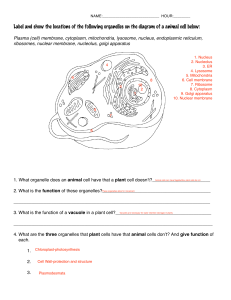
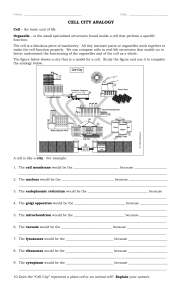
7 SCIENCE Second Quarter – Module 3 Cell: The Basic Structural and Functional Unit of Life Department of Education ● Republic of the Philippines _ Science – Grade 7 Alternative Delivery Mode Second Quarter – Module 3: Cell: The Basic Structural and Functional Unit of Life First Edition, 2020 Republic Act 8293, Section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or office wherein the work is created shall be necessary for exploitation of such work for profit. Such agency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of royalties. Borrowed materials (i.e., songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand names, trademarks, etc.) included in this module are owned by their respective copyright holders. Every effort has been exerted to locate and seek permission to use these materials from their respective copyright owners. The publisher and authors do not represent nor claim ownership over them. Published by the Department of Education – Region 10 Regional Director: Dr. Arturo B. Bayocot, CESO III Assistant Regional Director: Dr. Victor G. De Gracia Jr., CESO V Development Team of the Module Author/s: Myla M. Guillena Shalome H. Balignot Reviewers: Marecel B. Compania Ivan M. Guillena Corason A. Baluyos Evaluators: Marisol P. Moreno Marissa M. Olarte Michelle S. Balat Grace Marie S. Doong Jessah Mae M. Luza Vincent M. Millante Ferdinand Bonito L. Taclob Jr. Illustrators: Ivan M. Guillena Fritz E. Balignot Management Team Chairperson: Dr. Arturo B. Bayocot, CESO III Regional Director Co-Chairpersons: Dr. Victor G. De Gracia Jr. CESO V Asst. Regional Director Edwin R. Maribojoc, EdD, CESO VI Schools Division Superintendent Myra P. Mebato,PhD, CESE Assistant Schools Division Superintendent Mala Epra B. Magnaong, Chief ES, CLMD Members Neil A. Improgo, EPS-LRMS Bienvenido U. Tagolimot, Jr., EPS-ADM Samuel C. Silacan, EdD, CID Chief Marites A. Caguindangan, EPS - Science Rone Ray M. Portacion, EdD, EPS – LRMS Asela I. Elumbareng, DM, PSDS Nelia T. Lanzaderas, PhD, Principal III/District In-charge Agnes P. Gonzales, PDO II Vilma M. Inso, Librarian II Printed in the Philippine by Department of Education – Region 10 Office Address: Zone 1, DepEd Building, Masterson Avenue, Upper Balulang Cagayan de Oro City 2 Contact Number: (088) 880 - 7072 E-mail Address: region10@deped.gov.ph e 7 Scienc 7 Quarter 2 – Module 3 Cell: The Basic Structural and Functional Unit of Life This instructional material is collaboratively developed and reviewed by educators from public schools. We encourage teachers and other education stakeholders to email their feedback, comments, and recommendations to the Department of Education- Region X at region10@deped.gov.ph. Your feedback and recommendations are highly valued. Department of Education ● Republic of the Philippines FAIR USE AND CONTENT DISCLAIMER: This SLM (Self Learning Module) is for educational purposes only. Borrowed materials (i.e songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand names, trademarks, etc.) included in these modules are owned by their respective copyright holders. The publisher and authors do not represent nor claim ownership over them. Sincerest appreciation to those who have made significant contributions to these modules. 3 Introductory Message For the learner: Welcome to the Science 7 Alternative Delivery Mode (ADM) Module 3A: Cell Parts and Their Functions! Learning Biology is fun. You will learn more facts, adventures, and a lot of knowledge on all living things. Did you know that the study of cells is known as Cytology? Cytology is a branch of Biology that deals with the foundation of life, which is the cell. Brace yourself, because you are just about to learn the basic unit of life! This module will expand your views on the beauty of life. Read thoroughly each part of this module, so you will fully understand and appreciate the existence of life. This module has the following parts and corresponding icons: This gives you an idea of the skills or in the module. What I Need to Know This part includes an activity that aims to check what you already know about the What I Know lesson to take. If you get all the answers competencies you are expected to learn correct (100%), you may decide to skip this module. What’s InThis is a brief drill or review to help you link the current lesson with the previous one. What’s NewIn this portion, the new lesson will be introduced to you in various ways such as a story, a song, a poem, a problem opener, an activity, or a situation. What is ItThis section provides a brief discussion of the lesson. This aims to help you discover and understand new concepts and skills. iv 4 What’s MoreThis comprises activities for independent practice to solidify your understanding and skills of the topic. You may check the answers to the exercises using the Answer Key at the end of the module. What I Have LearnedThis includes questions or blank sentences/paragraphs to be filled in to process what you learned from the lesson. What I Can DoThis section provides an activity which will help you transfer your new knowledge or skill to real life situations or concerns. AssessmentThis is a task which aims to evaluate your level of mastery in achieving the learning competency. Additional ActivitiesIn this portion, another activity will be given to you to enrich your knowledge or skill of the lesson learned. This also tends retention of learned concepts. Answer KeyThis contains answers to all activities in the module. 