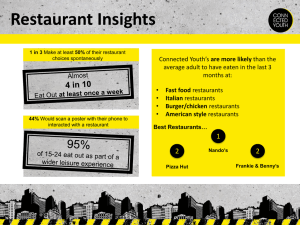
The Restaurant Business ACTIVITY • Explain the differences between an independent and chain ownership restaurant. • List examples of these two types of restaurants which are available in Egypt. The Restaurant Business • Why Restaurants are a vital part of our everyday life styles? • because we are a society on the go, we patronize them several times a week to socialize, well as eat and drink. What is the word restaurant come from? • Restaurants offer a place to relax and enjoy the company of family, friends, groups, and business associates, to restore our energy level before heading off to the next class whatever. Actually, the word restaurant is from the word restore. Classifications of Restaurants • There are two main categories: independent restaurants and chain restaurants. Individual restaurants • Owned by one or more owners • Usually involved in the day-to-day operation of the business • These restaurants are not associated with any national brand or name. • They offer the owner independence, creativity, and flexibility, but are accompanied by risk Chain restaurants • Comprise a group of restaurants, each have the same market, concept, design, service, food, and name. • The same menu, food quality, level of service, and atmosphere can be found in any one of the restaurants, regardless of location. • These are usually owned by family teams or other entrepreneurs Full-Service Restaurant • Restaurant types included in this category are fine dining, theme, celebrity, and some ethnic restaurants. Fine Dining • A fine dining restaurant is one where a good selection of menu items is offered; generally at least fifteen or more different entrees cooked to order. • Many of these restaurants serve haute cuisine, which is a French term meaning elegant dining or high food. • Many of the fine restaurants in the United States are based on French or Northern Italian cuisine, which, together with fine Chinese cuisine, are considered by many Western experts to be the finest in the world. Cont. Fine Dining • Most fine dining restaurants are independently owned and operated by an entrepreneur or a partnership. These restaurants are in almost every city. • Today, with value-conscious guests expecting more for their money, it is becoming increasingly more difficult to make a profit in this segment of the business because of strong competition from other restaurants. Cont. Fine Dining • The level of service in fine dining restaurants: is generally high, with a hostess or host to greet and seat patrons. Captains and food servers advise guests of special items and assist with the description and selection of dishes during order taking. If there is no separate sommelier (wine waiter), the captain or food server may offer a description of the wine that will complement the meal and assist with the order taking. Some upscale or luxury full-service restaurants have table-side cooking and French service from a gueridon cart. Reasons for the Small Number of Luxury restaurants: • Labor intensive and require a higher level of skilled labor Small percentage can afford high prices Overhead costs may not be reasonable Economies of scale are not as easily earned Consistency and quality are not easy to maintain Limited market appeal. Theme Restaurants • Many theme restaurants are designed around a particular theme, this theme is used or reflected in every element of the establishment's ambiance, They generally serve a limited menu but aim to wow the guest by the total experience. Possibilities for theme are railroad cars or stations, airplanes, dining cars, rock and roll, and many others. Examples of theme restaurants are: TGI Friday’s, Hard Rock Cafe, Studio Misr, and Bedouin Nights. Cont. Theme Restaurants • People are attracted to theme restaurants because they offer a total experience and a social meeting place. This is achieved through decoration and atmosphere and allows the restaurant to offer a limited menu that blends with the theme. Celebrity Restaurants • Celebrity-owned restaurants have been growing in popularity. Some celebrities, such as Wolfgang Puck, came from a culinary background, while others, like Naomi Campbell, Claudia Schiffer, and Elle Macpherson (owners of the Fashion Café), did not. • A number of sports celebrities also have restaurants. Among them is Michael Jordan. Television and movie stars have also gotten into the act. Oprah Winfrey has been part owner of The Eccentric in Chicago for a number of years. • Celebrity restaurants generally have an extra zing to them—a winning combination of design, atmosphere, food, and perhaps the thrill of an occasion visit by the owner(s). Top Restaurants • Refer to food and beverage operations located on the top floors of hotels or other tall buildings, usually located in some part of a major city where there is an interesting or spectacular view. • An example is windows on the world at the top of one of twin towers of the world trade center in New York. (till 9/11 booming) • Example in Egypt, Cairo Tower Restaurant, Capital Club ( ) نادى العاصمةand Window of the World (Hilton Ramses, Cairo) Casual Dining and Dinner House Restaurants • The types of restaurants that can be included in the casual dining restaurants category are as follows: • a) Casual Restaurants • b) Family Restaurants • c) Ethnic Restaurants • Casual Dining is relaxed and could include restaurants from sever classifications: chain or independent, ethnic, or theme. Hard Rock Cafe, and TGI Friday’s, are good examples of casual dining. • Family Restaurants is one that caters to family groups-parents with children and other contemporary family grouping. Most offer an informal setting with a simple menu and service designed to please all the family. Prices are kept in a low to moderate range. • Ethnic Restaurants are specialized in foods associated with a particular culture, such as Chinese Mexican, or Greek. Ethnic restaurant vary service, and ambiance. Quick-Service / Fast-Food Restaurants • Quick-service restaurants consist of diverse operating facilities whose slogan is “quick food.” • The following types of operations are included under this category hamburger, pizza, chicken, pancakes, sandwich shops, and delivery services. Cont. Quick-Service / Fast-Food Restaurants • Quick-service or fast-food restaurants offer limited menus featuring food such as hamburgers, fries, hot dogs, chicken (in all forms), tacos, various finger foods, and other items for the convenience of people on the go. • Customers order their food at a counter under a brightly lit menu featuring color photographs of food items. Customers are even encouraged to clear their own trays, which helps reduce costs. Cont. Quick-Service / Fast-Food Restaurants • The following are examples of the different types of quick-service/fast-food restaurants: • • • • • • • • Hamburger—McDonald’s, Burger King, Hardee’s Pizza—Pizza Hut, Domino’s, Steak—Bonanza, Ponderosa Seafood—Long John Silver’s Chicken—KFC, Sandwich—Subway Mexican—Taco Bell, Drive-Thru-In Delivery—Domino’s, Pizza Hut, McDonald’s Trends in the Restaurant Business • Branding: Restaurant operators are using the power of branding, both in terms of brand name recognition from a franchising viewpoint and in the products utilized. Alternative outlets: Increased competition from convenience “c-stores” and home meal replacement outlets. Globalization: Continued transnational development. Continued diversification within the various dining segments. More twin and multiple locations. More points of service (e.g., Taco Bell at gas stations). More hyper theme restaurants. Chains vs. independents. Restaurant Operations • Restaurant operations are generally divided between what is commonly called front of the house and back of the house. • The front of the house includes any one with guest contact from the hostess to the busperson. • The back of the house is generally run by the kitchen manager and refers to all the areas that guests do not normally come in contact with. This includes purchasing, receiving, storing/issuing, food production, stewarding, budgeting, accounting, and control. .