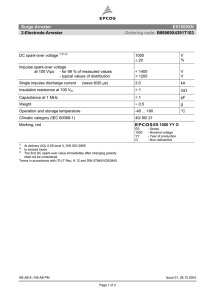
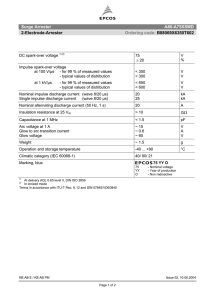
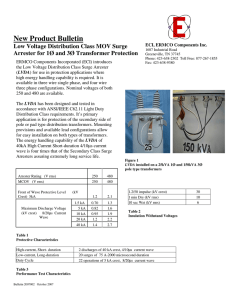
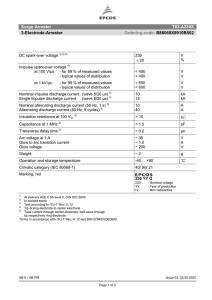
Lighting arresters https://www.slideshare.net/younistanzeela/lightning-power-system-presentation The typical lightning arrester has a high-voltage terminal and a ground terminal. When a lightning surge (or switching surge, which is very similar) travels along the power line to the arrester, the current from the surge is diverted through the arrester, in most cases to earth. TYPES OF LA https://circuitglobe.com/types-of-lightning-arresters.html 12 types 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Road Gap Arrester Sphere Gap Arrester Horn Gap Arrester Multiple-Gap Arrester Impulse Protective Gap Electrolytic Arrester 7. Expulsion Type Lightning Arrester 8. Valve Type Lightning Arresters 9. Thyrite Lightning Arrester 10. Auto valve Arrester 11. Oxide Film Arrester 12. Metal Oxide Lightning Arresters LOCATION OF LA Lightning arrester should be located close to the equipment that it is expected to protect. In large substations, arrestors should be installed at take-off points of the lines and of the terminal apparatus. RANGE OF LA On structures less than 30 metres (about 100 feet) in height, a lightning rod provides a cone of protection whose ground radius approximately equals its height above the ground. On taller structures, the area of protection extends only about 30 metres from the base of the structure. Lightning Arrester Ratings https://studyelectrical.com/2014/06/lightning-arrester-location-rating-and.html The rating of a lightning arrester is given below, Normal or rated voltage: It is designated by the maximum permissible value of power frequency voltage which it can support across its line and earth terminal while still carrying effectively and without the automatic extinction of the follow-up current. The voltage rating of the arresters should be greater than the maximum sound phase to ground voltage. Normal Discharge current: It is the surge current that flows through the LA after the spark over, expressed in crest value (peak value) for a specified wave shape. Example 10, 5, 2.5, 1.5, 1 kA rating. Power frequency spark over voltage: It is the RMS value of the power frequency voltage applied between the line and earth terminals of the arrester and earth which causes spark over of the series gap. As per IS 3070, the recommended spark overvoltage is 1.5 times the rated voltage. There are also other ratings like maximum impulse spark over-voltage, residual or discharge voltage, maximum discharge current, etc. Selection of LA Here we are selecting an appropriate rating of lightning arresters for the substation. For the protection of substation above 66kV, an arrester of 10kA rating is used. Voltage rating of LA = Line to line voltage × 1.1 × coefficient of earthing. Power frequency spark over voltage = 1.5 ×Voltage rating of LA (Assuming the coefficient of earthing equals 0.8 for the effectively earthed system) For 220KV side: Voltage rating = 1.1 × 220 × 0.8 = 193.6KV Power frequency spark over voltage = 1.5 ×193.6 = 290.4KV Rated discharge current = 10 kA For 110KV side: Voltage rating = 1.1 × 110×0.8 = 96.8KV Power frequency spark over voltage = 1.5 × 96.8 = 145.2KV Rated discharge current = 10kA For 66kV Side Voltage rating = 1.1 × 66×0.8 = 58.08kV Power frequency spark over voltage = 1.5 × 58.08 = 87.12kV Rated discharge current = 10kA For 11 KV side: Voltage rating = 1.1× 11×0.8 = 9.68KV Power frequency spark over voltage = 1.5×9.68 = 14.52KV Nominal discharge current = 5kA https://www.nemaarresters.org/understanding-arrester-datasheet/