5 At the end of this module you will also find: ReferencesThis is a list of all sources used in developing this module. The following are some reminders in using this module: 1. Use the module with care. Do not put unnecessary mark/s on any part of the module. Use your science activity notebook in answering the exercises. 2. Don’t forget to answer What I Know before moving on to the other activities included in the module. 3. Read the instruction carefully before doing each task. 4. Observe honesty and integrity in doing the tasks and checking your answers. 5. Finish the task at hand before proceeding to the next. 6. Return this module to your teacher/facilitator once you are through with it. If you encounter any difficulty in answering the tasks in this module, do not hesitate to consult your teacher or facilitator. Always bear in mind that you are not alone. We hope that through this material, you will experience meaningful learning and gain a deep understanding of the relevant competencies. You can do it! vi 6 Table of Contents What I Need to Know - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1 What I Know - - - - - - ---------2 Lesson 1 Cell Parts and their Functions What’s In - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4 What’s New - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5 What is It - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 6 What’s More - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 10 Lesson 2 The Plant Cell What’s In - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 11 What’s New - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 12 What is It - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 13 What’s More - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 14 Lesson 3 The Animal Cell What’s In - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 15 What’s New - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 16 What is It - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 17 What’s More - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 18 Lesson 4 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells What’s In - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 19 What’s New - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 20 What is It - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 20 What’s More - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 22 What I Have Learned - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 23 What I Can Do - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 25 Assessment - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 26 Additional Activities - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 28 Answer Key - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 29 References - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -3 vii 7 What I Need to Know Life comes from life. Have you ever wondered what your body is made up of? Or how your body maintains, adapts, and changes through time? How about animals and plants? Have you ever wondered what comprises the internal structures of plants and animals? In this module, you are going to learn the “unseen workers” within a human’s body and what makes up the marvellous structures of plants and animal. This module consists of four (4) lessons: ∙ Lesson 1 - Cell Parts and Their Functions ∙ Lesson 2 - The Plant Cell ∙ Lesson 3 - The Animal Cell ∙ Lesson 4 - Comparing Plant and Animal Cell After going through this module, you are expected to: 1. differentiate plant and animal cells according to the presence or absence of certain organelles (S7LT-IIc-3); and 2. explain why the cell is considered the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms (S7LT-IIe-5) Enjoy reading the module and have fun accomplishing all the activities prepared for you! 1 What I Know I. Multiple Choice: Read each question carefully and choose the best answer from the given choices A to D. Write the letter of your answer in your Science activity notebook. 1. Which of the following statements is TRUE? A. All cells have cell wall. C. All cells contain chloroplast. B. All cells contain centriole. D. All cells have cell membrane. 2. Why are lysosomes considered as the “cleaners” of the cell? A. Lysosomes digest damage cell parts. B. Lysosomes support and protect the cell. C. Lysosomes pump materials that enter the cell. D. Lysosomes transport materials from one cell to another. 