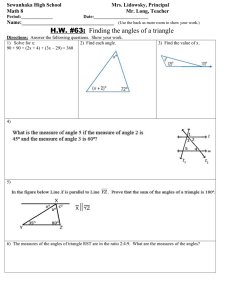
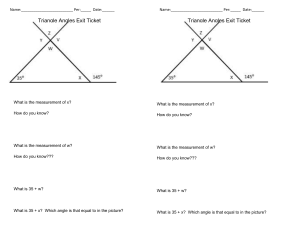
Classifying Triangles Angle Measures of Triangles Triangle • A triangle is a figure formed by three segments joining three noncollinear points. Classifying Triangles by Sides • Equilateral Triangle • Isosceles Triangle • Scalene Triangle Equilateral Triangle • An equilateral triangle has three congruent sides. Isosceles Triangle • An isosceles triangle has at least two congruent sides. Scalene Triangle • A scalene triangle has no congruent sides. Classify the triangle by its sides. Classification of Triangles by Angles • • • • Equiangular triangle Acute triangle Right triangle Obtuse triangle Equiangular Triangle • An equiangular triangle has three congruent angles. Acute Triangle • An acute triangle has three acute angles. Right Triangle • A right triangle has one right angle. Obtuse Triangle • An obtuse triangle has one obtuse angle Classify the triangle by its angles. Vertex • A vertex of a triangle is a point that joins two sides of the triangle. • The side across from an angle is the opposite side. Name the side that is opposite the angle. • Angle J • Angle K • Angle L Triangle Sum Theorem • The sum of the measures of the angles of a triangle is 180º. • In ΔABC, mA + m B + m C = 180º Find the measure of the missing angle. Corollary to the Triangle Sum Theorem • The acute angles of a right triangle are complementary. • In ΔABC, if m C = 90º, then m A + m B= 90º A C B ΔABC is a right triangle. Find the measure of angle A. Interior Angles • When the sides of a triangle are extended, other angles are formed. • The three original angles are the interior angles. Exterior Angles • The angles that are adjacent to the interior angles are the exterior angles. • It is common to show only one exterior angle at a vertex. Exterior Angles Theorem • The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two remote interior angles. • m 1 = m A + m B Find the measure of angle 1.