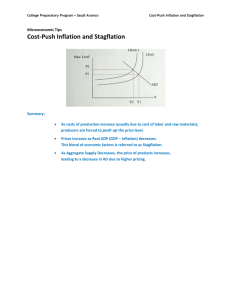
Brazilian stagflation Executive summery This report is designed to look into Brazilian Stagflation which is to be based specifically on rising inflation and unemployment in Brazil in the year 2015. The author is also going to investigate on how the Central Bank of Brazil approached the problem. The author is to make recommendation concerning to why Tombini need to keep on raising interest rates or why should Contents is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m not. Introduction.................................................................................................................................................1 Background.................................................................................................................................................2 Definition of the word stagflation............................................................................................................2 Discussion...................................................................................................................................................3 Political factor.........................................................................................................................................3 High interest rate effects on Brazil’s economy........................................................................................4 Negative effects of imposing high interest rate........................................................................................5 Fiscal crisis..............................................................................................................................................5 The Alexandre Tombini impact on Brazil economy..............................................................................6 Conclusion and recommendation................................................................................................................7 Th List of references.....................................................................................................................................9 Introduction sh In July 2015, it was reported that Alexandre Tombini who was by then the Governor of the Brazil central Bank encountered economic hardship known as Stagflation. At this economic difficulty situation Brazil inflation doubled above the estimated inflation of 4.5% whereas at the same period unemployment rose from 4.5% to 10%. This means that the Central Bank Governor 1 This study source was downloaded by 100000804325520 from CourseHero.com on 05-23-2021 23:03:33 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/49583477/Brazilian-stagflationdocx/ Brazilian stagflation (Alexandre Tombini ), was to take an immediate action towards reducing or curbing this inflation and the alarming increase of unemployment rate in the country . To control this alarming inflation and unemployment increments, Alexandre Tombini found himself in a dilemma due to the reason that he lacked administrative independent. Background is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m Definition of the word stagflation Economically, stagflation is also known as recession inflation. This economic condition, involves a situation in which the inflation rate of a country is high while the economic growth rate of that country is slow and when the rate of unemployment is also high,( Knotek, E. and Khan, S. 2014). This type of economic period, for example what happened to Brazil economy in the year 2015, there was a decline in gross domestic product (GDP). This condition is caused by cost-push inflation particularly when some force in the economy increases the costs of production. For example The Central Bank or the government in a country decide to expand the money supply and at the same time constraint supply. Th If stagflation hit an economy such as Brazil condition in 2015, Government decide to cut taxes, increase its spending or undertake both measure at the same time. To control the sh stagflation in Brazil, Alexandre Tombini who was by then the Governor of the Brazil central Bank; was to quickly make short term decision on raising interest rates which could increase the value of money . What is reported as the root cause and major contributing factor to costpush inflation in Brazil was its administration approach to devaluate its currency that led to 2 This study source was downloaded by 100000804325520 from CourseHero.com on 05-23-2021 23:03:33 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/49583477/Brazilian-stagflationdocx/ Brazilian stagflation Brazil increased on costs of production and also consumer prices,( Anon, 2019). At that particular period investors hoped that the government could have advised the control bank to lower its interest rate in which could have reduced the government borrowing costs but lowering interest rate means lowering value for money hence sky rocket the inflation further. The stagflation that hit Brazil in the year 2015 is said to be as a results of forces outside Alexandre Tombini control, major projects were run by the state such oil company petrobras which mean that Tombini could not make critical decisions independently without consulting is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m state executives who are portrayed as incompetence and practicing corruption to its finest. The immediate president at that period (president Rousef wanted Tombini the Central Bank Governor to undertake expansionary fiscal policy as the measure to curb stagflation. This could have contributed to Brazil debt to increase which in long-run could have found Brazil economy at difficulty financial crisis although in short-run could be the suitable approach to improve on employment and economic growth but Tombini was for raising interest rate,(Moreira, R. 2016). Despite that, Tombini as the Central Bank Governor went ahead and raised the interest rate which resulted to increase in unemployment as well as accelerate the Brazil economic slowdown in the country but reduced inflation in the country. Th Discussion Political factor sh It was well portrayed from the case study that political paralysis has contributed much for Brazil loyal and competence leaders like Tombini efforts to control Brazil economic problems which includes handling stagflation and the country deficit budget of 10.8 % of the Brazil GDP. 3 This study source was downloaded by 100000804325520 from CourseHero.com on 05-23-2021 23:03:33 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/49583477/Brazilian-stagflationdocx/ is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m