3. Which part of the cell controls the “entry and exit” of materials? A. Cell membrane C. Endoplasmic Reticulum B. Cell wall D. Golgi bodies 4. Mitochondria are organelles that produce energy for the cell. Which part of the body has many mitochondria? A. Hair C. Nails B. Heart D. Nose 5. Which organelle packages and sorts the product of the cell? A. Cell Wall C. Chloroplast B. Cell Membrane D. Golgi Bodies 6. Which organelle serves as the “brain” of the cell? A. Cell Membrane C. Lysosome B. Cytoplasm D. Nucleus 7. What is the function of chloroplasts in plants? A. Enable the plant to make their own food B. Make the plants rigid and rectangular in shape C. Give the plants energy needed to make food D. Store food, water, and waste products of the plants 2 II. Identification: Label the parts of the animal and plant cells using the word/s found in the box below. WORD BANK Cell Membrane Lysosomes Nucleolus Cell Wall Vacuole Nucleus Chloroplast Mitochondrion Cytoplasm Ribosomes Centriole Golgi Body 8 9 12 2 13 3 14 4 10 0 15 5 11 1 The Plant Cell The Animal Cell 3 Lesson 1Cell Parts and Their Functions In the previous lesson, you have learned that all living things possess a unique and complex biological organization arranged in ascending order from cell to biosphere. Answer Activity 1 to refresh your knowledge about the levels of biological organization. What’s In Activity 1: Fill Me! Directions: Copy the inverted pyramid in your Science activity notebook. Place the words in the inverted pyramid according to the correct order (from simple to complex) of the levels of biological organization. COMMUNITY POPULATION ECOSYSTEM ORGAN SYSTEM BIOSPHERE CELL ORGANISM ORGANS TISSUES complex simple Figure 1. Levels of Biological Organization Figure 1. Levels of Biological 4 What’s New Activity 2: Try Me! Directions: Try this at home following the steps shown in Figure 2 below. Step 1: Fill in a clear, small plastic bottle with water about one fourth (¼) of its container. Step 2: Pour in a few powdered soap or detergent. Step 3: Shake the bottle. Step 4: Observe the bubbles formed inside the bottle The plastic bottle represents the organism and the bubbles inside represents the cells. As you have observed, the bubbles stick together side by side. Cells of all living things are like this. They grouped together to form an organism. Figure 2. Plastic Bottle with Soap Bubbles The plastic bottle represents the organism and the bubbles inside it represent the cells. As you have observed, the bubbles stick together side by side. Cells of all living things are like this. They are arranged side by side and grouped together to form tissues, tissues into organs, organs into organ systems, and organ systems into organisms. Warning: DO NOT DRINK THE CONTENTS OF THE BOTTLE. 5 What is It Cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. It is the structural unit of life because the entire body of an organism is made up of cells which provide structure for the body. The cell is also known as the functional unit of life because it regulates all the functions, like taking in of nutrients from food, converting food into energy and carrying out specialized functions inside an organism. When Robert Hooke carefully examined a very thin slice of cork, he thought the close-up view resembled small, empty rooms. He referred these tiny rooms as cells (from the Latin word Cellulae, which means “small rooms”). A cell is made up of tiny organs called organelles that perform specific functions. These are called organelles because these are like “little organs” that has their own function. In this lesson, you are going to study the different cell organelles which are found in a cell and their corresponding functions. Table 1. Cell Organelles and Their Functions CELL ORGANELLE FUNCTION NUCLEUS ∙ houses DNA (the hereditary material) as well as various proteins including the nucleolus ∙ considered as “brain” of the cell because it controls all its activities Source:https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-cell differentiation-process-importance-examples.html Source: https://study.com/academy/lesson/mitochondrion definition-function-structure.html Plural: Mitochondria ∙ one of the largest organelles within a cell ∙ also known as the “powerhouse” of the cell ∙ it is where the energy of the cell, the ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate), is produced MITOCHONDRION 6 within the cell Ribosomes RIBOSOMES ∙ dot-like organelles that contain RNA and specific proteins within the cytoplasm ∙ manufacture proteins Source: https://www.genome.gov/genetics glossary/Endoplasmic-Reticulum-rough Source: https://joshandkarlasproject.weebly.com/nucleolus nucleous-ribosomes-and-vacuole.html ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM antibodies and insulin ∙ transportation channel of produced proteins