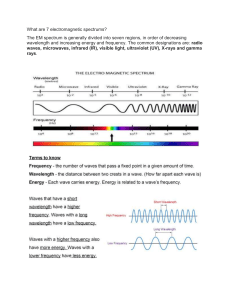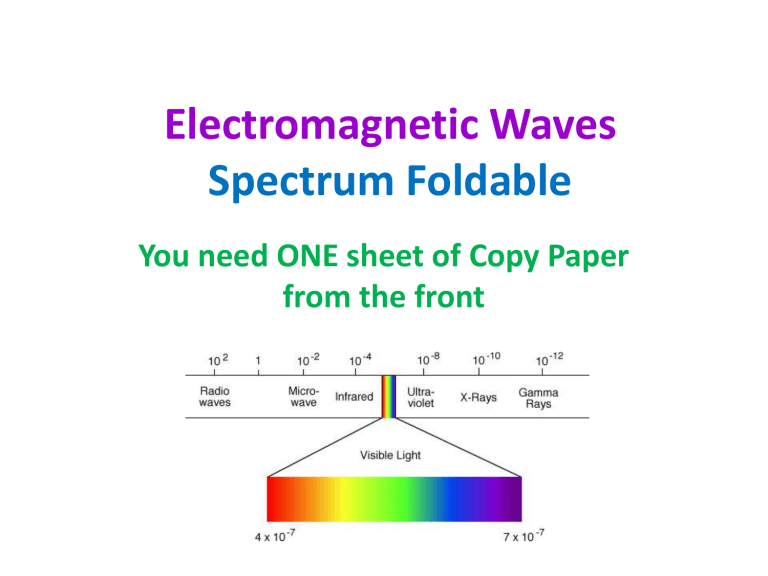
Electromagnetic Waves Spectrum Foldable You need ONE sheet of Copy Paper from the front Cut along the dashed lines. Fold on the solid line. Gamma Rays X-rays Ultraviolet Rays Visible Light Infrared Rays Microwaves Radiowaves outside flaps Sketch a model of the Electromagnetic This is also in the class reading Electromagnetic Spectrum • The full range of frequencies, from radio waves to gamma rays, that characterizes light • The electromagnetic spectrum can be expressed in terms of energy, wavelength, or frequency. Each way of thinking about the EM spectrum is related to the others in a precise mathematical way. Wavelength and Frequency important vocabulary- copy on back of foldable • For any kind of wave there exists a simple relationship between wavelength and frequency. • The wavelength (a) is measured as the distance between two successive crests in a wave. • The frequency is the number of wave crests that pass a given point in space each second. • (b has a higher frequency that a) Gamma Rays • Shortest wavelengths • Highest frequencies • Most penetrating of all waves X-rays • Can penetrate most matter • Too much exposure can cause cancer • Useful in medicine Ultraviolet Rays • Energy is great enough to damage or kill living cells • Insects can see this Images of a Mimulus flower in visible light (left) and ultraviolet light (right) showing a dark nectar guide that is visible to bees but not to humans Visible Light • We can see it! • White light can be separated into red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet Infrared Rays • Wavelengths are shorter than radiowaves • We feel them as heat • Ex: heat lamps and infrared cameras Microwaves • Radiowaves with the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies • Ex: radar guns Radiowaves • Longest wavelengths • Lowest frequencies • Used in broadcasting • Click on icon below for short video