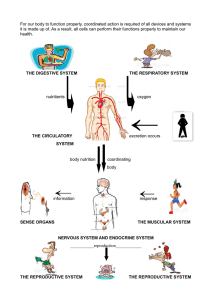
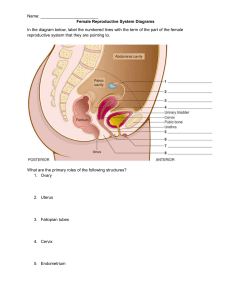
4.00 Understand the body’s hormone control systems. Objective 4.03 Understand the structures, functions, and disorders of the male and female reproductive systems. HU40 Health Science I Structures & Functions of the Female Reproductive System Structures of the female reproductive system HU40 Health Science I Structures of the female reproductive system • Ovary - Female gonad located in the pelvic cavity, about the size of an almond, the ovum is the largest cell in the human body • Ova – female gamete • Fallopian Tubes – oviduct or uterine tube, 4” long and is NOT attached to the ovaries HU40 Health Science I Structures of the female reproductive system Uterus – hollow pear-shaped thickwalled muscular organ located posterior to the urinary bladder and anterior to the rectum • Endometrium – inner lining of the uterus • Myometrium – muscular layer of the uterus • Perimetrium – visceral peritoneum, layer around the uterus 0 0 HU40 Health Science I Structures of the female reproductive system • Cervix – lower end of the uterus on top of the vagina and is about 1’ in length • Vagina – also called the birth canal, 10 cm long smooth muscle lined with a mucous membrane • Hymen – external opening of the vagina that may be covered by a perforated membrane 0 0 HU40 Health Science I Structures of the female reproductive system External genitalia - Vulva • Clitoris – erectile tissue • Labia – folds of skin surrounding the vagina • Labia majora - outer fatty folds • Labia minora – inner folds • Perineum - area between vagina and rectum Perineum HU40 Health Science I Structures of the female reproductive system • Mammary glands (breasts) – accessory organ that contains granular and adipose tissue • Stimulated by prolactin breasts are where the production of milk for the baby occurs • Areola – darkened area that surrounds the nipple • Nipple - center of breast HU40 Health Science I Functions of the female reproductive system Ovary – produces ova and female hormones • Hormones • Estrogen – Develops and maintains both the reproductive and female characteristics • Progesterone - Regulates condition of inner lining of the uterus, prepares this lining for the potential to accept a fertilized egg HU40 Health Science I Functions of the female reproductive system • Fallopian tubes – Serves as the passageway for the ova to travel to the uterus every month, fertilization usually occurs in the fallopian tubes • Uterus – Expands to hold the growing fetus • Cervix – allows for flow of menstrual blood to exit, allows for entrance of sperm HU40 Health Science I Functions of the female reproductive system Vagina • Serves as a conduit for menstrual flow • Allows for penis during sexual intercourse • Serves as a passageway for a baby during the birth process HU40 Health Science I Functions of the female reproductive system Mons Pubis External genitalia (vulva) serves to protect the internal reproductive organs • Mons pubis is covered with hair and lies over the symphysis pubis • Clitoris contain nerve endings • Perineum separates the vagina and the rectum Perineum HU40 Health Science I Functions of the female reproductive system Mammary glands (breasts) • Accessory organs • Stimulated by prolactin breasts are where the production of milk for the baby occurs HU40 Health Science I Functions of the female reproductive system Menstrual Cycle • First cycle in females is referred to as menarche • Counted from day one of menstruation to the next first day of menstruation • Averages 28 days with four stages • • • • Follicle stage Ovulation stage Corpus luteum stage Menstruation stage HU40 Health Science I Functions of the female reproductive system Follicle stage • Lasts about 10 days • The pituitary releases follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) • FSH stimulates the follicle and ovum to mature • Results in the release of estrogen and preparation of the uterine lining HU40 Health Science I Functions of the female reproductive system Ovulation stage • Pituitary stops producing FSH and starts producing Luteinizing hormone(LH) • LH, FSH and estrogen are now all three circulating • Around day 14, the follicle ruptures and the ovum is released which is referred to as ovulation HU40 Health Science I Functions of the female reproductive system Corpus luteum stage (luteal