Brazilian stagflation In this report, the Brazil president Dilemma Roussef , is practicing accounting irregularities for her popularity among her support to keep up hence she is not ready to cut the country spending or raise interest rate but keep the interest rate low which will benefit the country for a short period and after results to the cost of double digit inflation that may worsen the Brazil economy than ever. Th High interest rate effects on Brazil’s economy sh Tombinis approach to handle stagflation seems to favour imposing high interest rate as the suitable method to curb inflation in Brazil. The policy keeps inflation in check but on the other hand imposing high interest rate in the country will hamper businesses at large and as a results leads to an employment increase,( Kamal, M. 2019). Therefore, Brazil will face economic 4 This study source was downloaded by 100000804325520 from CourseHero.com on 05-23-2021 23:03:33 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/49583477/Brazilian-stagflationdocx/ Brazilian stagflation slowdown which may leads to financial and social problems in the short run but in the long-run Brazil economy will enjoy increase value for money that will help to maintain inflation stability and economic growth as well. Negative effects of imposing high interest rate It is worth noting that , Timbini as the central governor has taken the right turn although implementation of raising interest rate may not be enough to correct the mistake of the past in competencies done by president Roussef and her executives .therefore, Imposing high interest is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m rate to the Brazilian economy resulted to slower investment, lower also consumer spending in the economy increase Brazil government financing costs and also lower tax revenue. Brazil lowing interest rate as per Roussef administration point of view is to sunk the country into a burden of debt which will further make it unable to execute its local development projects and cater for its households social needs such as providing for good healthcare, education and infrastructural development. In addition , Brazil need to address the issues to do with high cost of doing business so as to encourage foreign investors to invest and as a results this economy will be in a better position to create more jobs for its citizen rather than relies heavily on import substitution for it to achieve its economic growth,( TERZİ, H. and Th TÜTÜNCÜ, A. 2017). Conclusion and recommendation. sh It can be concluded that Brazil stagflation that hit this economy was due to incompetence of the ruling government and its executive failure to address financial crisis in Brazil as well as state official’s involvement to state businesses rather than creating an independent body to deal with economic matters in the country. Brazil economy at this time 5 This study source was downloaded by 100000804325520 from CourseHero.com on 05-23-2021 23:03:33 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/49583477/Brazilian-stagflationdocx/ Brazilian stagflation needed a quick response to address alarming inflation and unemployment which was worsens the economic growth. Roussef who was the seating president was in dilemma on what to do to ensure peace, employment restoration, and stabilize inflation that was rising at alarming rate. The appointment of Alexandre Tombini as the Brazil central Governor , made Roussef feel relieved but the two could not agree on the control policy to stabilize the Brazil economy. Roussef was for contraction fiscal policy while Tombini was for expansionary fiscal policy. Furthermore, Tombini faced a more challenge to implement his policy to stabilize inflation is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m because state was in control of state companies and the central bank in Brazil was not an independent body therefore, there he had to be face difficulties dealing with Roussef administrative procedural. Lowering interest rate seems to be suitable for short-run solution to improve economic growth of Brazil and promote employment but would bring in a negative impact on over burden the country to huge debts and in the long run inflation will rise significantly beyond control. Therefore, Tombini reject that ideology and went ahead to raise interest rate that seems to slowdown growth and increase unemployment in the short-run but will significant curb inflation . Government need to address cost of doing business in this country as the interest rate will be passed to consumers where in the long run stabilize the economy because investors will be Th encouraged to invest more in Brazil if the business environment will be favourable. As a results employment will be created and revenue will increase to both government and the households. sh Finally, the Brazil government is required to continue raising interest rate as the policy to control inflation but Brazil Government will be recommended to cut red tape as well as lower costs of doing business in the country. The reason being is that the cost to be reduced can be passed on to consumers and thereafter reduce inflation in the country. 6 This study source was downloaded by 100000804325520 from CourseHero.com on 05-23-2021 23:03:33 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/49583477/Brazilian-stagflationdocx/ Brazilian stagflation List of references Anon, (2019). [online] Available at: https://brainly.com/question/2881486 [Accessed 14 Sep. 2019]. is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m Knotek, E. and Khan, S. (2014). Drifting Inflation Targets and Monetary Stagflation. SSRN Electronic Journal. Moreira, R. (2016). Measuring the Monetary Policy’s Structural Credibility by the Expected Inflation Determinants: a Kalman Filter Approach for Brazil. Brazilian Review of Econometrics, 99(99). Kamal, M. (2019). Economics - VU. [online] Issuu. Available at: https://issuu.com/munir/docs/toc_of_eco401_-_introduction_to.pdf [Accessed 14 Sep. 2019]. TERZİ, H. and TÜTÜNCÜ, A. (2017). Examination of the Relationship between Producer Price Index and Consumer Price Index: ARDL Bounds Testing Approach. Sosyoekonomi, pp.173-186. Th Paulo Travisani, (2015). Brazil’s Tombini Reinforces Inflation –Target pledge; The Wall Street 1442330701 sh Journal : https://www.wsj.com/articles/brazils-tombini-reinforces-inflation-target-pledge- 7 This study source was downloaded by 100000804325520 from CourseHero.com on 05-23-2021 23:03:33 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/49583477/Brazilian-stagflationdocx/ Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)