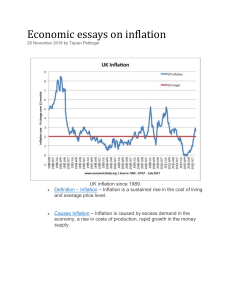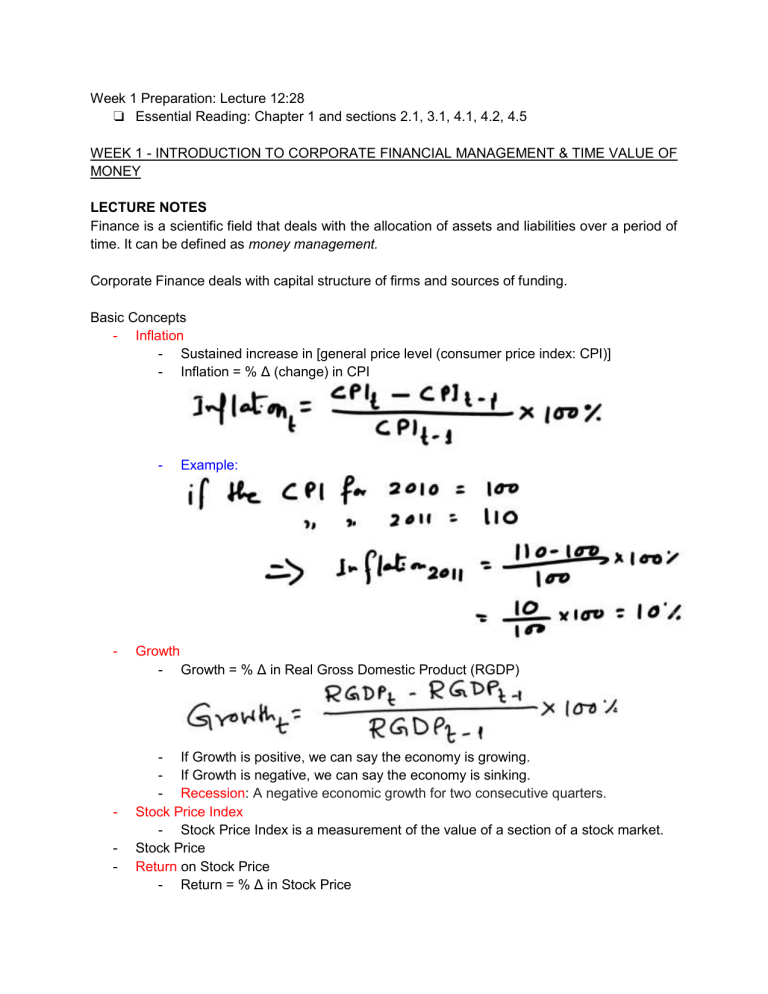
Week 1 Preparation: Lecture 12:28 ❏ Essential Reading: Chapter 1 and sections 2.1, 3.1, 4.1, 4.2, 4.5 WEEK 1 - INTRODUCTION TO CORPORATE FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT & TIME VALUE OF MONEY LECTURE NOTES Finance is a scientific field that deals with the allocation of assets and liabilities over a period of time. It can be defined as money management. Corporate Finance deals with capital structure of firms and sources of funding. Basic Concepts - Inflation - Sustained increase in [general price level (consumer price index: CPI)] - Inflation = % Δ (change) in CPI - - - Example: Growth - Growth = % Δ in Real Gross Domestic Product (RGDP) - If Growth is positive, we can say the economy is growing. - If Growth is negative, we can say the economy is sinking. - Recession: A negative economic growth for two consecutive quarters. Stock Price Index - Stock Price Index is a measurement of the value of a section of a stock market. Stock Price Return on Stock Price - Return = % Δ in Stock Price - - - - - Where Pt = Price of the stock at time t - Where Pt-1 = Price of the stock one period before - Where Ct = Dividend given by an organisation at time t Elasticity % Δ in quantity demanded / % Δ in price Interest Rates (Nominal and Real) - Real Interest Rate = Nominal Interest Rate - Inflation - If inflation is above 3%, then RBA (Reserve Bank of Australia) increases the interest rate - If inflation is below 2%, RBA decreases the interest rate Monetary Policy Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) Simple and Compound Interest - NOTES IN NOTEBOOK