phase) • Progesterone is secreted and if the egg is fertilized, the hormone will continue to be secreted • The uterine lining is maintained and further ovulation is prevented • Lasts about 14 days HU40 Health Science I Functions of the female reproductive system Menstruation stage • Occurs when the unfertilized ovum is discharged as well as degenerated endometrium if pregnancy has not occurred • Progesterone secretion is diminished • The uterine lining is discharged over about six days HU40 Health Science I Functions of the female reproductive system • Conception – occurs when sperm travels up through the vaginal canal, into the uterus and then fertilizes an egg if found in the fallopian tubes • Pregnancy – Sperm and egg join to form a fertilized egg and then three to four days later the fertilized egg implants itself in the lining of the uterus HU40 Health Science I Functions of the female reproductive system Menopause – when the menstrual cycle ends and usually occurs between the ages of 45-55, may also occur with the removal of the ovaries (oophorectomy) HU40 Health Science I Disorders of the Female Reproductive System Disorders of the female reproductive system Cervical cancer • Change in cells in the cervix • Usually caused by sexual transmission with Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) • Slow growing so is usually detected early by pap smears • Surgery and radiation are most common treatments • Gardasil vaccine helps protect individuals ages 9 to 45 against the following diseases caused by 9 types of HPV: cervical, vaginal, and vulvar cancers in females, anal cancer, certain head and neck cancers, such as throat and back of mouth cancers HU40 Health Science I Disorders of the female reproductive system Endometriosis • Endometrial tissue grows in other places outside of the uterus leaving no way for the lining to leave the body • Symptoms include sever cramps, heavy menstruation, pain during or after intercourse, • Treatments include pain management, hormone birth control for heavy menstruation, surgical removal of tissue HU40 Health Science I Disorders of the female reproductive system Pelvic Inflammatory Disease • Infection of the reproductive organs including the uterus, fallopian tubes and cervix • Most often caused by sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia or gonorrhea • Treated with antibiotics and pain medications • Scarring of the fallopian tubes is possible HU40 Health Science I Disorders of the female reproductive system Toxic Shock Syndrome • Overgrowth of Staphylococcus aureus (staph) bacteria in a woman’s body • Typically affects menstruating women and usually those that use super-absorbent tampons • Symptoms include hypotension, high fever, vomiting and respiratory distress • Treatment is hospitalization and antibiotics HU40 Health Science I Disorders of the female reproductive system Yeast Infections • Overgrowth of candida in the vaginal area • Occurs when environment of vagina becomes less acidic and is often after use of antibiotics • Symptoms include burning, redness and swelling of the vagina and vulva; pain and burning with urination; and a thick white odorless discharge • Treatment includes antifungal creams or ointments and possibly oral medications HU40 Health Science I Disorders of the female reproductive system • Menstrual cycle disorders • Amenorrhea is the absence or menstruation, missing at least three menstrual periods in a row • Dysmenorrhea is menstrual cramps • Menorrhagia is heavy or prolonged bleeding with menstrual periods • Premenstrual syndrome • Symptoms of headaches, bloating and mood changes one to two weeks before menstruation • Other symptoms include craving and acne • Possibly caused by changes in hormone levels HU40 Health Science I Disorders of the female reproductive system • Breast cancer • Cancer that forms in the cells of the breast and is most common cancer in women • May also occur in men • Signs and symptoms are breast lump, change in size or appearance of breast, newly inverted nipple, redness or pitting of the breast • Becoming aware of your breast through self breast exams allows for early detection • Mastitis • • • • Inflammation of breast tissue often involving an infection Most common in breast feeding mothers Symptoms include breast tenderness and warmth, pain during Breast feeding, general illness with fever HU40 Health Science I