in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum ∙ site of protein synthesis in the cell has no ribosome on its surface ∙ smoother in appearance as compared to the rough ER ∙ involved in the synthesis of lipids (e.g. phospholipids) and carbohydrates that are used to build the cell membrane ∙ also involved in the transportation of vesicles, enzyme production in the liver, contraction of muscle cells in the muscles, and synthesis of hormones in the brain cells Source: https://www.genome.gov/genetics glossary/Endoplasmic-Reticulum-Smooth GOLGI BODIES/ GOLGI APPARATUS Source: https://www.dreamstime.com/structure-golgiapparatus animal-plant-cell-major-organelle-most-eukarytoiccells image137227168 ∙ has ribosomes attached to its surface ∙ involved in the production of ∙ responsible for transporting, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids into vesicles for delivery to targeted destinations ∙ located in the cytoplasm next to the endoplasmic reticulum and near the cell nucleus ∙ many types of cells contain only one or several Golgi apparatus such as plant cells that can contain hundreds 7 LYSOSOMES CELL/PLASMA MEMBRANE Source: https://microbenotes.com/lysosomes-structure enzymes-types-functions/ Source: https://www.timvandevall.com/science/plant-cell diagram/ VACUOLES Source: https://sites.google.com/site/kmhvacuole/ CYTOPLASM ∙ plant cells contain large vacuoles that occupies 50% of its volume ∙ encloses the contents of the cell ∙ is like a fence or a gatekeeper that protects the cell from the outside environment ∙ controls what materials can go in and out of the cell ∙ made up of two layers of phospholipids (phospholipids bilayer) Source: www.clker.com/clipart-animal-cell.html. ∙ act as the waste disposal system of the cell by digesting obsolete or unused materials in the cytoplasm, from both inside and outside the cell ∙ the “cleaners” of the cell ∙ rarely seen in plant cell ∙ a space inside the cell that does not contain cytoplasm, surrounded by a membrane and filled with fluid which stores food and water materials for the cell ∙ is a jelly-like fluid where organelles are located 8 CELL WALL Source: https://www.thoughtco.com/cell-wall 373613. CHLOROPLAST Source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zpt_0lvwXbc CENTRIOLE ∙ contains pigments such as chlorophyll is needed for photosynthesis and gives plants its green appearance Source: https://www.genome.gov/sites/default/files/tg/en/illustra which tion/ centriole.jpg ∙ adds covering for which provides support, protection and shape to the cell ∙ tube-like structure that aid in cell division; responsible for separating the chromosomes during animal cell division 9 What’s More Activity 3: What am I? Directions: Answer the two (2) sets of activities below. Write your answer in your Science activity notebook. 1. Guess the Riddle! What is present in a CALL but not in a BALL; It is present in a WELL but not in a WALL; And is mostly seen twice in ALL. Answer: ________________ 2. Explain this statement: Why is the cell considered as the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms? Answer: ____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 10 Lesso n The Plant Cell 2 What’s In In our previous lesson, you have learned that cells have so many workers, the cell organelles, that work together to carry out life functions. In this module, you will learn the significant organelles that can only be found in a plant cell. Enjoy this lesson and have fun while discovering amazing facts about plant cell. Activity 1: Word Hunt Directions: Form a word out of the given number in sequence based on the numbers corresponding to the letters in the alphabet inside the box below. A description of the organelle is already provided for you to easily come up with the name of the organelles asked. Write your answer in your Science activity notebook. A – 1 B – 2 C – 3 D – 4 E – 5 F – 6 G – 7 H – 8 I – 9 J – 10 K – 11 L – 12 M – 13 N – 14 O – 15 P – 16 Q – 17 R – 18 S – 19 T – 20 U – 21 V – 22 W – 23 X – 24 Y – 25 Z – 26 Example: Description: The basic unit of life. Example: 3 – 5 – 12 – 12 Answer: CELL 1. Description: Controls the activities of the cell. Code: 14 – 21 – 3 – 12 – 5 – 21 – 19 Answer: _________________________ 11 2. Description: Gives the cell its shape. Code: 3 – 5 – 12 – 12 13 – 5 – 13 – 2 – 18 – 1 – 14 – 5 Answer: ____________ __________________________ 3. Description: Jellylike fluid where the organelles are located. Code: 3 – 25 – 20 – 15 – 16 – 12 – 1 – 19 – 13 Answer: ________________________________ 4. Description: Manufacturer of proteins within the cell. Code: 18 – 9 – 2 – 15 – 19 – 15 – 13 – 5 – 19 Answer: _______________________________ 5. Description: Powerhouse of the cell. Code: 13 – 9 – 20 – 15 – 3 – 8 – 15 – 14 – 4 – 18 – 9 – 15 – 14 Answer: _____________________________________________ What’s New A plant cell has almost the same organelles with that of an animal cell but there are organelles