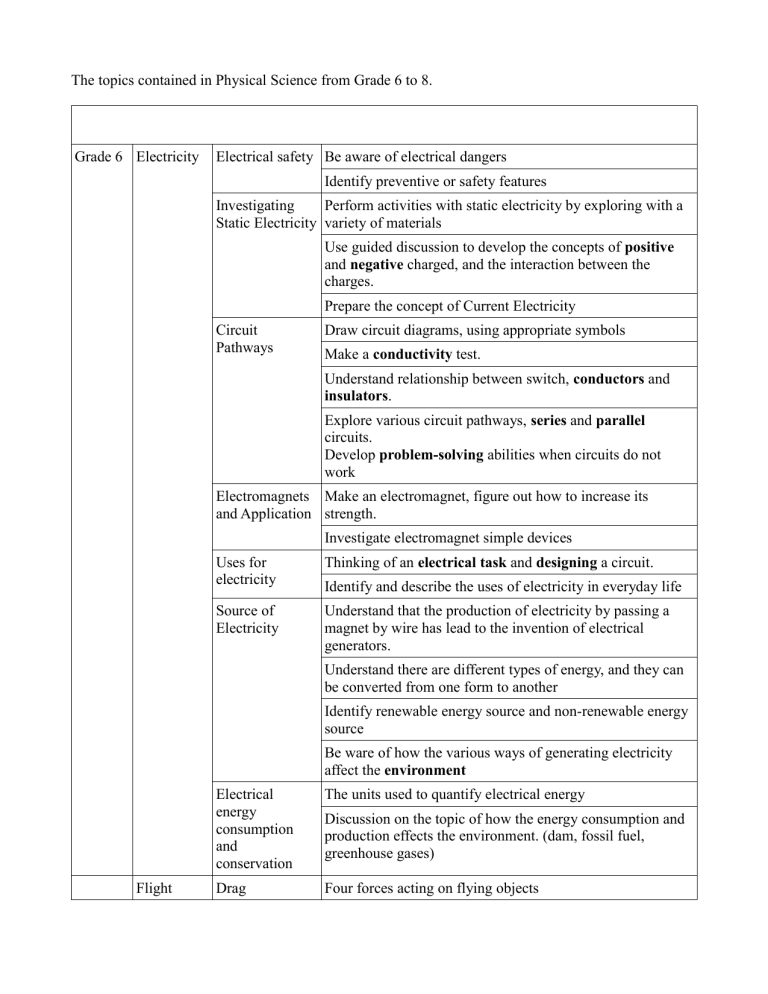
The topics contained in Physical Science from Grade 6 to 8. Grade 6 Electricity Electrical safety Be aware of electrical dangers Identify preventive or safety features Investigating Perform activities with static electricity by exploring with a Static Electricity variety of materials Use guided discussion to develop the concepts of positive and negative charged, and the interaction between the charges. Prepare the concept of Current Electricity Circuit Pathways Draw circuit diagrams, using appropriate symbols Make a conductivity test. Understand relationship between switch, conductors and insulators. Explore various circuit pathways, series and parallel circuits. Develop problem-solving abilities when circuits do not work Electromagnets Make an electromagnet, figure out how to increase its and Application strength. Investigate electromagnet simple devices Uses for electricity Thinking of an electrical task and designing a circuit. Source of Electricity Understand that the production of electricity by passing a magnet by wire has lead to the invention of electrical generators. Identify and describe the uses of electricity in everyday life Understand there are different types of energy, and they can be converted from one form to another Identify renewable energy source and non-renewable energy source Be ware of how the various ways of generating electricity affect the environment Flight Electrical energy consumption and conservation The units used to quantify electrical energy Drag Four forces acting on flying objects Discussion on the topic of how the energy consumption and production effects the environment. (dam, fossil fuel, greenhouse gases) Be aware of the tangible effect of air although it is invisible. Two main factors that affect the amount of drag are shape and texture. (observation, experiment, design activities) Lift and Wing Shape Understand how wings' shape and angle of attack affect lift Be aware that the temperature difference is another way of generating lift. Observation and discussion on the objects in our daily life to understand lift Grade 7 Heat Lift and Bernoulli's Principle Explanation on Bernoulli's Principle Thrust and Propulsion Explain two main types of propulsion Temperature Compare various instruments used to measure temperature and demonstrate how to use and read a thermometer properly Investigations in wind tunnels Explain propeller and its difference between jet propulsion Provide example of temperature-measuring technologies used in the past Construct, test, and display data of an air thermometer Temperature and Determine the general relationship between temperature matter changes and volumes of solids, liquids, and gases Explain temperature, using the concept of kinetic energy and the particle model of matter Heat transfer Compare transmission of heat by conduction, convection, and radiation Describe the science underlying heat transfer in solar heating systems and central heating systems Compare, in qualitative terms, the heat capacities of some common materials Carry out a procedure to investigate how various surfaces absorb radiant heat and control major variables Identify potential sources of error in data while investigating how various surfaces absorb radiant heat Communicate results of experiments and/or investigations related to colour and heat absorption by using language and a variety of tables, charts, and/or graphs Describe how various surfaces absorb radiant heat: - colour - texture Technology, Describe how our needs related to heat can lead to temperature and developments in science and technology heat Identify examples of science- and technology-based careers that are associated with heat and temperature Provide example of insulating technologies used in the past were developed through trial and error Grade 8 Fluids Floating and Sinking -Density Describe the relationship among the mass, volume, and density of solids, liquids, and gases using the particle model of matter Analyses qualitatively the density of various substances and suggest explanation for discrepancies in data, such as the measurement of the volume of irregular objects by water displacement Explain the effects of changes in temperature on the density of solids, liquids, and gases and relate the results to the particle model of matter Describe situations in life where the density of substances naturally changes or is intentionally changed Understand and appreciate that the density of objects determines why they float or sink Forces in Fluids Compare units of mass with the forces Describe the movement of objects in terms of balanced and unbalanced forces Provide and understand examples of technologies that have been developed because of our understanding of density and buoyancy Archimedes principle Explain quantitatively the relationship between force, area and pressure Pascal's principle Viscosity of Liquids Compare the viscosity of various liquids Test the viscosity of various common fluids and identify the major variables Describe factors that can modify the viscosity of a liquid Use a temperature-measuring technology effectively and accurately for collecting data in temperature-viscosity investigations Demonstrate a knowledge of WHMIS standards Propose and learn about potential, everyday applications related to the viscosity of liquids Optics Properties of Travels in a straight line Visible Light speed of light in air is 300,000 km/s reflection refraction and dispersion travels in a vacuum and in some types of media Reflection Describe the laws of reflection of visible light and their applications in everyday life ➔ regular versus diffuse reflection ➔ angle of incidence = angle of reflection Formulate operational definitions for incidence, reflection, and the normal Estimate angles of incidence and reflection Refraction and Dispersion Rephrase questions related to refraction in a testable form Predict the effect of transparent media of varying densities on the angle of refraction of light Estimate angles of refraction Describe qualitatively how visible light is refracted Estimate focal length of a convex lens by finding its focal point Investigate and describe the development and evolution of an optical technology. Describe how optical technologies have developed through systematic trial-and-error processes Electromagnetic Describe different types of electromagnetic radiation Radiation (infrared, ultraviolet, X-rays, microwaves, radio waves) Basic introduction to wave theory (amplitude, wavelength, frequency). Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves and do not require a medium to travel Spectrum is an indication of a continuum of colours with different wavelength Investigate common technologies that incorporate the use of electromagnetic radiation and discuss their possible positive and negative effects.