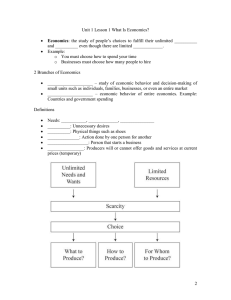
ECONOMICS Summary What is Economics? Needs are unlimited but Resources are scarce. Economics aims at satisfying our unlimited needs with the Limited available resources in an optimal way. Economic aims at optimum use of resources. Economics is the study of human activities performed in the motive of profit. i n d What is Economic Growth? ia Economic growth is the change- increase or decrease in the value of goods and services produced by an economy. A positive change indicates an increase in output of an economy. 1. There are many definitions, as the subject keeps on evolving, the definition also keeps on evolving. 2. Adam Smithd = Father of Economics 3. Economics studies how an entity allocate ia resources at its disposal s 4. A n e nt it y ca n h b e i n d i v i d u al, b u s i n e s s, governments or nationa s h s t a r a are cheaper Things which are more useful s t r a Micro-econmics Micro-economy is the study of units or an individuals. It examines the economic behaviour of units such as consumers, business, households. i n d ia Macroeconomics s h Macroeconomy is the study of aggregates. a Macroeconomy studies the economysas a t whole and its features like national r income, employment, poverty and balancea of payments and inflation. Macro studies in general rather than studying specific ECONOMICS in d ia Adam Sm ith in h is Wealth of Natio ns observed--> Things which have greatest value in in exchange has little to no use and things d have little to no value in exchange has which ia greatest use. For example Air which is useful s than anything else is available for free and h a has hardly any use is sold dear. diamond which s t r What is Economy? a s h a Any region with well defined set of rules and established institutions to implement those rules is called Economy. s t Factors of Production r a Inputs needed for the production of goods and services.Land, Labour, Capital and Entrepreneur 1. Land = Site of production or natural resources 2. Labour = Does the work at ground level 3. Capital = For investing in machines, technology and people 4. Entrepreneur = Takes risk, administers and regulate all other factors. What is an Economic Activity? All activities which create value and utilise resources are called economic activities.