that are found only in plant cell. Activity 2: Describe Me! Directions: You are asked to describe an unknown specimen as shown in the picture below. In three (3) sentences, describe what you see in the picture. Write your descriptions in your Science activity notebook. Answer: _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ Figure 1. Unknown Specimen 12 What is It What is a Plant Cell? Plant cells contain nucleus along with other organelles as discussed in Lesson 1: Cell Parts and their Functions. However, there are organelles which are distinct and can be found only in plant cells as emphasized in the figure below. Figure 2. Plant Cell 13 What’s More Activity 3: Label Me! Directions: Label the picture by using the names of the organelles inside the word bank below the picture. Write your answers in your Science activity notebook. 1 7 2 8 3 9 10 4 11 12 5 6 Figure 3. The Plant Cell Word bank Cell Wall Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Vacuole Chloroplast Mitochondrion Ribosomes Lysosomes Nucleus Rough ER Smooth ER Golgi Bodies 14 Lesso n 3 THE ANIMAL CELL What’s In In the previous module, you learned about plant cells. Plant cells have cell wall that surrounds the cell membrane. This gives the plant cell its unique rectangular shape and rigidity. You have also learned that plant cells have chloroplast which contains pigments such as chlorophyll needed for photosynthesis and gives plants their green color. In this module, you will study about animal cells, its organelles, and functions. Activity 1: Complete Me! Directions: Complete the words below by filling in the missing letters. Write the complete word in your Science activity notebook WORD: CLUE: 1._UCL_US It controls all the activities of the cell. 2. CY_OPL_ _M It is where all the organelles are located. 3. V_CUOL_ It holds water, food and waste materials. 4. CH_ORO_LAS_ It is the site of photosynthesis in plant cells. 5. CELL WA_ _ It provides support, protection, and shape to the plant cell. 15 What’s New Activity 2: Word Hunt! Directions: Form a word out of the given number in the code sequence to form the mystery word. Write your answer in your Science activity notebook. An example is done for you. A – 1 B – 2 C – 3 D – 4 E – 5 F – 6 G – 7 H – 8 I – 9 J – 10 K – 11 L – 12 M – 13 N – 14 O – 15 P – 16 Q – 17 R – 18 S – 19 T – 20 U – 21 V – 22 W – 23 X – 24 Y – 25 Z – 26 Example: Description: The study of living things. Example: 2 – 9 – 15 – 12 – 15 – 7 – 25 Answer: BIOLOGY 1. Description: Living things that have capacity for spontaneous movement. Code: 1 – 14 – 9 – 13 – 1 – 12 Answer: ___________________ 2. Description: The basic unit of life. Code: 3 – 5 – 12 – 12 Answer: ____________ 3. Description: “Considered the little organs” of the cell. Code: 15 – 18 – 7 – 1 – 14 – 5 – 12 – 12 – 5 – 19 Answer: __________________________________ 16 What is It What Is an Animal Cell? An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell, which also contains nucleus and other membrane-bound “little organs” called organelles, that perform different functions inside the cell as discussed in Lesson 1: Cell Parts and their functions. Animal cells are found within every animal. They are of different sizes for which the largest known animal cell is the ostrich egg, that can stretch over 5.1 inches across and weigh about 1.4 kilograms. This is in complete opposite to the nerve cells in the human body which is too small to be visible without the use of a microscope. Animal cells also have irregular shapes. They are different from other cells because they do not have cell wall, which allows them to take on different shapes. Also, the most distinct organelle found only in animal cell is the centriole (Figure 1) which is a tube-like structure that aid in cell division. They are generally found close to the nucleus. It is responsible for separating the chromosomes during animal cell division. Source: https://www2.palomar.edu/users/warmstrong/images/animal4.gif Figure 1: Parts of Animal Cell 17 What’s More Activity 3: Let’s CELLebrate! Directions: Use the diagram to complete the chart with the needed information. The first item has been completed for you as an example. Write your answers in your Science activity notebook. A B E F C D Label Organelle Function 1. A Mitochondrion The powerhouse of the cell. Modifies and packages proteins and lipids. 2. B 3. C 4. D Cytoplasm 5. E Encloses the contents of the cell. 6. F 18 Lesso Comparing Plant 4 and Animal Cells n What’s In Activity 1: Remember Me? Directions: Study the diagram of a plant and an animal cell below. Then, complete the statements that follow. Write your answers in your Science activity notebook. Figure 1. The Plant and Animal Cell Organelles 1. The structure labeled A are found in both types of cells. The name of the structure is _____. 2. Unlike animal cells, plant cells have cell walls. In the diagram it is labeled as _______. 