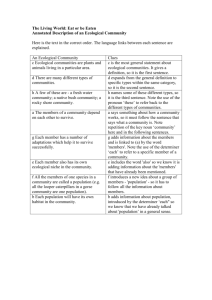
APPROACHES CURRICULUM DEVELOPMENT R. Shilpa Manogna APPROACHES TO CURRICULUM DEVELOPMENT Developmental Approach Functional Approach Ecological Approach Community Referenced Approach Task Analytic Approach Systems Approach Unit Approach Some Approach and Eclectic Approach. Developmental Approach The main philosophy behind this approach is the normal development pattern based upon known milestones of normal development. Skills appearing early in the developmental hierarchy are prerequisites for skills appearing later in normal development. Functional Approach Functional curriculum includes those skills a student would need in the immediate environment and in the next environment. Skills listed in functional curriculum are activities that are utility based and age appropriate and not developmentally based. The functional curriculum includes Personal skills, Social skills, Domestic skills, Community skills, Functional academics, and Leisure and recreation skills. Functional Assessment Functional assessment refers to the assessment of functional skills that are most likely to be required in the everyday life of an adult with mental retardation. Functional skills may include any skills that can influence a person’s ability to function independently and productively in the community. Steps for Functional Assessment Conduct an ecological inventory. Assess the current functioning of the student vis a vis the ecological inventory, determining those skills currently possessed by the student and those that are needed. From the list of student needs, prioritize with the students’, parents or guardians the instructional items to be taught. From this prioritization, prepare with the parents or guardians the instructional items to be taught. Ecological Approach Environment or community is very essential for curricular development. Emphasizes to develop in children the skills needed to live and function adequately in the social, vocational and economic environments in which the students live. Five phases for Ecological (environmental) Assessment. Initial description of the environment and perception of the problem. Expectation of the environment from the person to be assessed. Description of the interaction and skills. Summary of the above data Assessment of the child for skills and deficits and setting of reasonable expectation for the child, based on the comprehensive information gathered. Task Analytical Approach The curricular items selected are broken down to tasks. Each task is analyzed in a sequential manner for teaching the child. This breaking down of tasks to teach the child has the advantage of analyzing error and correcting them. Community Referenced Approach In this approach the instruction takes place in environments where the activities naturally occur, which minimizes the generalization of skills from simulated to natural environments. Community skills include street crossing, using public transportation, shopping, eating in restaurants and using other public facilities such as parks, post office, banks etc. Requirements for Implementation of Community Referenced Curriculum Administrators and parents need to be informed. Teachers require more time for developing and planning of community referenced curriculum Parents’ involvement in every aspect of developing and implementing community training programme is essential. Written parental permission should be obtained before giving community experience to students. Materials and personnel resources. Extra funding required. Eg. Money for travel, buying items Eclectic Approach Eclecticism has been derived from the verb root “elect”. To elect means to choose and pick up. good ideas, concept and principles from various schools of thought have been chosen, picked up blended together to make a complete philosophy. Eclecticism is nothing but fusion of knowledge from all sources. Eclecticism is a conceptual approach that does not hold rigidly to a single paradigm or set of assumptions. It draws upon multiple theories, styles, or ideas to gain complementary insights into a subject, or applies different theories in particular cases. It can sometimes seem inelegant or lacking in simplicity, and eclectics are sometimes criticized for lack of consistency in their thinking. unity in diversity is found through eclectic approach.