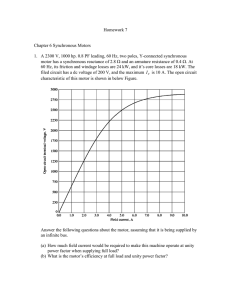
B. Tech II Year II Semester 18EEE107 INDUCTION AND SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES Course Prerequisite: 18EEE101, 18PHY102 L T P C 3 0 0 3 Course Description: This course is designed to obtain thorough knowledge on AC machinery fundamentals, machine parts, operation of Single phase and Three phase AC machines. The course also equips students with ability to understand and analyse the phasor diagrams and equivalent circuits of AC Induction and Synchronous Machines. Course covers Theory, performance, testing, applications and control of electromechanical energy converters like Induction machines, synchronous machines. To have hands-on experience by testing Single phase, three phase Induction motor and synchronous machines to evaluate their performance. Course Objectives: 1. To emphasize the basic concepts of AC rotating machines. 2. To deal with the detailed analysis of Synchronous generators and motors. 3. To introduce the concept of parallel operation of synchronous generators. 4. To deal with the detailed analysis of polyphase induction motors. 5. To understand operation, construction and types of single phase motors and their applications in house hold appliances and control systems. UNIT I: FUNDAMENTALS OF AC MACHINE WINDINGS Physical arrangement of windings in stator and cylindrical rotor; slots for windings; single turn coil active portion and overhang; full-pitch coils, concentrated winding, distributed winding, winding axis, Rotating Magnetic field: Windings spatially shifted by 90 degrees, Addition of pulsating magnetic fields, three windings spatially shifted by 120 degrees (carrying three-phase balanced currents), revolving magnetic field. (9) UNIT II: SYNCHRONOUS GENERATOR EMF equation, equivalent circuit and phasor diagram, armature reaction, synchronous impedance, voltage regulation by synchronous impedance method, M.M.F. method, Parallel operation of alternators - synchronization and load division, control of P and Q outputs - operating chart for synchronous machine. Salient pole machine - two reaction theory, Synchronous Condenser. (9) UNIT III: SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR Principle of operation - different starting methods- equivalent circuit - effect of load changes on synchronous motor - mechanical load diagram - armature current as function of power developed and excitation - V curves - inverted V curves - transition of a machine from generator mode to motor mode - phasor diagram - torque and power relations - hunting - periodicity of hunting - suppression. (9) UNIT IV: INDUCTION MOTORS Construction, Types (squirrel cage and slip-ring), Torque Slip Characteristics, Starting and Maximum Torque. Equivalent circuit, Circle diagram, Phasor Diagram, Losses and Efficiency. Effect of parameter variation on torque speed characteristics (variation of rotor and stator resistances, stator voltage, frequency). Methods of starting, braking and speed control for induction motors. Induction Generator operation. (9) UNIT V: FRACTIONAL HORSE POWER MACHINES Constructional features, double revolving field theory, equivalent circuit, determination of parameters. Split-phase starting methods and applications, Introduction to BLDC, SRM, Stepper Motors. (9) Course Outcomes: At the end of this course, students will demonstrate the ability to 1. Understand the operating principles of different ac machines. 2. Understand the design of stator and rotor of ac machines. 3. Demonstrate practical testing of different ac machines. 4. Inference the theory of single phase induction motor. 5. Evaluate the performance of Three phase, Single phase Induction motor and synchronous motor. Text Books: 1. E. Fitzgerald and C. Kingsley, "Electric Machinery”, McGraw Hill Education, 2013. 2. M. G. Say, “Performance and design of AC machines”, CBS Publishers, 2002. 3. P. S. Bimbhra, “Electrical Machinery”, Khanna Publishers, 2011. 4. I. J. Nagrath and D. P. Kothari, “Electric Machines”, McGraw Hill Education, 2010. References: 1. S. Langsdorf, “Alternating current machines”, McGraw Hill Education, 1984. 2. P. C. Sen, “Principles of Electric Machines and Power Electronics”, John Wiley & Sons, 2007. 3. E.G. Janardanan, ‘Special electrical machines’, PHI learning Private Limited, Delhi, 2014. 4. K. Venkataratnam, ‘Special Electrical Machines’, Universities Press (India) Private Limited, 2008. Mode of Evaluation: Assignment, Written Examination