3. The organelle labeled E is known as “The Brain” of the cell. It is the _______. 4. It is the site of photosynthesis. The organelle I is _______. 5. The powerhouse of the cell is the mitochondrion. In the diagram it is labeled as _____. 19 What’s New Activity 2: Take a Pic! Directions: Study carefully the pictures below and answer questions 1 and 2. Write your answer in your Science activity notebook. 1. Which one is a plant cell? _________________ 2. Which is an animal cell? _________________ 3. Write the differences that you observe in the Pictures A and B of the cells according to: a. size _________________ b. shape _________________ B A Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Plagiomniu m_affine_laminazellen.jpeg(2006) Source: http://omsscience7.oregonsd.net/cells Figure 2. The Plant and Animal Cell What is It Both plant and animal cells are eukaryotic which means they contain membrane-bound organelles like the nucleus and mitochondria. However, plant cells and animal cells do not look exactly the same or has all of the same organelles, since each of them have different needs. For example, plant cells contain chloroplasts since they need to perform photosynthesis, but animal cells do not. 20 So, how are plant cell and animal cell similar to or different from each other? Why do plants and animals have differences? Plant and animal cells differ because they have to perform different functions. Both animal and plant cells have mitochondria, but only plant cells have chloroplasts. Plants don’t get their sugar from eating food, so they need to make sugar with the help of the sunlight. This process which is known as photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplast. Once the sugar is made, it is then broken down by the mitochondria to make energy for the cell. Because animals get sugar from the food they eat, they do not need chloroplasts: just mitochondria. Both plant and animal cells have vacuoles. A plant cell contains a large, singular vacuole that is used for storage and maintaining the shape of the cell. In contrast, animal cells have many, smaller vacuoles. Plant cells have a cell wall and a plasma membrane. In plants, the cell wall surrounds the plasma membrane. This gives the plant cell its boxlike shape. This also allows the plants to remain strong and stand upright even if it grows to great heights. Animal cells simply have a plasma membrane, but no cell wall. The table below summarizes the similarities and differences of animal cells and plant cells. Notice the organelles that can be found in both types of cells and observe carefully the organelles which are present only in animal cell or in plant cell. Table 1. Comparison Between Plant & Animal Cell Basis of Comparison Plant Cell Animal Cell Cell Wall Present Present Centrioles Absent Present Chloroplast Present Absent Cytoplasm Present Present Endoplasmic reticulum Present Present Golgi body Present Present Lysosome Rarely present Present Mitochondria Present Present Nucleus Present Present Plasma membrane Present Present Ribosomes Present Present Only one huge vacuole Many and smaller in size Vacuole 21 What’s More Activity 3: Fill Me! Directions: Copy the Venn Diagram in your Science activity notebook. Compare and contrast plant and animal cells by filling in the Venn Diagram with the organelles listed in the box below. The common organelles must be written in the overlapping area (A), while the differences are in the non-overlapping areas (B) and (C). Cell Wall Endoplasmic reticulum Nucleus Centrioles Golgi body Plasma membrane Chloroplast Lysosome Ribosomes Cytoplasm Mitochondria Vacuole BC Plant Cell Animal Cell A Differences Similarities Differences Figure 5. Venn Diagram of the Comparison Between Plant and Animal cell 22 What I Have Learned A. Cell Analogy Directions: Fill in the blanks below with the specific cell organelle that works for its specific function. Choose your answer from the box and write your answers in your Science activity notebook. Ribosomes Mitochondria Cell Nucleus Cell Wall Golgi Bodies Cell Membrane Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Vacuoles Chloroplast Imagine you are inside a factory. The factory itself is the (1) _____. To protect it from robbers and looters, the factory is protected by an inner wall that represents the (2) _____, and the outer wall represents the (3) _____. Inside the factory is the control room where computers are located that direct the movements of the machineries. The control room represents the (4) _____. In another area, workers are busily performing their duties. The workers represent the (5) _____. These workers translate the information sent by the control room to the machineries used. Also, inside the factory is the power supply room represented by the (6) _____ which provides energy for the continuous operation of the factory. There is also the packaging room where products are being sorted out, ready for delivery. The packaging room represents the (7) _____. Prior to the delivery, the packages are transported through a conveyor which represents the (8) _____. They serve as the channel where products are moved. The products will then be stored in the storage room. The storage room represents the (9) _____. On the other hand, the machinery which produces the products represents the (10) _____. They are responsible for making the products produced inside the factory. 