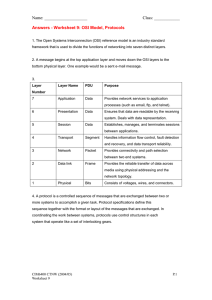
Buffer overflow Key slides to learn Slide 1 – what is buffer overflow? Slide 9 – types important Slide 10 - C and C+ most susceptible to buffer overflow but ppl keep using C because it is the fastest and most robust even than Java. Slide 12 – preventing buffer overflow attack Slide 14 – antiviruses look out for these codes that cause buffer overflow. Antivirus needs updating often since attackers come up with new patterns to attack all the time. Slide 16 – preventing buffer overflow again Slide 21 – simple buffer overflow code Slide 22 – prevent buffer overflow checking strings Slide 23 – prevent buffer overflow via checking memory to ensure it doesn’t exceed the memory size needed for the programme. page tables check size of programmes Lecture 3, 4 and 5 Networking Majority of attacks come from networking Things to know Architecture of networks OSI models and layers, protocols used Sockets – smart port (programmable ports) Network sniffing – first form of attack…evesdropping..macoin Standard protocols used for computers, web browsers to communicate. So study these protocols and then u can attack. It begins at the OSI model. What are the protocols for OSI models? Lecture 3 Learn slide 5 OSI model Note each device that sits on a specific layer a router on the network layer will have network protocols. A device sitting on a particular layer in the OSI model doesn’t have to go thru the protocols for all seven layers. Re each layer has its own protocols. What is OSI encapsulation? Sockets Are smart ports. They can be programmed. Two types. o Stream sockets (like telephones o- two way communication), emails) and o Datagram sockets (streaming media or network games – one way communication). Datagram + UDP (no confirmation that data is transferred). TCP not suitable for high quantity data transfer Data are transmitted in packets. The communicate using TCP Works at layer 5 and layer 4 Definition: A socket is one endpoint of a two-way communication link between two programs running on the network. A socket is bound to a port number so that the TCP layer can identify the application that data is destined to be sent to. Sockets send confirmation that data is sent. Ports do not send any confirmation that the data is sent. But ports sends data fast. Or use high speed net together with a socket. What is TCP? What are socket functions? Peeling back the lower layers 7 layers. Each needs to communicate with each other protocols for proper communication. Data link layer lowest layer to ping or communicate with. Every device in a layer is given a unique MAC address similar to how everyone has their own id card number. Each layer has different MAC addresses for its devices IP addresses however may change regularly – changes at layer 4 – e.g. number u get in the line in the bank. ARP maps MAC address to IP address. Slide 22 – how does ARP do this? Network sniffing – data link Layer How does network sniffing work? All sniffing occurs at layer 2 – data link layer, hand shaking happens at that layer. telnet, FTP, POP3 data are not encrypted What is an unswitched network? These allow for network sniffing Use switched network. If not, use a network that has encryption of the data at a mimimum How to sniff data on switched networks using man in the middle