is given in the problem, along with units, in the upper left hand corner of a conversion chart 3. Choose a conversion factor that will get you to the next unit. Make sure the unit from the upper left appears also on the lower right 4. Let the units guide the conversion by lining up conversion factors so units cancel 5. After canceling units, multiply all the number in the numberator together, as well as all the numbers in the denominator, and then deivide the numerator by the demoniator 6. Check the units and your answer Copyright © 2017 Georgia Public Broadcasting. All rights reserved. Use or distribution by an unintended recipient is prohibited. Name: QUESTIONS TO CONSIDER: Unit 6, SEGMENT B Date: After watching the video and performing any associated labs and/or experiments, you should be able to answer the following: 1. “Avogadro’s Number” was named in honor of Amedeo Avogadro. What is Avogadro’s number? 2. How many atoms are found in one mole of atoms? 6.023 x 10^23 6.02 x 10^23 3. Show the dimensional analysis conversion chart for this question: How many molecules of water are there in 0.360 moles of water? 0.360 mol H2O 6.02 x 10^23 molecules H2O = mol H2O 2.17 x 10^23 molecules of water 4. Show the dimensional analysis conversion chart for this question: How many moles of Mg are in 1.25 x 1023 Mg atoms? 1.25 x 10^23 1 mol Mg Mg atoms = 6.02 x 10^23 Mg atoms 0.208 5. How many grams of carbon are found in 1 mole of carbon atoms? mol Mg 1.99 X 1-^-23 grams 6. Define molar mass. the mass in grams of a mole of a substance At this point in the lesson, the teacher should pass around the classroom some containers filled with one mole of some well-known substances (iron, aluminum, zinc, salt, water, etc.) 7. Show the dimensional analysis conversion chart for this question: How many grams are in 9.45 moles of N2O3? 9.45 mol N2O3 76.02 grams N2O3 = 1 mol N2O3 718 grams N2O3 8. Show the dimensional analysis conversion chart for this question: How many moles are in 92.2 g Fe2O3? 92.2 g Fe2O3 1 mol Fe2O3 159.69 g Fe2O3 = 0.577 mol Fe2O3 Make sure you complete the Weighing Moles Lab before you continue to the next video. This activity will clarify the dimensional analysis used in mole conversions. Copyright © 2017 Georgia Public Broadcasting. All rights reserved. Use or distribution by an unintended recipient is prohibited.