23 What I Can Do To show your learnings about the lesson, make your own 3D model of either a plant and animal cell. You can use any materials available at home such as cardboards, egg shell, yarn, sticks, pebbles, and other materials you find useful. Please take note on the important organelles that are only present in a plant cell and/or animal cell. The table below will serve as your basis as to the equivalent points that you will receive in making your own plant and animal cell model. Table 1. Cell Model Rubric Excellent Satisfactory Needs (5 points) (4 points) Improvement (3 points) Appearance Project is accurate and Project shows Project is not shows the evidence of neatness and neatly done. considerable effort. organization. Organelles are not organized. Creativity Cell model uses materials Cell model uses Minimal creativity not often seen in most good materials. is shown in the projects. Details project. All organelles are Most organelles are Some organelles accurately detailed and accurately detailed are not clearly clearly and clearly presented. Few presented. Actual numbers presented. Actual organelles are of organelles are number of represented. represented. organelles are represented. Labelled 11+ organelles are 8-10 organelles 5-7 organelles are Organelles correctly located and are correctly correctly located labelled in the model. located and and labelled in the labelled in the model. model. 24 Assessment I. Multiple Choice: Read each question carefully and choose the best answer from the given choices A to D. Write the letter of your answer in your Science activity notebook. 1. Which of the following statements is TRUE? A. All cells have cell wall. C. All cells contain chloroplast. B. All cells contain centriole. D. All cells have cell membrane. 2. Why are lysosomes considered as the “cleaners” of the cell? A. Lysosomes digest damage cell parts. B. Lysosomes support and protect the cell. C. Lysosomes pump materials that enter the cell. D. Lysosomes transport materials from one cell to another. 3. Which part of the cell controls the “entry and exit” of materials? A. Cell membrane C. Endoplasmic Reticulum B. Cell wall D. Golgi bodies 4. Mitochondria are organelles that produce energy for the cell. Which part of the body has many mitochondria? A. Hair C. Nails B. Heart D. Nose 5. Which organelle packages and sorts the product of the cell? A. Cell Wall C. Chloroplast B. Cell Membrane D. Golgi Bodies 6. Which organelle serves as the “brain” of the cell? A. Cell Membrane C. Lysosome B. Cytoplasm D. Nucleus 7. What is the function of chloroplasts in plants? A. Enable the plant to make their own food B. Make the plants rigid and rectangular in shape C. Give the plants energy needed to make food D. Store food, water, and waste products of the plants 25 II. Identification: Label the parts of the animal and plant cells using the word/s found in the box below. WORD BANK Cell Membrane Lysosomes Nucleolus Cell Wall Vacuole Nucleus Chloroplast Mitochondrion Cytoplasm Ribosomes Centriole Golgi Body 8 12 2 9 13 3 14 4 10 0 15 5 11 1 The Plant Cell The Animal Cell 26 Additional Activities Activity: Name Game I. Directions: Let’s play a name game. An organelle is given to you and you are going to describe it in one word based on its function or description. Number one is done as an example. 1. Mitochondria - Powerful mitochondria 2. Cell Membrane 3. Chloroplast 4. Vacuoles 5. Cytoplasm II. Directions: Compare a cell to a “sunny side up” egg. Provide its similarities by identifying labels A, B, and C. A B C Figure 3. Sunny-side Up Egg 27 Answer Key 15. Mitochondrion 19.20. 14. Centriole 18. 13. Nucleus 17. the functions inside an organism. 12. Lysosome 16. Vacuole 11. 15. 10. Chloroplast 14. 9. Cell membrane 13. 8. 1. CELL Cell wall 12. 22. What’s In 7. A 11. 1. NUCLEUS organisms; 2. CELL MEMBRANE 3. structure of the CYTOPLASM bodies of 4. RIBOSOMES unit of life because it forms 5. MITOCHONDRION the 2. The cell is 6. D 10. 5. D 9. 4. B 8. 3. D 7. 2. A 6. 1. D 5. the basic structural MITOCHONDRION A 1. What I Know 33. 32. CELL MEMBRANE 6. F ROUGH ER - 5. E CYTOPLASM - D 4. CENTRIOLE - C 3. GOLGI BODIES - B 2. Lesson 2 unit of life because it regulates all The cell is the basic functional 4. CELL TISSUES ORGANS What’s More 3. 23. What’s New 24. (ANSWERS MAY VARY.) 25. What’s More 1. CELL WALL POPULATION COMMUNITY ECOSYSTEM BIOSPHERE What’s In 1. Lesson 1 2. CELL MEMBRANE 3. GOLGI BODIES 4. CHLOROPLAST 5. MITOCHONDRION 6. CYTOPLASM 7. LYSOSOMES 8. RIBOSOMES 9. SMOOTH ER 10. NUCLEUS 11. ROUGH ER 12. VACUOLE ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM membrane cell C. cytoplasm B. nucleus A. II. Answers may vary. 5) - (1 I. Additional What’s More 31. 