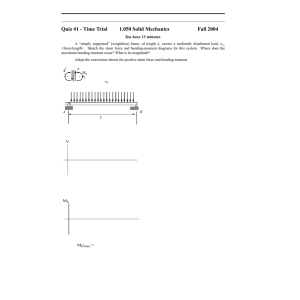
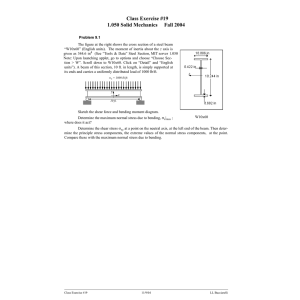
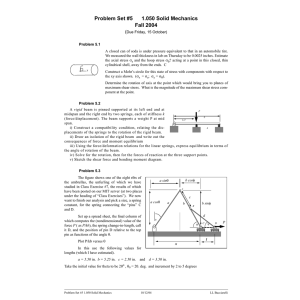
2nd stage /Mechanical Eng. Sheet No. 2: Chapter 6 Strength of materials Q1/ For the beam and loading shown, consider section n-n and determine (a) the largest shearing stress in that section, (b) the shearing stress at point a. Ans: Q2/ The composite beam shown is made by welding C200×17.1 rolled-steel channels to the flanges of a W250 80 × wide-flange rolled-steel shape. Knowing that the beam is subjected to a vertical shear of 200 kN, determine (a) the horizontal shearing force per meter at each weld, (b) the shearing stress at point a of the flange of the wide-flange shape. Ans: a) q=146 kN/m b) 19.99 kN/mm2 2nd stage /Mechanical Eng. Sheet No. 2: Chapter 6 Strength of materials Q3/ The assembly is subjected to a vertical shear of V=7 kips . Determine the shear flow at points A and B and the maximum shear flow in the cross section. Ans: qA=196 Ib/in qB= 452 Ib/in qmax = 641 Ib/in Q4/ The beam is constructed from two boards fastened together with three rows of nails. If the allowable shear stress for the wood is 150 psi, determine the maximum shear force V that can be applied to the beam. Also, find the maximum spacing s of the nails if each nail can resist 650 lb in shear. Ans: V=1.8 kip S=2.167 in 2nd stage /Mechanical Eng. Sheet No. 2: Chapter 6 Strength of materials Q5/The box beam is constructed from four boards that are fastened together using nails spaced along the beam every 2 in. If each nail can resist a shear of 50 lb, determine the greatest shear V that can be applied to the beam without causing failure of the nails. Ans: V= 317 Ib