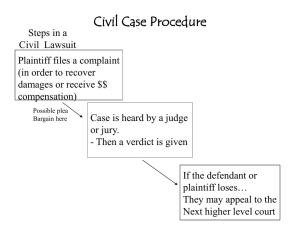
Units 1-3 Court of General Jurisdiction Circuit Court Civil and Criminal Over 25k and Felonies Court of Limited Jurisdiction District, Probate, Small Claims Court Lower amount of money, misdemeanors, and preliminary hearings Court of Equity Actions where remedy is not monetary (compare court of law) Federal Diversity Federal Question Special Statute conferring jurisdiction Supplemental jurisdiction [28 USC 1367] Michigan Supreme Court and Court of Appeals Circuit Court (Incl. Probate & Family Division) District Court Court of Claims – claims against state and agencies Only in Federal Courts Exists when plaintiff & defendant are from different states Or one party is a foreign citizen Must be complete diversity-every plaintiff and defendant must be of separate states And the amount in controversy exceeds 75k Courts power over a person Person/property must be within the jurisdiction of the court Long Arm Statutes-when defendant is not in state Domicile Incorporated Continuous & systematic part of general business Consent In rem-rights of all persons to specific property Quasi in rem-rights of specific person and specific property Summons Complaint-essential elements of claim/defense Answer Reply Amendment Counter Claim-defendant claim against plaintiff Affirmative Defenses Compulsory & Permissive (MI = permissive) Cross Claim-defendant claim against co-defendant Non-compulsory Special type of joinder 3rd party (stakeholder) holds property subject to conflicting claims by multiple parties Used to avoid double liability by bringing all parties together in a single action Generally deposit the property (stake) with the court until rights are determined Once deposited with the court, no longer liable Lack of personal jurisdiction Lack of subject matter jurisdiction Service of process was insufficient Party lacks legal capacity to sue The claim is barred because of release, payment, prior judgment, immunity granted by law, statute of limitations, statute of frauds, an agreement to arbitrate, infancy or other disability of the moving party, or assignment or other disposition of the claim before commencement of the action. Opposing party has failed to state a claim on which relief can be granted Except as to the amount of damages, there is no genuine issue as to any material fact, and the moving party is entitled to judgment or partial judgment as a matter of law. Personal service – serve the person or authorized agent Service by mail Service by publication Federal – First class mail Michigan – Registered (certified) mail Defendant resides out of state Whereabouts of defendant & residence are unknown E-service Fax Proof of service - affidavit Failure to serve properly does not mean dismissal Numerousness – greater than 40 Common questions of law and fact Typicality – claims of rep must be typical of class Adequate Rep (lawyer) Meet Any of Rule 23(b) Separate actions yield inconsistent results Defendant has refused to act and injunctions or declatory relief is appropriate Common questions are predominant over individuals and class action is superior method FEDERAL Minimal diversity Amount in controversy exceeds $5 million Class has at least 100 members MICHIGAN Same as Fed except: Class action must be superior method Notice is required Class members must have ability to opt out Purpose is to make sure all parties are on same foot and to ensure fairness (No Surprises) Broad discovery rules and duty to supplement Initial disclosures Names of people who could have info, documents, computation of damages, Insurance info Methods Interrogatories Admissions Depositions Motion to dismiss Motion for summary judgment No genuine issue of material fact Motion to compel Any of the grounds of affirmative defenses Usually used to make party comply with discovery Show cause Somebody is in trouble!! Preponderance of the evidence Clear and convincing Most common in civil cases Least burden – prove by 51% Highest burden in civil cases usually parent termination proceedings Beyond a reasonable doubt Highest burden to meet Used in criminal cases only Jury Trial v Bench Trial Petit Jury (Trial jury) Bench – Judge sits as finder of fact and law – must give specific rulings Jury – Citizens sit as finders of fact (only) and verdict can be inconsistent Criminal-must waive right to jury Civil – must assert right or lose it Jury made up of the people 6-12 jurors plus 1-2 alternates Grand Jury-only for criminal and only to determine if enough to charge (closed hearings) Voir Dire – Picking of the jury (fair and impartial) Challenge for cause or peremptory challenges Subpoenas – method for getting people or exhibits for trial Exhibits – any document or object admitted into evidence (by judge) Direct Examination Ad testificandum v duces tecum Questions of a party’s own witness Open ended questions Cross Examination Questions of an opposing party or adverse witness Leading questions – questions that suggest an answer (yes or no) Broad scope or latitude during cross exam Directed Verdict JNOV Used to overturn a jury verdict If erroneously granted, can reinstate jury verdict instead of granting new trial Verdict against the evidence Generally after presenting party’s case in chief or before going to jury If after all evidence in, opposing party must prevail In the light most favorable to the nonmoving party If erroneously granted, must have new trial Used to overturn jury verdict also Judge is 13th Juror Sufficiency of Evidence Mistrial – stopping trial before verdict is reached Hung Jury Serious error that can’t be corrected by court INJUNCTION Prevent a wrong or injury Legal remedy is inadequate (damages) Property right is involved Enforcement is practical Hardship to def is not outweighed by benefit to plaintiff TRO Irreparable and immediate harm Done in emergency Has an expiration date Can be done ex parte Not favored by the courts Also called preliminary injunction UNIT 3 Arrest-detention of a person (custody) Arraignment-Start of judicial proceedings Indictment/Information-formal document of charges against a defendant GJ-Citizens determine probable cause PE-Judge determines probable cause Bail-determine if defendant should remain in jail or be released Grand Jury=Indictment Prosecutor=Information Grand Jury v Preliminary exam-determination of probable cause to see if defendant should proceed to trial Brought before judge, rights are read, and bail is set Judge determines if defendant is flight risk and/or danger to community Plea-plea guilty for lesser offense or lesser penalty Sentence-probation, parole, or incarceration 4th Amendment 5th Amendment-due process Right to be free from unreasonable search & seizure Warrant requirement-probable cause Terry Stop-stop & frisk (reasonable suspicion) Exclusionary rule-remedy for violating the 4th Amendment-suppress evidence which usually leads to dismissal Miranda-right to an attorney when being interrogated (custodial interrogation) 6th Amendment Right to Counsel-attaches at arraignment Speedy Trial-attaches at arrest Double Jeopardy-attaches at conviction Actus Reus-physical component Mens Rea-mental component Need both Actus Reus and Mens Rea to be charged with a crime Malice Does not mean ill will Depraved heart or depraved indifference Reckless disregard for the safety of others Felony-crime where imprisonment can exceed 1 year Misdemeanor-crime where imprisonment is 1 year or less Assault & Battery Arson Burglary-Home Invasion Bigamy Embezzlement Extortion Rape-Criminal Sexual Conduct Robbery Sodomy Homicide-killing of another Murder-1st and 2nd degree Issue is intent to kill Felony Murder-killing someone during the commission of a felony Felonies: Arson, Rape, Child abuse, Drug Delivery, Robbery, Carjacking, Breaking & Entering, Larceny, Extortion, Kidnapping, Vulnerable adult abuse, torture, and Aggravated stalking Accessory Manslaughter-killing in the heat of passion Same as aiding & abetting except in Mich In Mich-Accessory after the Fact-concealing or hiding the defendant Aiding & Abetting-encourages and assists in the commission of crime Conspiracy-Agreement to commit a crime Don’t actually have to commit the crime-agreement is enough Self-Defense Defendant must have an honest and reasonable belief of imminent danger Deadly force can only be used in response to deadly force Alibi Insanity Defendant did not appreciate his actions (impulsive) Cannot tell the difference between right and wrong Few mental diseases are recognized Very easy to be found legally sane