30. ORGANELLES 3. CELL 2. ANIMAL 1. New What’s 29. 5.CELL WALL 4.CHLOROPLAST 3.VACUOLE 2.CYTOPLASM 1.NUCLEUS 28. In What’s 27. Lesson 3 Activities , lysosomes vacuole plasma membrane, ribosomes, nucleus, 26. reticulum, golgi body, mitochondria, cytoplasm, endoplasmic C. Similarities: Centrioles B. Animal Cell: Cell wall, chloroplast Plant Cell: A. What’s More 5. H CHLOROPLAST 4. may vary. 3. Answers 3. NUCLEUS 2. A 2. C 1. B CYTOPLASM 1. 36. New What’s nI What’s Lesson 4 28 References Books Asuncion, Alvie J., et. al. Science 7 Learner's Material. Pasig City: pp 103-104. Department of Education, 2017. Carale, Lourdes R., and Elvira R. Galvez. Science and Technology II, Biology Textbook.pp.28. Pasig City: Department of Education, 2009 Faraon, Genevieve Darvin. Phoenix Science Series BIOLOGY Teacher's Guide.pp.125-137. Quezon City: Phoenix Publishing House, Inc., 2004 Laurente, Jomar Aries T. et al. Science for the 21st Century Learner. pp. 138- 143. DIWA Learning System, Legaspi Village, Makati City, Philippines. 2015. Electronics 2019. wordmint.com. January 04. https://wordmint.com/public_puzzles/1108045. (Accessed June 01, 2020) Armstrong, W.P. 2012. palomar.edu. January 22. https://www2.palomar.edu/users/warmstrong/images/animal4.gif. (Accessed May 22, 2020) Bailey, Regina. 2019. thoughtco.com. August 26. Accessed June 01, 2020. https://www.thoughtco.com/cell-wall-373613. Biology Experts Notes. 2019. medium.com. December 7.https://medium.com/@biologynotes/animal-cell67442ef5f51b. (Accessed May 22, 2020) Deep, Akash. n.d. scribd.com. Accessed June 13, 2020. https://www.scribd.com/document/217949146/Cell-Model-Rubric. Goldman, Michael A. 2015. science.sciencemag.org. May 29. https://science.sciencemag.org/content/348/6238/979.full. (Accessed June 22, 2020) n.d. byjus.com. https://byjus.com/biology/animal-cell/. (Accessed June 02, 2020) n.d. cookinglight.com. https://www.cookinglight.com/recipes/pristine-sunny-side up-eggs. (Accessed June 01, 2020) 29 n.d. dreamstime.com. https://www.dreamstime.com/structure-golgi-apparatus animal-plant-cell-major-organelle-most-eukarytoic-cells-image137227168. (Accessed June 01, 2020) n.d. en.wikipedia.org. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lysosome. (Accessed June 01, 2020) n.d. genome.gov. https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Endoplasmic Reticulum-Smooth. (Accessed June 01, 2020) n.d. genome.gov. https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Endoplasmic Reticulum-rough. (Accessed June 01, 2020) n.d. genome.gov. ttps://www.genome.gov/sites/default/files/tg/en/illustration/centriole.jpg . (Accessed June 22, 2020) n.d. https://www.microscopemaster.com/organelles.html. (Accessed June 01, 2020) n.d. joshandkarlasproject.weebly.com. https://joshandkarlasproject.weebly.com/uploads/4/0/8/3/40833201/9707 7 2_orig.jpg. (Accessed June 01, 2020) n.d. microbenotes.com. https://microbenotes.com/lysosomes-structure-enzymes types-functions/. (Accessed June 01, 2020) n.d. pngbarn.com. https://www.pngbarn.com/png-imagebxrcb. (Accessed June 01, 2020) n.d. science4fun.info. https://science4fun.info/wp-ontent/uploads/2019/03/human skeleton.jpg. (Accessed June 22, 2020) n.d. sites.google.com. https://sites.google.com/a/asu.edu/the-almighty-cell/the source/animal-cell/centriole. (Accessed June 01, 2020) n.d. sites.google.com. Accessed June 01, 2020. https://sites.google.com/site/kmhvacuole/. n.d. slideshare.net. https://www.slideshare.net/lhoralight/science-37094718. (Accessed June 01, 2020) n.d. study.com. https://study.com/cimages/videopreview/videopreview-full/what is-cell-differentiation-pros-importance-examples_01002512_111306.jpg. (Accessed June 01, 2020) n.d. study.com. https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-an-ecosystem definition-lesson-quiz.html. (Accessed June 22, 2020) 30 n.d. study.com. https://study.com/academy/lesson/mitochondrion-definition function-structure.html. (Accessed June 01, 2020) n.d. timvandevall.com. https://www.timvandevall.com/science/plant-cell-diagram/. (Accessed June 01, 2020) n.d. vedantu.com. https://www.vedantu.com/biology/animalcell. (Accessed May 22, 2020) Ocal. 2010. clker.com. August 27. http://www.clker.com/clipart-animal-cell.html. (Accessed June 01, 2020) Rogers, Kara. n.d. https://www.britannica.com/. Accessed June 01, 2020. https://www.britannica.com/science/Golgi-apparatus. siyavula.com.www.siyavula.com/read/grade-9/cells-as-the-basic-units-oflife/01- cells-as-the-basic-units-of-life?id=toc-id-5. (Accessed May 28, 2020) 31 For inquiries or feedback, please write or call: Department of Education – Region 10 Zone 1, DepEd Building Masterson Avenue, Upper Balulang Cagayan de Oro City, 9000 Telefax: (088) 880 7072 E-mail Address: region10@deped.gov.ph 32